Vol 6, No 3 (2025)
- Year: 2025
- Published: 14.11.2025
- Articles: 13
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/9913
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.63
Full Issue
Original Study Articles
Predicting high proliferative Ki-67 index in patients with adrenocortical carcinoma based on texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Adrenocortical carcinoma is characterized by a high risk of aggressive disease progression and limited effectiveness of available treatment. Therefore, early diagnosis and assessment of its potential development are crucial. Although computed tomography is highly accurate in detecting the structural characteristics of tumors, its ability to predict adrenocortical carcinoma progression is unclear.
AIM: This study aimed to evaluate the accuracy of using texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images in predicting a high index of proliferative activity (Ki-67) in patients with adrenocortical carcinoma.
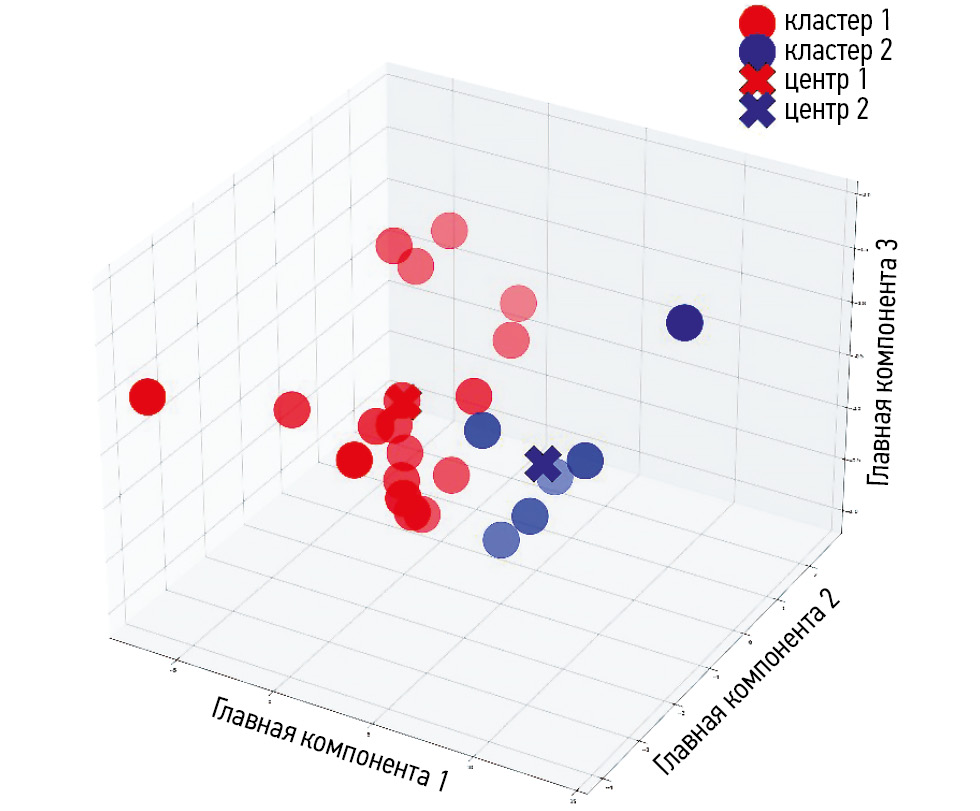
METHODS: The study examined four-phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of patients with histologically verified adrenocortical carcinoma (retrospective part) and reevaluated these images (prospective part). Computed tomography image analysis included labeling a tumor lesion, assessing and post-processing texture features, decreasing dimensions, and performing a cluster analysis to evaluate the discriminatory ability of computed tomography texture parameters. The predictive accuracy of texture analysis of computed tomography images was assessed based on its ability to identify increased proliferative activity (KI-67 > 10%). The index was derived from the results of immunohistopathological testing of adrenal tissue samples obtained during surgery.
RESULTS: Texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of 24 patients with histologically diagnosed adrenocortical carcinoma was performed: Ki-67 ≤ 10% in 9 patients and Ki-67 > 10% in 15 patients. The analysis revealed a statistically significant association (p = 0.015, Fisher’s exact test) between two fuzzy clusters based on texture features and the Ki-67 classification of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma. These results indicate the ability to predict high proliferative activity with a 0.05 level of significance.
