Predicting high proliferative Ki-67 index in patients with adrenocortical carcinoma based on texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images: a cross-sectional study
- Autores: Manaev A.V.1,2, Tarbaeva N.V.1, Roslyakova A.A.1, Beltsevich D.G.1, Urusova L.S.1, Mokrysheva N.G.1, Sinitsyn V.E.3,4
-
Afiliações:
- Endocrinology Research Centre
- National Research Nuclear University “MEPhI”
- Lomonosov Moscow State University
- Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
- Edição: Volume 6, Nº 3 (2025)
- Páginas: 360-372
- Seção: Original Study Articles
- ##submission.dateSubmitted##: 28.12.2024
- ##submission.dateAccepted##: 03.07.2025
- ##submission.datePublished##: 26.08.2025
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/article/view/643532
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD643532
- EDN: https://elibrary.ru/JRXXMQ
- ID: 643532
Citar
Texto integral
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Adrenocortical carcinoma is characterized by a high risk of aggressive disease progression and limited effectiveness of available treatment. Therefore, early diagnosis and assessment of its potential development are crucial. Although computed tomography is highly accurate in detecting the structural characteristics of tumors, its ability to predict adrenocortical carcinoma progression is unclear.
AIM: This study aimed to evaluate the accuracy of using texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images in predicting a high index of proliferative activity (Ki-67) in patients with adrenocortical carcinoma.
METHODS: The study examined four-phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of patients with histologically verified adrenocortical carcinoma (retrospective part) and reevaluated these images (prospective part). Computed tomography image analysis included labeling a tumor lesion, assessing and post-processing texture features, decreasing dimensions, and performing a cluster analysis to evaluate the discriminatory ability of computed tomography texture parameters. The predictive accuracy of texture analysis of computed tomography images was assessed based on its ability to identify increased proliferative activity (KI-67 > 10%). The index was derived from the results of immunohistopathological testing of adrenal tissue samples obtained during surgery.
RESULTS: Texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of 24 patients with histologically diagnosed adrenocortical carcinoma was performed: Ki-67 ≤ 10% in 9 patients and Ki-67 > 10% in 15 patients. The analysis revealed a statistically significant association (p = 0.015, Fisher’s exact test) between two fuzzy clusters based on texture features and the Ki-67 classification of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma. These results indicate the ability to predict high proliferative activity with a 0.05 level of significance.
CONCLUSION: Texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma enables noninvasive assessment of tumor progression risk following surgical removal.
Texto integral
ОБОСНОВАНИЕ
Адренокортикальный рак (АКР) — редкая злокачественная опухоль коры надпочечников, характеризующаяся, как правило, агрессивным клиническим течением и неблагоприятным прогнозом [1]. Общая 5-летняя выживаемость составляет 60–80% для опухолей, ограниченных надпочечником, 35–50% — для местнораспространённых случаев, менее 28% — при метастазировании [2]. Описаны редкие случаи более благоприятного, индолентного, течения заболевания с медленным прогрессированием и поздним метастазированием. Единственным возможным вариантом полного излечения при АКР является своевременное хирургическое удаление опухоли. Срочность хирургического вмешательства связана с быстрым увеличением опухоли и высокой вероятностью метастазирования [1, 2].
АКР характеризуется высокой вариабельностью морфологической картины (классический, онкоцитарный, миксоидный и саркоматоидный варианты), пролиферативной активности, клинического течения, ответа на терапию, а также связанными с этим общей и безрецидивной выживаемостью [1–3]. Гетерогенность АКР определяет трудности прогнозирования течения болезни и выбора лечебной тактики [4]. Одним из ключевых предикторов рецидива АКР считают пролиферативный индекс Ki-67. При значениях индекса Ki-67 >10% вероятность рецидива АКР даже после адекватной резекции в пределах здоровых тканей (R0-резекция) составляет не менее 80%. При Ki-67 ≤10% прогноз более благоприятный, и адъювантная химиотерапия не показана [1]. A.A. Ahmed и соавт. [5] оценивали корреляцию пролиферативного индекса Ki-67 с текстурными признаками изображений компьютерной томографии (КТ) с контрастным усилением у 53 пациентов с АКР. Так, авторы установили, что признаки геометрической формы shape elongation и flatness дифференцируют случаи АКР с высоким (Ki-67 >10%) и низким индексом пролиферации (Ki-67 ≤10%) со значением площади под ROC-кривой (Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve, AUC-ROC) 0,70 и 0,78 соответственно. Кроме того, в многомерной модели линейной регрессии получены следующие показатели: коэффициент детерминации R2=0,67, скорректированный R2=0,462, корреляция Пирсона r=0,824. Выявлены значимые признаки, включая shape elongation (удлинение формы), shape flatness (уплощённость формы), GLCM cluster shade (Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix — матрица пространственной смежности уровней серого), GLRLM long run emphasis (Gray Level Run Length Matrix — матрица длин серий уровней серого), interquartile range (межквартильный размах распределения рентгеновской плотности) и NGTDM (Neighbouring Gray Tone Difference Matrix — матрица различий соседних оттенков серого), GLSZM (Gray Level Size Zone Matrix — матрица размеров областей уровней серого). Ещё в нескольких исследованиях изучали точность текстурного анализа и методов глубокого обучения в бинарной классификации образований надпочечников неопределённого фенотипа КТ по критерию злокачественности [6–8]. Однако результаты этих исследований являются предварительными, а работа L. Tucci и соавт. [8], выполненная с применением нейросетевой модели и радиомики, опубликована в виде материалов конференции. Именно поэтому неясными остаются архитектура модели, её параметры и характеристики выборки. Вместе с тем КТ с контрастным усилением, благодаря более высокому по сравнению с другими методами инструментальной диагностики пространственному разрешению, является доступным и информативным способом выявления АКР [1, 2].