CONCLUSION: Texture analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma enables noninvasive assessment of tumor progression risk following surgical removal.
 360-372
360-372


Consensus-based labeling algorithms for texture analysis of prostate lesions
Abstract
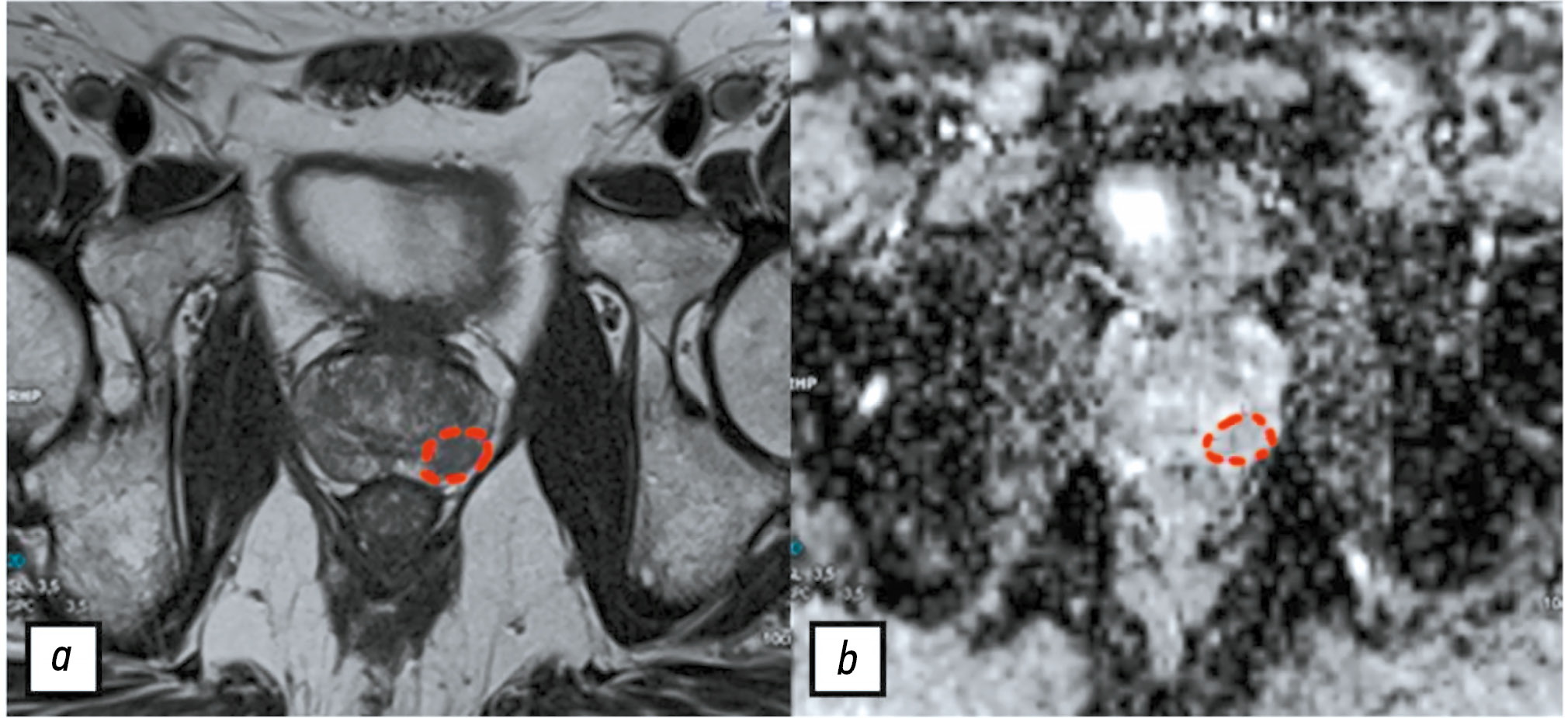
BACKGROUND: Texture analysis improves the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and differential diagnosis of prostate lesions, which are primarily segmented through manual labeling, resulting in significant inter-expert variability of masks. A consensus-based technique can help reduce inconsistencies in prostate lesion segmentation. However, global scientific studies have not described any standardized, consensus-based labeling protocols.
AIM: This study aimed to develop a consensus algorithm for manual labeling of prostate lesions by several independent experts and evaluate inter-expert consistency in lesion segmentation.
METHODS: This retrospective study included 60 biparametric magnetic resonance imaging scans of the prostate gland performed according to PI-RADS 2.1 technical specification. The scans showed PI-RADS 3, 4, and 5 lesions. Two independent radiologists manually segmented the prostate lesions using 3D Slicer. Then, the resulting masks were compared using the Dice–Sørensen coefficient (DSC). For lesions with DSC ≥ 0.75, the final mask was based on the overlap between the two original masks. Conversely, for lesions with DSC < 0.75, the final mask was determined using the proposed consensus algorithm.
RESULTS: The proposed consensus algorithm significantly increased the DSC values, from 0.61 [0.48; 0.73] for primary labeling to 0.74 [0.62; 0.79] for labeling using the proposed algorithm (p = 0.01).
CONCLUSION: The proposed consensus-based algorithm for labeling prostate lesions using magnetic resonance imaging data is crucial in addressing inadequate approaches to objective segmentation in research and clinical settings.
 373-384
373-384


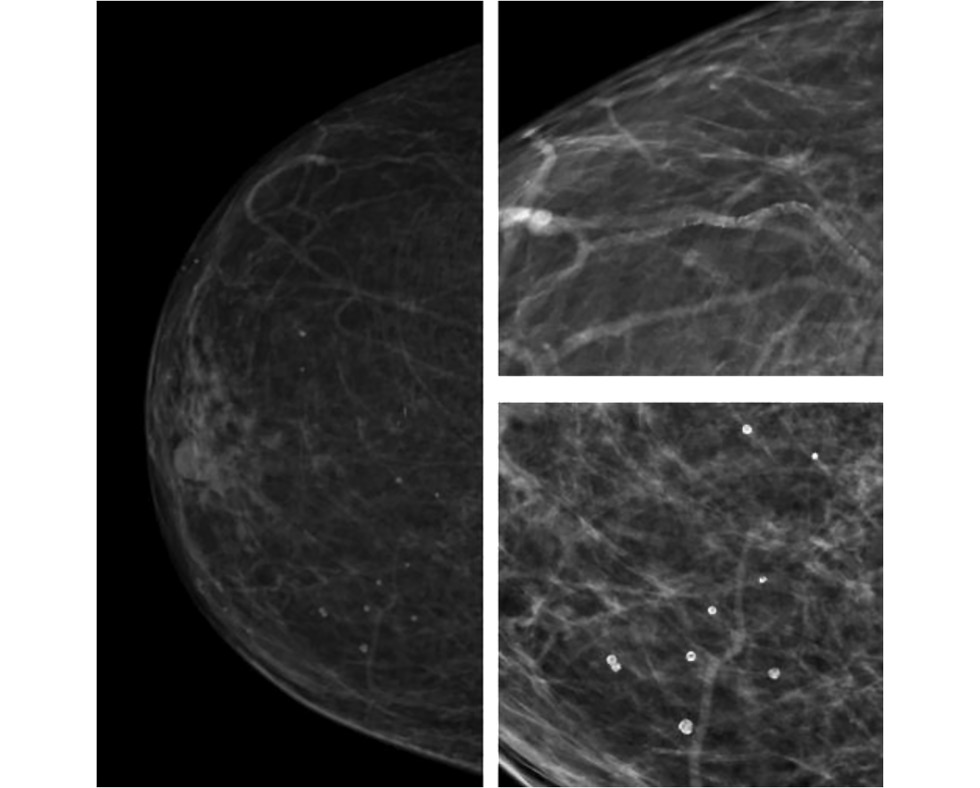
Radiographic markers of cardiovascular risk based on digital mammograms: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Studies have demonstrated an association between cardiovascular risk and mammographic density and breast arterial calcification. However, their combined impact remains poorly understood.
AIM: This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between mammographic density, breast artery calcification, and cardiovascular risk category in asymptomatic women aged ≥40 years.