ЦЕЛЬ
Изучить точность предсказания высокого индекса пролиферативной активности Ki-67 у пациентов с АКР методом текстурного анализа изображений КТ с контрастным усилением.
МЕТОДЫ
Дизайн исследования
Проведено одноцентровое несравнительное одномоментное ретроспективное исследование в части проведения КТ, проспективное — в части повторного анализа изображений КТ.
Условия проведения
В исследование включали данные пациентов, зарегистрированных в медицинской информационной системе Национального медицинского исследовательского центра (НМИЦ) эндокринологии имени академика И.И. Дедова (Москва) в период с апреля 2014 г. по октябрь 2024 г. Для выделения из информационной системы подходящих случаев на первом этапе поиска сформировали список всех пациентов, проходивших хирургическое лечение по поводу образования надпочечника (код по Международной классификации болезней 10-го пересмотра — C74.0) в отделении хирургии НМИЦ эндокринологии. В период исследования КТ выполняли в отделении компьютерной и магнитно-резонансной томографии, а иммуногистохимические исследования — в отделе патоморфологии того же центра.
Критерии соответствия
Критерии включения:
- гистологически подтверждённый диагноз АКР;
- наличие дооперационных изображений четырёхфазной КТ с контрастным усилением органов брюшной полости, полученных не ранее чем за месяц до оперативного вмешательства (нативная, артериальная, венозная, отсроченная фазы).
Критерии исключения: наличие артефактов в области надпочечников на изображениях КТ [артефакты движения, кольцевые артефакты (Ring Artifacts)].
Проведение компьютерной томографии
В исследование включены изображения, получение с помощью следующих томографов:
- Optima® CT660 (GE HealthCare, США) — используют с 2015 года по настоящее время;
- Revolution® CT (GE HealthCare, США) — c 2019 года по настоящее время;
- BrightSpeed® 16 (GE HealthCare, США) — применяли в 2014 году.
Параметры компьютерных томографов и реконструкции изображений приведены в табл. 1. Контрастирование проводили с помощью двухколбового автоматического инжектора Medrad Stellant® (Bayer, Германия), скорость введения 3,5–4 мл/с в течении всего периода сбора данных. Артериальную фазу выполняли на 10 с после срабатывания триггера болюса, установленного на нисходящем отделе аорты на уровне диафрагмы (120 НU), венозную фазу — на 30 с от триггера болюса, отсроченную фазу — на 10–15 мин после введения контрастного препарата.
Таблица 1. Параметры компьютерной томографии и реконструкции изображений | ||||
Параметры | Фаза сканирования | |||
Нативная | Артериальная | Венозная | Отсроченная | |
Optima® CT660 (GE HealthCare, США) | ||||
Напряжение на трубке, кВ | 120, 100 | 120, 100 | 120, 100 | 120, 100 |
Сила тока на трубке, мА | автоматическая модуляция 380, 390, 410, 480 | автоматическая модуляция 380, 400 | автоматическая модуляция 335, 390, 400 | автоматическая модуляция 250 |
Экспозиция, мА×с | 9, 14, 18, 19, 20, 22, 24, 25, 26, 28 | 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 | 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 | 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12, 20 |
Расстояние между срезами, мм | 0,625 | 0,625 | 0,625 | 0,625 |
Толщина среза, мм | 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 |
Ядро свёртки | Standard | Standard | Standard | Standard |
Revolution® CT (GE HealthCare, США) | ||||
Напряжение на трубке, кВ | 100, 120 | 100, 140 | 140 | 140 |
Сила тока на трубке, мА | автоматическая модуляция 100, 120 | автоматическая модуляция 100, 240, 405, 485 | автоматическая модуляция 240, 405, 485 | автоматическая модуляция 240, 320, 485 |
Экспозиция, мА×с | 1, 2, 3 | 1, 2, 4, 5 | 2, 4, 9, 10 | 2, 3, 4, 6 |
Расстояние между срезами, мм | 0,625 | 0,625 и 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 |
Толщина среза, мм | 0,625 | 0,625 и 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 |
Ядро свёртки | Standard | Standard | Standard | Standard |
BrightSpeed® 16 (GE HealthCare, США) | ||||
Напряжение на трубке, кВ | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
Сила тока на трубке, мА | 400 | 380 | 380 | 380 |
Экспозиция, мА×с | 28 | 27 | 27 | 27 |
Расстояние между срезами, мм | 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 |
Толщина среза, мм | 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 1,25 |
Ядро свёртки | Standard | Standard | Standard | Standard |
Анализ изображений компьютерной томографии
Сегментация изображений
Дооперационные изображения КТ экспортировали на персональный компьютер из системы архивации и передачи медицинских изображений PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) в формате DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine). Перед обработкой данные деперсонализировали — из файлов удалена вся информация, позволяющая идентифицировать пациента (ФИО, дата рождения, идентификационный номер, дата исследования). Области, соответствующие образованиям надпочечников, размечали вручную врачи-рентгенологи (опыт работы по специальности более 5 лет) с помощью программного пакета 3D Slicer® версии 5.6.2, (Slicer Community, США) для каждой фазы сканирования отдельно. Файлы с разметкой сохраняли в формате DICOM вместе с файлами исходных изображений КТ. Их повторный анализ проводили «вслепую», без доступа врачей-рентгенологов к клинической информации, включая предыдущие результаты КТ и лабораторные данные (до последних, выполненных перед оперативным вмешательством).