METHODS: This retrospective, single-center, selective study included women who underwent preventive screening mammography at the University Clinic of Lomonosov Moscow State University between 2019 and 2023. The Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation 2 was used to determine cardiovascular risk categories. A radiologist evaluated mammograms at a workstation to obtain data on mammographic density and glandular calcifications. The data were analyzed using a machine learning technique called Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection. Univariate logistic regression was employed to calculate odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals. The reference group included mammograms showing high breast density and no calcifications. The odds ratio for each selected group is presented relative to the reference. The contingency tables were assessed using Pearson’s chi-squared (χ2) test. The significance level for all tested hypotheses was set at 0.05.
RESULTS: The mammograms of 1030 women aged 40–89 years were evaluated. Based on the study results, eight groups (G7–G0) were formed, depending on combinations of the following criteria: high or low glandular density, presence or absence of vascular and nonvascular calcification, and extent of calcification. Women with low mammographic density and vascular calcifications in more than one quadrant were found to have a >75% likelihood of high or extremely high cardiovascular risk. The probability exceeded 90% for a combination of vascular and nonvascular calcifications in two or more quadrants.
CONCLUSION: A correlation was found between calcifications, mammographic density, and cardiovascular risk category.
 398-413
398-413


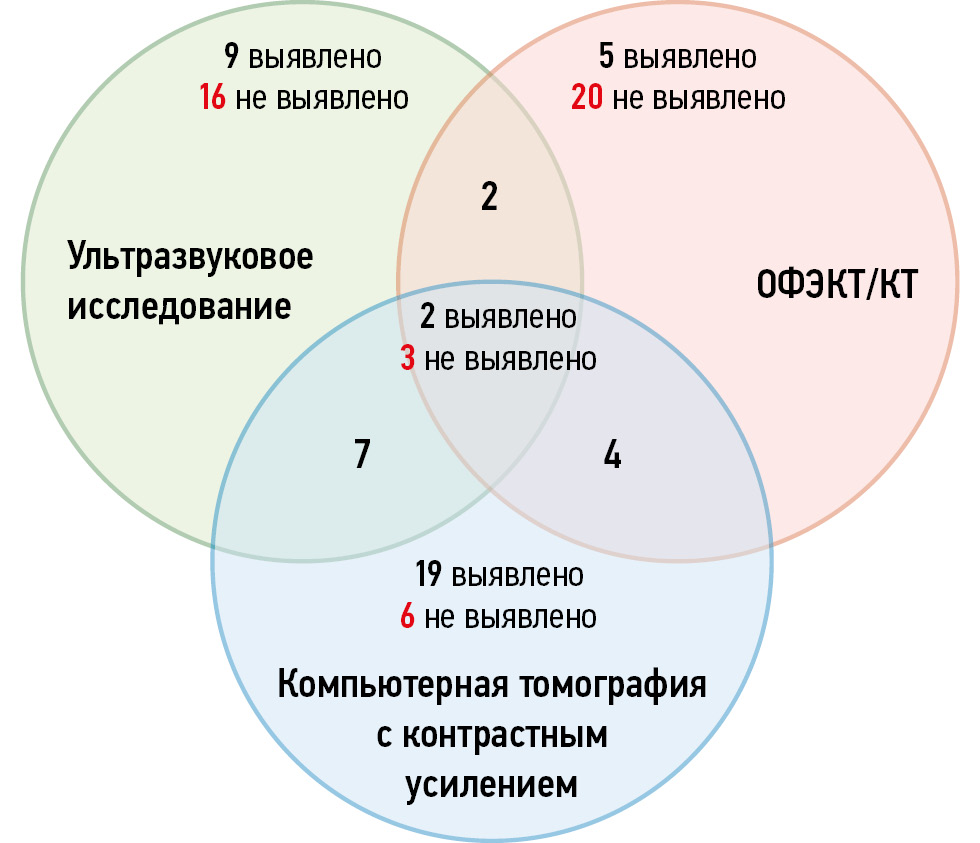
Diagnostic accuracy of radionuclide imaging for parathyroid lesions in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and nodular and autoimmune thyroid disorders: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Concomitant thyroid disorders can decrease the diagnostic accuracy of topical imaging modalities used to localize primary hyperparathyroidism. Therefore, in such cases, the effectiveness of radionuclide imaging for parathyroid lesions should be confirmed.
AIM: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of nodular and autoimmune thyroid disorders on the diagnostic accuracy of radionuclide imaging for parathyroid lesions in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and compare the accuracy of radionuclide imaging with that of other imaging modalities.
METHODS: The study included three patient groups: patients with primary hyperparathyroidism without a concomitant thyroid disease (group 1; n = 50), patients with autoimmune thyroid disorder (group 2; n = 50), and patients with thyroid nodule/multinodular goiter (group 3; n = 50). All the patients underwent ultrasound, planar scintigraphy, and single-photon emission computed tomography with X-ray computed tomography prior to parathyroidectomy. If negative or equivocal results were obtained (e.g., suspected parathyroid lesion), a contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan was performed. The intervals between scans and between the first scan and parathyroidectomy did not exceed 6 months and 12 months, respectively. Sensitivity and the positive predictive value were estimated.
RESULTS: In group 2, the diagnostic accuracy of radionuclide imaging for parathyroid lesions was lower than that of other imaging modalities. Moreover, in group 2, contrast-enhanced computed tomography demonstrated a diagnostic sensitivity of 79%, and its combination with ultrasound achieved a higher sensitivity of 85%. In group 3, the highest diagnostic value was obtained for single-photon emission computed tomography combined with X-ray computed tomography (85%) or ultrasound (88%). The results of radionuclide imaging of parathyroid lesions in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and autoimmune thyroid disease depended on the volume, density, and vascularization of the thyroid gland.
CONCLUSION: Single-photon emission computed tomography combined with X-ray computed tomography is an accurate diagnostic modality for identifying parathyroid lesions in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and concomitant nodular thyroid disorder. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography showed the highest sensitivity in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and autoimmune thyroid disease.