Текстурный анализ изображений
Изображения КТ вместе с файлами разметки экспортировали в платформу PyRadiomics®, версия 3.1.0 (Computational Imaging & Bioinformatics Lab, США). Изображения анализировали без применения специальных фильтров. Для каждого изображения (каждой фазы КТ) после интерполяции снимков к изотропному вокселу 1×1×1 мм в 3D режиме определяли 106 признаков, относящихся к 7 классам:
- статистические признаки первого порядка — 18 признаков;
- признаки геометрической формы — 14 признаков;
- признаки на основе матрицы пространственной смежности уровней серого [Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM)] — 23 признака;
- признаки на основе матрицы длин линий уровней серого [Gray Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM)] — 16 признаков;
- признаки на основе матрицы разности соседних оттенков серого (Neighbouring Gray Tone Difference Matrix (NGTDM)] — 5 признаков;
- признаки на основе матрицы зависимости уровней серого [Gray Level Dependence Matrix (GLDM)] — 14 признаков;
- признаки на основе матрицы размеров областей уровней серого [Gray Level Size Zone Matrix (GLSZM)] — 16 признаков.
Вычисление проводили в окне чисел Хаунсфилда, соответствующих протоколу абдоминального исследования [−160; 240] HU. Все остальные параметры, регулирующие предобработку изображений (нормализация, алгоритм интерполяции, наличие пороговой сегментации для уточнения области интереса и др.), оставлены по умолчанию в соответствии с настройками модуля PyRadiomics [9].
Предсказываемое событие
Для оценки предсказательной точности текстурного анализа изображений КТ использовали значения индекса пролиферативной активности Ki-67 >10%. Порог 10% выбран на основании его клинической значимости и использования для разграничения опухолей с низкой и высокой пролиферативной активностью, что определяет прогноз и тактику лечения пациентов с АКР [1].
Из гистологического материала АКР, полученного при хирургическом лечении пациентов в НМИЦ эндокринологии по стандартной методике, изготовлены препараты, окрашенные гематоксилином и эозином. Осуществляли стандартную гистологическую проводку надпочечников с помощью гистопроцессора Leica® ASP6025 S (Leica Biosystems, Германия), затем — их заливку в парафин.
Экваториальные срезы изготавливали с помощью микротома Leica® RM 2125 RTS (Leica Biosystems, Германия) и после депарафинирования окрашивали гематоксилином и эозином на аппарате Leica® ST5010 AXL (Leica Biosystems, Германия).
Изучение гистологических препаратов надпочечников проводили методом световой микроскопии с использованием микроскопа Leica® DM2500 (Leica Microsystems, Германия) и компьютерной морфометрии с помощью программы Aperio® ImageScope (Leica Microsystems, Германия).
Все опухоли коры надпочечников оценивали в соответствии со следующими патологическими критериями:
- общий размер и масса опухоли;
- ядерный полиморфизм;
- количество митозов в 10 полях зрения при увеличении микроскопа ×400;
- цитоплазма опухолевых клеток (прозрачность 0–25 и 26–100%) и архитектура роста (диффузный и недиффузный);
- наличие или отсутствие атипичных митозов, некрозов и однозначной капсулярной, венозной, синусоидальной и смежной инвазии органов.
Для определения злокачественного потенциала опухоли использовали шкалу Weiss, а в случае онкоцитарных новообразований надпочечника, характеризующихся зернистой и ярко-эозинофильной цитоплазмой клеток, высоким ядерным полиморфизмом и диффузным характером роста, применяли модифицированную шкалу Lin–Weiss–Bisceglia. Все адренокортикальные карциномы в этом исследовании имели 4 гистологических критерия по шкале Weiss или более [10].
Митотическую скорость определяли путём подсчёта 50 полей высокой мощности (×400) с помощью микроскопа Leica® DM2500 (Leica Microsystems, Германия). Выбранные области предметного стекла содержали самые высокие концентрации митотических фигур. Каждые 10 полей высокой мощности подсчитывали на разных предметных стёклах по мере возможности.
Архитектуру определяли как «диффузная», когда доля слоёв клеток без характерного рисунка роста составляла более 33% опухоли.
Сосуды, выстланные эндотелием и имеющие мышечный слой в стенке, рассматривали как вены, тогда как синусоиды представляли сосуды с эндотелиальной выстилкой и небольшим количеством поддерживающей ткани. Венозную или синусоидальную инвазию устанавливали при обнаружении в просвете таких сосудов опухолевых клеток, прилежащих к их стенке, как внутри, так и за пределами опухоли надпочечника. Капсулярную инвазию определяли в случаях полного прорастания опухолью окружающей капсулы.
Иммуногистохимическое исследование проводили на полностью автоматизированном иммуногистостейнере Leica® Bond III (Leica Microsystems, Германия) по стандартным протоколам, рекомендованным производителем. Для иммуногистохимического анализа использованы моноклональные антитела к Ki-67 [MIB-1 в разведении 1:150 (Dako, Дания)]. Подсчёт пролиферативной активности опухолевых клеток (Ki-67) осуществляли визуально в 10 полях зрения при увеличении ×400. Показатель определяли как процент окрашенных клеточных ядер в участках опухоли с наибольшей активностью («горячие точки»). На протяжении периода исследования методика иммуногистохимического анализа была неизменной.
Анализ в группах
Пациенты разделены на две группы в зависимости от значения индекса Ki-67:
- 1-я группа — Ki-67 ≤10%;
- 2-я группа — Ki-67 >10%.
Этическая экспертиза
Протокол исследования одобрен локальным этическим комитетом НМИЦ эндокринологии имени академика И.И. Дедова (протокол № 20 от 13.11.2024). Все пациенты при обращении за медицинской помощью в данный центр подписывали информированное добровольное согласие на использование результатов исследования и лечения с научной целью.
Статистический анализ
Принципы расчёта размера выборки. При планировании исследования необходимый размер выборки не рассчитывали.
Отсутствующие данные. При формировании выборки исследования все пациенты, включённые в анализ после применения критериев включения и исключения, имели полный набор необходимых данных. Случаев отсутствия данных не выявлено.