 385-397
385-397


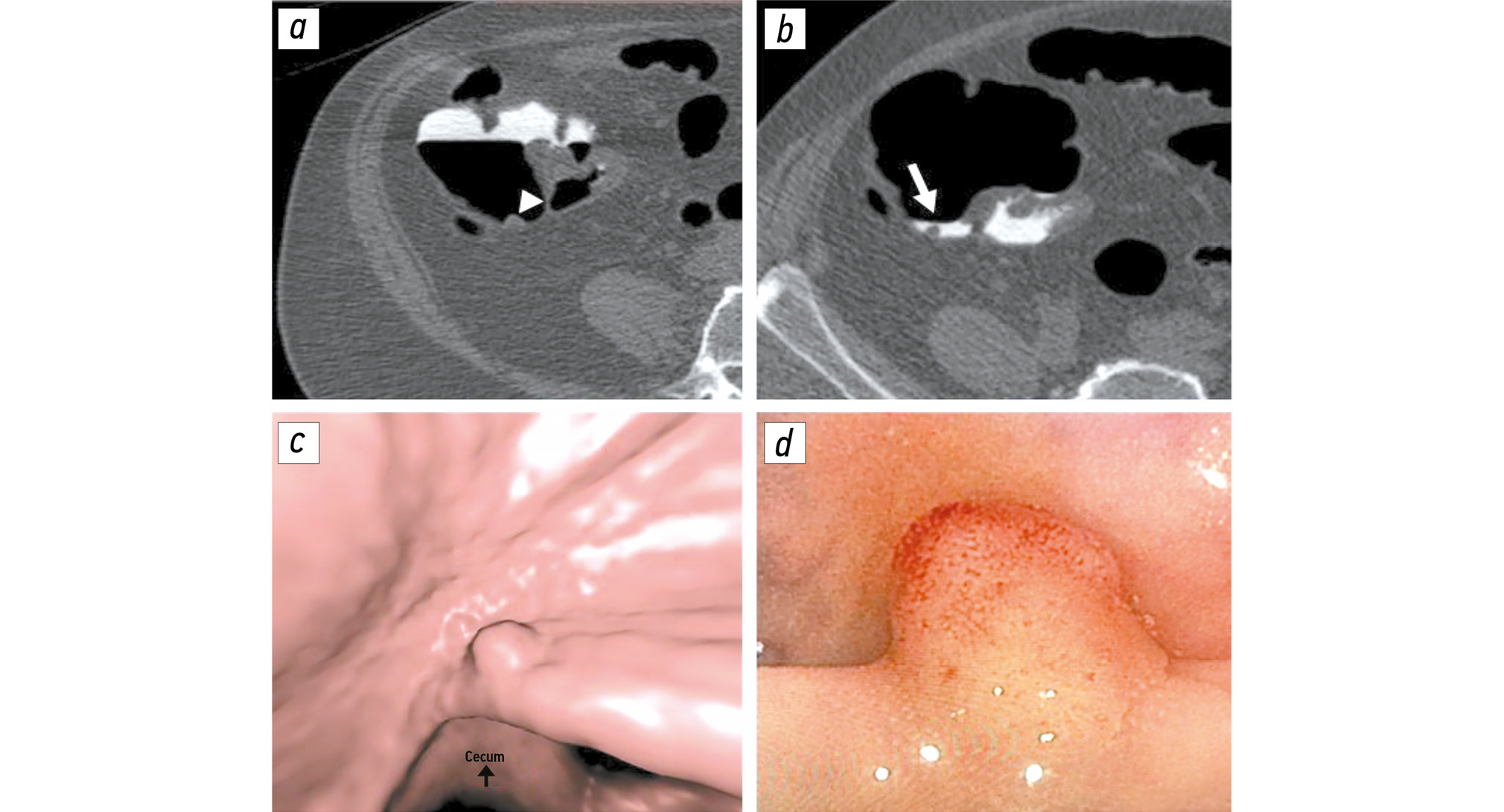
Comparison of single-dose and split-dose fecal tagging with iohexol in computed tomographic colonography
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Proper fecal tagging allows for high-quality computed tomography colonography. However, there is no single tagging scheme. Therefore, the effects of a contrast enhancement regimen on fecal tagging should be evaluated.
AIM: This study aimed to compare the quality of single-dose fecal tagging with that of split-dose fecal tagging with iohexol during computed tomographic colonography and to assess the impact of these regimens on procedure tolerability.
METHODS: In this retrospective, selective, single-center study, the patients were divided into two groups based on whether they received single-dose (group 1) or split-dose (group 2) fecal tagging. Both groups received 50 mL of the iodine-containing contrast agent iohexol, with iodine concentration of 350 mg/mL. The residual liquid density was assessed using three parameters: maximum, minimum, and mean values. Additionally, the residual fluid homogeneity was assessed by calculating the mean standard deviation within the region of interest. Tolerability of preparation for colonography was assessed using a 10-point visual analog scale.
RESULTS: The final sample included 338 patients: 116 in group 1 and 222 in group 2. The mean, minimum, and maximum density values in group 2 were significantly higher than those in group 1: 943 [722; 1245], 753 [525; 1082], and 1079 HU [801; 1456] versus 681 [420; 907], 570 [374; 820], and 825 HU [496; 1154], respectively (p < 0.001). The residual fluid homogeneity was significantly higher in group 2 than in group 1: 59 [46; 78] versus 67 HU [54; 81] (р = 0.012). Group 2 showed a significantly lower subjective difficulty of preparation than did group 1: 4 [2; 6] and 5 [4; 7], respectively (p = 0.004).
CONCLUSION: A single dose of 50 mL of iohexol (iodine concentration: 350 mg/mL) provides higher-quality fecal tagging than a split-dose provides because of higher residual fluid density with maintained homogeneity. Moreover, single-dose tagging was found to be more tolerable.