Методы статистического анализа данных. Анализ данных проводили с использованием языка программирования Python 3.9.21.
Данные по непрерывным переменным [возраст на момент проведения КТ с контрастным усилением (полных лет), максимальный линейный размер образования надпочечников по результатам КТ (мм), рентгеновская плотность по фазам КТ в единицах Хаунсфилда (HU), значение индекса Ki-67 (%)] представлены в виде M±SD, где M — среднее арифметическое, SD — стандартное отклонение. Для сравнения групп пациентов по значениям качественных переменных использовали точный критерий Фишера, непрерывных переменных — U-тест Манна–Уитни.
Постобработка текстурных признаков включала стандартизацию и отбор наиболее информативных признаков. Стандартизацию проводили центрированием к среднему значению для выборки (из каждого значения признака вычитали среднее значение по всей выборке) и масштабированием к стандартному отклонению (делением результата вычитания из каждого значения признака среднего значения признака по всей выборке на стандартное отклонение всей выборки). Перед отбором наиболее значимых признаков оценивали нормальность распределения с применением критерия Шапиро–Уилка. При p <0,05 для сравнения 1-й и 2-й группы использовали двусторонний тест Манна–Уитни. В случаях, когда критерий Шапиро–Уилка не выявлял значимого отклонения от нормальности (p ≥0,05), применяли двусторонний t-критерий Стьюдента. Признаки, для которых обнаружено статистически значимое различие в группах, использовали для кластерного анализа.
Оценку применимости текстурных признаков изображений КТ для дифференциации 1-й и 2-й групп проводили методом кластерного анализа с использованием алгоритма нечёткой кластеризации K-средних (fuzzy K-means). Данный метод позволяет оценить, насколько естественным образом данные разделяются на группы и существует ли внутренняя структура, соответствующая биологически значимым подгруппам [11]. Выбор метода fuzzy K-means для решения задачи кластеризации обусловлен возможностью определения вероятности принадлежности к тому или иному кластеру для каждой точки в пространстве главных компонент. Пространство признаков для решения задачи кластеризации сформировали после уменьшения размерности признакового пространства с применением метода главных компонент. Последний применяли также для исключения коррелирующих признаков и выделения наиболее информативных компонент. Количество главных компонент определяли на основании доли объяснённой дисперсии и возможности наглядной визуализации результатов, при этом сохраняя компоненты, объясняющие не менее 90% общей дисперсии данных. Процедура кластерного анализа включала следующие этапы:
- формирование матрицы признаков после предварительной обработки;
- применение алгоритма fuzzy K-means с итерационным уточнением центров кластеров;
- оценка полученного распределения объектов по кластерам и интерпретация выявленных групп с точки зрения их соответствия исходной классификации по значению индекса Ki-67.
При этом исходили из допущения, что основные паттерны в данных могут быть выражены через линейные комбинации исходных признаков. Кластеризацию проводили в предположении, что различия в признаках изображений КТ могут отражать границы между группами с разной пролиферативной активностью опухолей.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Формирование выборки исследования
В период с 2014 по 2024 год в отделении хирургии НМИЦ эндокринологии хирургическое удаление злокачественного образования надпочечника выполнено у 51 пациента. Патоморфологическая верификация диагноза проведена в 42 случаях, из которых изображения КТ с контрастным усилением доступны у 31 пациента. Из исследования исключены данные одного пациента из-за выраженных артефактов в области надпочечников на изображениях КТ и шести — из-за отсутствия результатов иммуногистохимического исследования. Таким образом, в исследование включены данные 24 пациентов с АКР:
- 1-я группа — со значением индекса Ki-67 ≤10% (n=9);
- 2-я группа — со значением индекса Ki-67 >10% (n=15).
Характеристика групп исследования
По данным КТ с контрастным усилением, выполненной на томографах Optima® CT660 (GE HealthCare, США) — у 10 пациентов, Revolution® CT (GE HealthCare, США) — у 13, BrightSpeed® 16 (GE HealthCare, США) — у 1, максимальное накопление контрастного препарата наблюдали в венозную фазу с умеренным вымыванием в отсроченную (табл. 2). Пациенты 1-й и 2-й группы сопоставимы по полу, возрасту и большинству параметров образований надпочечников, за исключением плотности в венозной фазе, значения которой были выше в 1-й группе (см. табл. 2).
Таблица 2. Сравнительная характеристика пациентов в группах | |||
Параметр | 1-я группа, n=9 | 2-я группа, n=15 | р |
Мужской пол, n (%) | 4 (44) | 4 (27) | 0,412 |
Возраст, лет | 41,4±15,2 | 47,1±14,3 | 0,220 |
Характеристики образований надпочечников | |||
Максимальный линейный размер, мм | 73,9±29,8 | 92,4±28,9 | 0,152 |
Плотность в нативной фазе, HU | 34,6±5,4 | 34,5±5,5 | 0,787 |
Плотность в артериальной фазе, HU | 63,6±16,9 | 53,5±11,9 | 0,160 |
Плотность в венозной фазе, HU | 93,7±26,7 | 68,9±13,2 | 0,027 |
Плотность в отсроченной фазе, HU | 57,9±10,6 | 53,7±4,5 | 0,339 |
Основные результаты исследования
По результатам теста Шапиро–Уилка установлено, что распределение значений 71 признака (67%) изображений КТ пациентов с АКР является нормальным. При их сравнении в группах использовали t-критерий Стьюдента. В остальных случаях применяли тест Манна– Уитни. Значимые для целей исследования признаки представлены в табл. 3. Наиболее полезной для количественного анализа была венозная фаза КТ с контрастным усилением. Последующее уменьшение размерности признакового пространства позволило выделить три главные компоненты, объясняющие 99,6% всей дисперсии данных.