 452-463
452-463


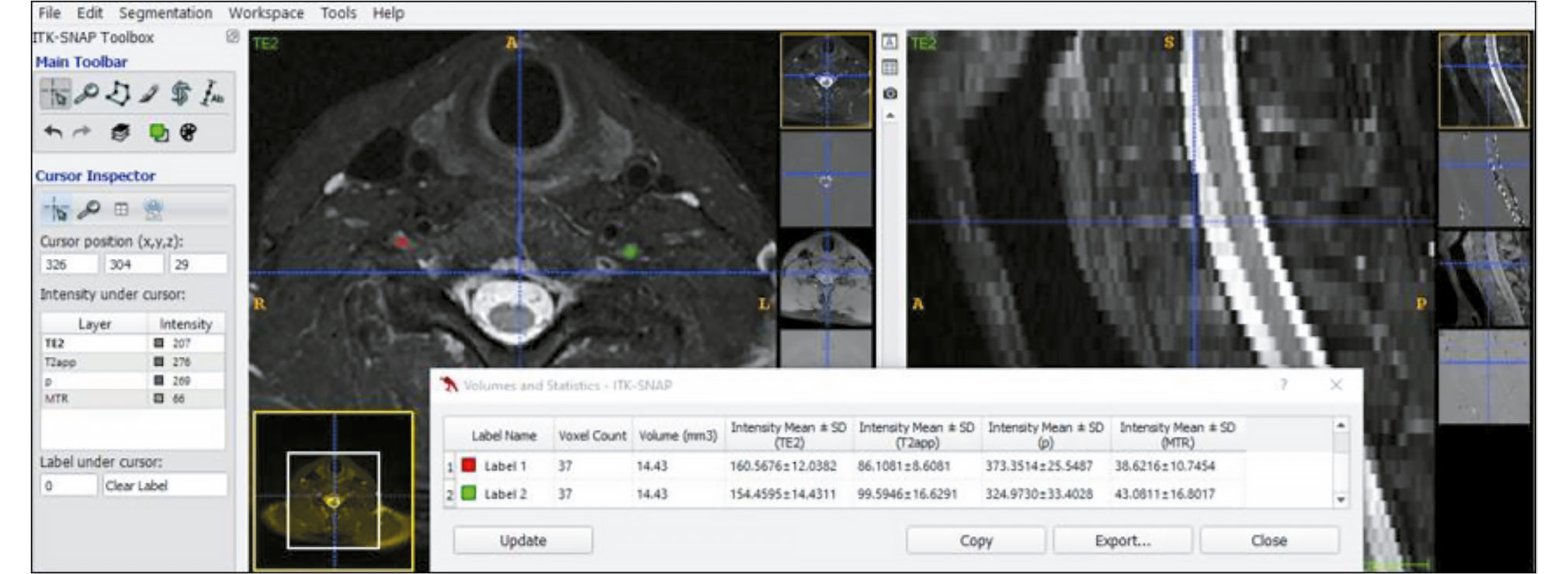
Quantitative parameters of magnetic resonance imaging of the brachial plexus in healthy adults and associated signs: a pilot cross-sectional study
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Standard magnetic resonance imaging sequences only provide qualitative image assessment, which is rather subjective. However, some quantitative techniques can interpret findings more objectively and expand diagnostic capabilities. Previously, they were mainly used for brain and joint scans; however, current technology allows using them for evaluating peripheral nerve function.
AIM: This study aimed to evaluate quantitative parameters of magnetic resonance imaging of the brachial plexus elements in healthy adults, depending on the side and level of spinal nerves and demographic and anthropometric characteristics.
METHODS: Ten healthy volunteers were included. Their main demographic and anthropometric characteristics were recorded before they underwent magnetic resonance imaging. A 3T magnetic resonance imaging scanner was used. In addition to standard sequences, the scan protocol included regimens for obtaining T2 relaxation times and magnetization transfer ratios from nerve elements of the brachial plexus. Data were post-processed using the MATLAB software package. Then, regions of interest were manually assigned to in the maps, and numerical values were obtained. Furthermore, thickness of the nerve elements was measured. Data were statistically processed using the SPSS software.
RESULTS: In each participant, the numerical values of the quantitative magnetic resonance imaging parameters (measured T2 relaxation time, proton density, magnetization transfer ratio, and thickness) in the anterior rami of the spinal nerves that form the brachial plexus were obtained. The thickness gradient of the normal anterior rami was revealed, with the highest value occurring at the level of the anterior rami of cervical spinal nerve C7. Significant positive correlations between T2 relaxation time and age were determined by analysis of the associations between quantitative magnetic resonance imaging parameters and demographic and anthropometric characteristics. In addition, negative correlations were found between height and measured T2 relaxation time and proton density.