Таблица 3. Значимые текстурные признаки компьютерной томографии | |
Фаза компьютерной томографии | Значимые признаки |
Нативная | Отсутствуют |
Артериальная | Отсутствуют |
Венозная | firstorder_10Percentile, firstorder_90Percentile, firstorder_Mean firstorder_Median, firstorder_RootMeanSquared, glcm_Autocorrelation, glcm_SumAverage, gldm_HighGrayLevelEmphasis, gldm_LargeDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis, gldm_LowGrayLevelEmphasis, gldm_SmallDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis, glrlm_HighGrayLevelRunEmphasis, glrlm_LongRunHighGrayLevelEmphasis, glrlm_LongRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis, glrlm_LowGrayLevelRunEmphasis, glrlm_ShortRunHighGrayLevelEmphasis, glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis, glszm_HighGrayLevelZoneEmphasis, glszm_LargeAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis, glszm_LowGrayLevelZoneEmphasis, glszm_SmallAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis, glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis |
Отсроченная | Отсутствуют |
Примечание. По результатам теста Стьюдента/теста Манна–Уитни p <0,05. Названия признаков отражают структурированную иерархию параметров, например, признак с названием glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis состоит из нескольких составляющих, каждая из которых имеет определённое значение: glszm означает, что это признак на основе GLSZM; SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis — непосредственно название признака. | |
Для обеспечения ясности относительно характера анализируемых данных, в табл. 4 представлена интерпретация отобранных признаков, сгруппированных по их категориям. Описания отражают, какие аспекты организации текстуры объёма опухоли они характеризуют на изображениях КТ.
Таблица 4. Значимые текстурные признаки и их интерпретация | ||
Группа признаков | Названия признаков | Интерпретация |
Признаки первого порядка (first order) |
| Описывают распределение значений рентгеновской плотности вокселей внутри области интереса без учёта их пространственного расположения, что соответствует качественной характеристике как среднее значение плотности |
Признаки на основе матрицы пространственной смежности уровней серого |
| Количественно оценивают пространственную неоднородность тканей, учитывая расположение вокселей относительно друг друга, что соответствует качественной характеристике как однородная структура (увеличение glcm_Autocorrelation), преобладание пар гиперденсных вокселей (увеличение glcm_SumAverage) |
Признаки на основе матрицы зависимости уровней серого |
| Количественно оценивают размер и плотность однородных зон в текстуре изображения, что соответствует качественной характеристике как гиподенсные участки (увеличение значения gldm_LargeDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis, gldm_LowGrayLevelEmphasis), гиперденсные включения (увеличение gldm_SmallDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis, gldm_HighGrayLevelEmphasis) |
Признаки на основе матрицы длин линий уровней серого |
| Количественно оценивают длину и плотность линейных однородных участков (серий последовательных вокселей одинаковой плотности) в текстуре изображения, что соответствует качественной характеристике как однородные гиперденсные участки (увеличение glrlm_HighGrayLevelRunEmphasis, glrlm_LongRunHighGrayLevelEmphasis), однородные гиподенсные участки (увеличение glrlm_LongRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis, glrlm_LowGrayLevelRunEmphasis), мелкие гиперденсные включения (увеличение glrlm_ShortRunHighGrayLevelEmphasis), мелкие гиподенсные включения (увеличение glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis) |
Признаки на основе матрицы размеров областей уровней серого |
| Количественно оценивают размер и яркость связанных однородных областей в текстуре изображения, что соответствует качественной характеристике как однородные гиперденсные участки (увеличение glszm_HighGrayLevelZoneEmphasis), крупные однородные гиподенсные участки (увеличение glszm_LargeAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis, glszm_LowGrayLevelZoneEmphasis), мелкие гиподенсные включения (увеличение glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis), мелкие гиперденсные включения (увеличение glszm_SmallAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis) |
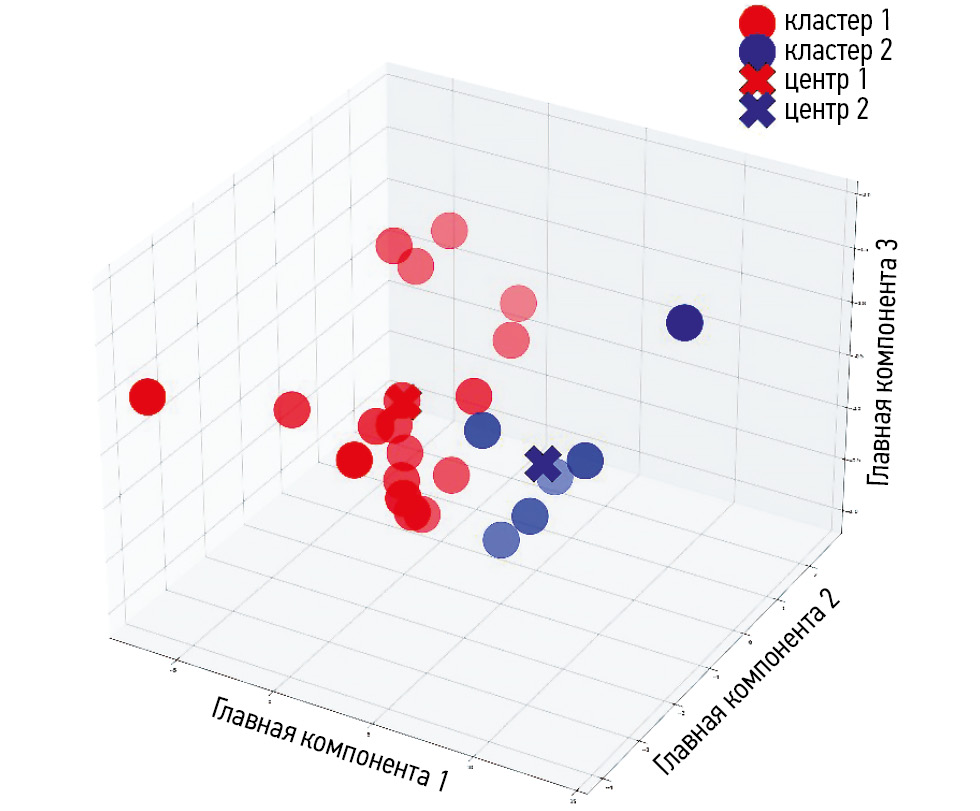
Результат кластеризации в полученном пространстве признаков приведён на рис. 1. Так, два кластера образуют относительно изолированные группы точек. На рис. 2 приведено исходное распределение случаев в зависимости от значения индекса Ki-67. Распределение пациентов по кластерам приведено в табл. 5: первый кластер преимущественно включает пациентов 1-й группы, тогда как второй — 2-й группы. Согласно точному тесту Фишера, значение p подтверждает, что алгоритм fuzzy K-means разделил выборку на две группы, связанные со значениями индекса Ki-67.
Рис. 1. Визуализация результата кластеризации методом fuzzy K-means в пространстве главных компонент.
Рис. 2. Визуализация исходного распределения адренокортикального рака на группы в зависимости от значения индекса Ki-67 в пространстве главных компонент. Ki-67 — индекс пролиферативной активности Ki-67.
Таблица 5. Распределение пациентов с адренокортикальным раком по кластерам | |||
Кластеры | 1-я группа, n=9 | 2-я группа, n=15 | р |
Кластер 1 | 5 | 1 | 0,015 |
Кластер 2 | 4 | 14 | |
Примечание. Значение p вычислено с использованием точного критерия Фишера. | |||
На тепловой карте представлены различия в средних значениях признаков между кластерами (рис. 3). Установлено, что для кластера с высокими значениями индекса Ki-67 интенсивность элементов текстуры областей АКР на изображениях венозной фазы КТ в среднем ниже, чем в кластере с его низкими значениями, что отражается в значениях признаков первого порядка. Кроме того, если анализировать текстурные признаки (на основе матриц), можно отметить более низкую степень однородности текстуры в кластере с высокими значениями индекса Ki-67 по сравнению с кластером с его низкими значениями.
Рис. 3. Тепловая карта значений признаков в группах. Интенсивность окрашивания варьирует в диапазоне от 0 до 1, где 0 — кластер, соответствующий высоким значениям индекса Ki-67, 1 — кластер, соответствующий низким значениям индекса Ki-67.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Резюме основного результата исследования
Алгоритм fuzzy K-means достоверно разделяет пациентов с АКР на два кластера, ассоциированных с низким (Ki-67 ≤10%) и высоким (Ki-67 >10%) индексом пролиферации. Кластер с высоким индексом Ki-67 характеризуется сниженной интенсивностью и меньшей однородностью текстуры на изображениях КТ венозной фазы по сравнению с кластером низких значений.
Интерпретация основного результата исследования
Полученные результаты подтверждают гипотезу о том, что текстурные признаки, извлечённые из изображений КТ с контрастным усилением, могут быть использованы для оценки индекса Ki-67. Данный вывод согласуется с результатами других исследований. Например, в исследовании A.A. Ahmed и соавт. [5] показано, что определённые радиомические признаки могут быть связаны с выраженностью пролиферативной активности АКР, оцениваемой по индексу Ki-67. Их многомерная модель линейной регрессии включала такие информативные признаки, как shape elongation, shape flatness, GLCM cluster shade, GLRLM long run emphasis, interquartile range (first order) и NGTDM Contrast, GLSZM Gray level non-uniformity normalised. В нашем исследовании значимыми были не только упомянутые выше, но и дополнительные признаки — firstorder_10Percentile, firstorder_90Percentile, firstorder_Mean, firstorder_Median, firstorder_RootMeanSquared, glcm_Autocorrelation, glcm_SumAverage, а также текстурные параметры GLDM и GLRLM. Тем не менее A.A. Ahmed и соавт. [5] не описывают особенности постобработки изображений и выбора параметров извлечения признаков радиомики, поэтому можно предположить, что различия между исследованиями обусловлены отличиями в методе обработки изображений, иным выбором параметров, определяющих их предобработку. Кроме того, необходимо учитывать характеристики выборки: средний размер АКР у наших пациентов меньше (73,9±15,2 и 92,4±14,3 мм в 1-й и 2-й группе соответственно) по сравнению с исследованием A.A. Ahmed и соавт. [5], где средний размер образований 115±64,8 мм, что могло повлиять на выявленные зависимости.
Кроме того, результаты нашего исследования согласуются с данными J. Liu и соавт. [12], поскольку обе работы демонстрируют возможность использования признаков, извлечённых из изображений КТ с контрастным усилением, в качестве прогностически значимых параметров АКР. В исследовании J. Liu и соавт. [12] показано, что радиомика превосходит традиционные системы ENSAT и S-GRAS в прогнозировании общей и безрецидивной выживаемости. Однако, в отличие от этой работы, в нашем исследовании акцент сделан на кластерный анализ и связь кластеров с индексом Ki-67. Наши результаты дополняют существующие научные сведения, подтверждая, что радиомика в сочетании с применением алгоритма кластеризации fuzzy K-means позволяет дифференцировать случаи АКР в зависимости от значения индекса Ki-67 — одного из ключевых маркёров степени злокачественности [1].
По данным нашего исследования, кластер с высокими значениями индекса Ki-67 характеризуется более низкой степенью однородности текстуры, чем кластер с низкими его значениями. Этот вывод соответствует результатам исследования M. Robertson-Tessi и соавт. [13], в котором моделирование и экспериментальные данные подтвердили, что опухоли с выраженной гетерогенностью демонстрируют более агрессивное поведение, что может объяснять нашу находку о неоднородности текстуры в кластере с высокими значениями индекса Ki-67, который также связан с агрессивностью опухоли.
Мы установили, что только на изображениях, полученных в венозную фазу с помощью КТ с контрастным усилением, присутствуют значимые для целей исследования признаки. Кроме того, в кластере с высокими значениями индекса Ki-67 интенсивность серого на изображениях КТ в среднем ниже, чем в кластере с низкими его значениями, что может свидетельствовать о меньшем накоплении контраста в опухолях с высоким индексом Ki-67.
Ограничения исследования
Выбор индекса Ki-67 в качестве маркёра риска прогрессирования АКР имеет свои ограничения. Несмотря на то что его широко используют в рутинной практике и считают важным прогностическим показателем, он не является единственным маркёром, отражающим биологическую агрессивность опухоли. Использование дополнительной информации, такой как молекулярные данные или данные о других маркёрах новообразований надпочечников, могло бы предоставить более полное представление о связи между текстурными признаками изображений КТ с контрастным усилением и степенью злокачественности опухоли. Например, известно, что высокое содержание стероидогенного фактора (SF-1) является прогностическим фактором, коррелирующим с неблагоприятным клиническим исходом АКР [14], а инсулиноподобного фактора роста 2 (IGF-2) — с более длительной общей выживаемостью [15]. Учёт подобных маркёров в будущих исследованиях может способствовать более точной интерпретации радиомических данных и повышению диагностической ценности моделей на основе данных КТ.
Другим ограничением настоящего исследования является относительно небольшой объём данных, что может влиять в том числе на обобщаемость (распространение за пределы исследования) полученных результатов. Включение дополнительных данных, полученных из многопрофильных медицинских центров и при различных протоколах сканирования, может повысить устойчивость модели и улучшить её точность. Похожий подход использовали в исследовании, представленном на 26-м Европейском эндокринологическом конгрессе [5], где анализ данных из семи центров позволил существенно повысить диагностическую точность моделей машинного обучения. Добиться более высокой предсказательной точности радиомики можно в случае применения более сложных архитектур нейросетевых моделей, способных учитывать нелинейные зависимости между признаками. Так, A.A. Ahmed и соавт. [5] разработали нейросетевой алгоритм для решения задачи бинарной классификации по критерию злокачественности со следующими оценками качества: AUC-ROC — 0,974, чувствительность — 92,7%, специфичность — 92,8%.
Применение КТ с контрастным усилением в нашем исследовании ограничено случаями АКР и конкретного прогностического маркёра — индекса Ki-67. Использование этого метода для оценки агрессивности других опухолей или в случае анализа других маркёров требует дополнительного исследования.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Роль количественного анализа изображений КТ с контрастным усилением в неинвазивной оценке риска прогрессирования АКР до настоящего времени оставалась недостаточно изученной: в России отсутствовали публикации по этой теме, а за рубежом встречались лишь единичные работы. В настоящем исследовании предложен подход к количественному описанию изображений КТ у пациентов с АКР с использованием кластеризации fuzzy K-means, позволяющий выявлять пациентов с потенциально агрессивным течением опухолевого процесса. Установлена связь количественных признаков изображений КТ с пролиферативной активностью опухоли, а статистически значимые различия между кластерами подтверждают применимость метода для оценки риска прогрессирования АКР. Полученные результаты демонстрируют потенциал разработанного подхода для предварительной оценки индекса Ki-67 на основе текстурных признаков КТ с контрастным усилением. Дальнейшие исследования должны быть направлены на стандартизацию методологии, интеграцию радиомики с клиническими характеристиками и повышение воспроизводимости подхода.
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНАЯ ИНФОРМАЦИЯ
Вклад авторов. А.В. Манаев — определение концепции, работа с данными, анализ данных, разработка методологии, написание черновика рукописи; Н.В. Тарбаева — определение концепции, администрирование проекта, написание черновика рукописи; А.А. Рослякова, Д.Г. Бельцевич, Л.С. Урусова — работа с данными, проведение исследования, обеспечение исследования, пересмотр и редактирование рукописи; Н.Г. Мокрышева, В.Е. Синицын — администрирование проекта, руководство исследованием, пересмотр и редактирование рукописи. Все авторы одобрили рукопись (версию для публикации), а также согласились нести ответственность за все аспекты работы, гарантируя надлежащее рассмотрение и решение вопросов, связанных с точностью и добросовестностью любой её части.
Этическая экспертиза. Протокол исследования одобрен локальным этическим комитетом Национального медицинского исследовательского центра эндокринологии имени академика И.И. Дедова (протокол № 20 от 13.11.2024). Все пациенты при обращении за медицинской помощью в данный центр подписывали информированное добровольное согласие на использование результатов исследования и лечения с научной целью.
Источники финансирования. Отсутствуют.
Раскрытие интересов. Авторы заявляют об отсутствии отношений, деятельности и интересов за последние три года, связанных с третьими лицами (коммерческими и некоммерческими), интересы которых могут быть затронуты содержанием статьи.
Оригинальность. При создании настоящей работы авторы не использовали ранее опубликованные сведения (текст, иллюстрации, данные).
Доступ к данным. Редакционная политика в отношении совместного использования данных к настоящей работе не применима.
Генеративный искусственный интеллект. При создании настоящей статьи технологии генеративного искусственного интеллекта не использовали.
Рассмотрение и рецензирование. Настоящая работа подана в журнал в инициативном порядке и рассмотрена по обычной процедуре. В рецензировании участвовали два внешних рецензента, член редакционной коллегии и научный редактор издания.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Author contributions: A.V. Manaev: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft; N.V. Tarbaeva: conceptualization, project administration, writing—original draft; A.A. Roslyakova, D.G. Beltsevich, L.S. Urusova: data curation, investigation, resources, writing—review & editing; N.G. Mokrysheva, V.E. Sinitsyn: project administration, supervision, writing—review & editing. All the authors approved the version of the manuscript to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work, ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Ethics approval: The study protocol was approved by the local Ethics Committee of the Dedov National Medical Research Center for Endocrinology (Minutes No. 20 dated November 13, 2024). All the patients provided written informed consent for the use of their clinical assessment and treatment data for research purposes on admission.
Funding sources: No funding.
Disclosure of interests: The authors have no relationships, activities, or interests for the last three years related to for-profit or not-for-profit third parties whose interests may be affected by the content of the article.
Statement of originality: No previously obtained or published material (text, images, or data) was used in this study or article.
Data availability statement: The editorial policy regarding data sharing does not apply to this work.
Generative AI: No generative artificial intelligence technologies were used to prepare this article.
Provenance and peer-review: This article was submitted unsolicited and reviewed following the standard procedure. The peer review process involved two external reviewers, a member of the Editorial Board, and the in-house science editor.
Sobre autores
Almaz Manaev
Endocrinology Research Centre; National Research Nuclear University “MEPhI”
Autor responsável pela correspondência
Email: a.manaew2016@yandex.ru
ORCID ID: 0009-0003-8035-676X
Código SPIN: 2902-9767
MD
Rússia, Moscow; MoscowNatalia Tarbaeva
Endocrinology Research Centre
Email: ntarbaeva@inbox.ru
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-7965-9454
Código SPIN: 5808-8065
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
Rússia, MoscowAnna Roslyakova
Endocrinology Research Centre
Email: aroslyakova12@gmail.com
ORCID ID: 0000-0003-1857-5083
Código SPIN: 5984-4175
MD
Rússia, MoscowDmitry Beltsevich
Endocrinology Research Centre
Email: belts67@gmail.com
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-7098-4584
Código SPIN: 4475-6327
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine)
Rússia, MoscowLiliya Urusova
Endocrinology Research Centre
Email: liselivanova89@yandex.ru
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-6891-0009
Código SPIN: 5151-3675
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine)
Rússia, MoscowNatalia Mokrysheva
Endocrinology Research Centre
Email: mokrisheva.natalia@endocrincentr.ru
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-9717-9742
Código SPIN: 5624-3875
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
Rússia, MoscowValentin Sinitsyn
Lomonosov Moscow State University; Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: vsini@mail.ru
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-5649-2193
Código SPIN: 8449-6590
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
Rússia, Moscow; MoscowBibliografia
- Adrenal Cortex Cancer (Adrenocortical Cancer): Clinical guidelines [Internet]. Moscow: Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation; 2020. [cited 2024 Dec 10]. Available from: https://cr.minzdrav.gov.ru/view-cr/341_1
- Fassnacht M, Dekkers OM, Else T, et al. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of adrenocortical carcinoma in adults, in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2018;179(4):G1–G46. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0608
- Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Klöppel G, et. al; World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. 4th edition. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer IARC; 2017. ISBN: 9-789-283-244-936 Available from: https://catalog.nlm.nih.gov/discovery/fulldisplay/
- Duregon E, Volante M, Rapa I, et al. Dissecting Morphological and Molecular Heterogeneity in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Turkish Journal of Pathology. 2015;31(suppl.):98–104. doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01317
- Ahmed AA, Elmohr MM, Fuentes D, et al. Radiomic Mapping Model for Prediction of Ki-67 Expression in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Clinical Radiology. 2020;75(6):479.e17–479.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2020.01.012 EDN: JKXPIQ
- Moawad AW, Ahmed A, Fuentes DT, et al. Machine Learning-Based Texture Analysis for Differentiation of Radiologically Indeterminate Small Adrenal Tumors on Adrenal Protocol CT Scans. Abdominal Radiology. 2021;46(10):4853–4863. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03136-2 EDN: EPKHHA
- Kusunoki M, Nakayama T, Nishie A, et al. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for the Diagnosis of Adrenal Adenoma: A New Trial Using CT. The British Journal of Radiology. 2022;95(1135): 20211066. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20211066 EDN: TESCDP
- Tucci L, Vara G, Morelli V, et al. Prediction of Adrenal Masses Nature Through Texture Analysis and Deep Learning: Preliminary Results From ENS@T RADIO-AI Multicentric Study. In: Proceedings of the 26th European Congress of Endocrinology. Stockholm: Bioscientifica; 2024. doi: 10.1530/endoabs.99.OC11.3 EDN: SYRWPF
- van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, et al. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Research. 2017;77(21):e104–e107. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339
- Weiss LM. Comparative Histologic Study of 43 Metastasizing and Nonmetastasizing Adrenocortical Tumors. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 1984;8(3):163–170. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198403000-00001
- Bezdek JC, Ehrlich R, Full W. FCM: The Fuzzy c-means Clustering Algorithm. Computers & Geosciences. 1984;10(2-3):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7
- Liu J, Lin W, Yan L, et al. Contrast CT Radiomic Features Add Value to Prediction of Prognosis in Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma. Endocrine. 2023;83(3):763–774. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03568-4 EDN: UJCDED
- Robertson-Tessi M, Gillies RJ, Gatenby RA, Anderson ARA. Impact of Metabolic Heterogeneity on Tumor Growth, Invasion, and Treatment Outcomes. Cancer Research. 2015;75(8):1567–1579. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1428
- Sbiera S, Schmull S, Assie G, et al. High Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Steroidogenic Factor-1 Expression in Adrenal Tumors. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2010;95(10):E161–E171. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0653 EDN: NZZFBP
- Babińska A, Pęksa R, Wiśniewski P., et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of SF1, IGF2, Ki67, p53, Adiponectin, and Leptin Receptors in Human Adrenal Cortical Tumors. Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2017;116(3):427–433. doi: 10.1002/jso.24665
Arquivos suplementares