CONCLUSION: The study results indicate that future research on T2 relaxation parameters should consider age and height in both healthy volunteers and patients with a brachial plexus condition. Additionally, when measuring the thickness of the anterior rami of the brachial plexus using standard sequences, the size and thickness gradient of the nerve elements should be considered.
 427-439
427-439


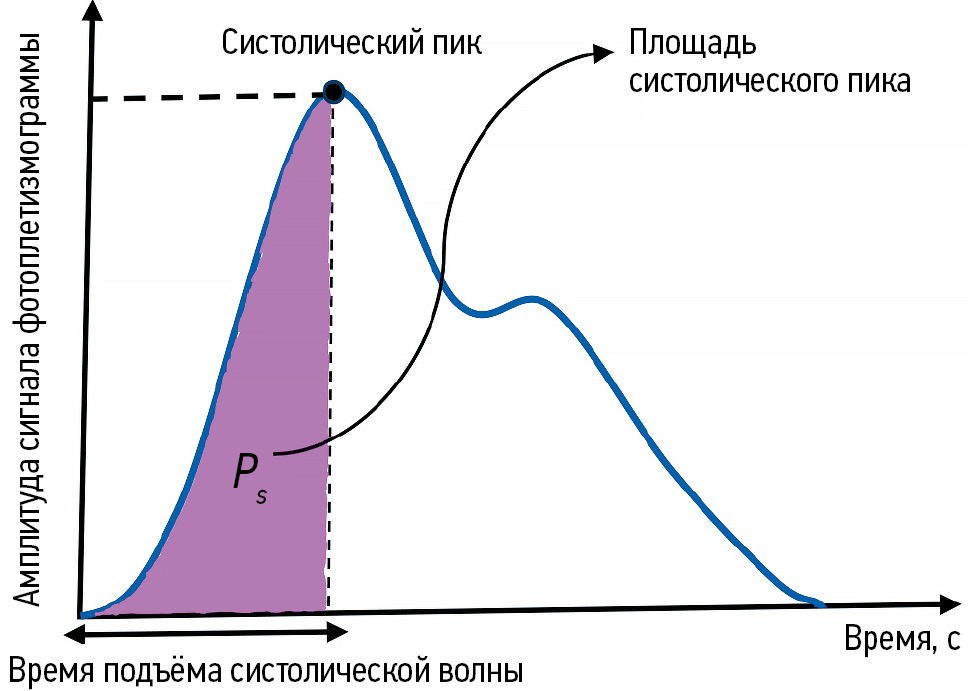
Fuzzy controller design for predicting the systolic area of photoplethysmogram signal using Persian medicine pulsology
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Photoplethysmography, a method used to measure blood volume changes per pulse, is widely applied in healthcare. In Persian medicine, pulsology is considered one of the most important methods for clinical diagnosis. However, recently the theory of fuzzy sets has provided a valuable foundation for developing knowledge-based systems in medical research.
AIM: To estimate and predict the systolic area of photoplethysmography signals using Persian medicine pulsology, by leveraging the potential of fuzzy systems.
METHODS: To design the fuzzy controller, a Persian medicine specialist simultaneously recorded data on PM pulse characteristics including pulse frequency and pulse strength—along with photoplethysmography signals, from 55 healthy volunteers. Initially, rules were generated based on the input and output variables. After evaluating these rules using the collected data, 35 were retained and presented in a two-input–one-output lookup table.
RESULTS: The fuzzy system was then constructed using MATLAB. It included 35 rules, triangular and trapezoidal membership functions, a singleton fuzzifier, a product inference engine, and a center-average defuzzifier. This system, which used pulse frequency and pulse strength as inputs and provided the systolic area as output, demonstrated acceptable performance within the defined input range.
CONCLUSIONS: The proposed fuzzy controller system reasonably predicted the systolic area of photoplethysmography signals using Persian medicine pulse parameters. The results revealed that increasing pulse frequency decreased the systolic area, while increasing pulse strength increased it, in alignment with previous results. Therefore, this system may boost the clinical skills of Persian medicine students and practitioners. It also holds promise for application in disease diagnosis and prediction and for facilitating integration between Persian medicine and mainstream medicine.
 414-426
414-426


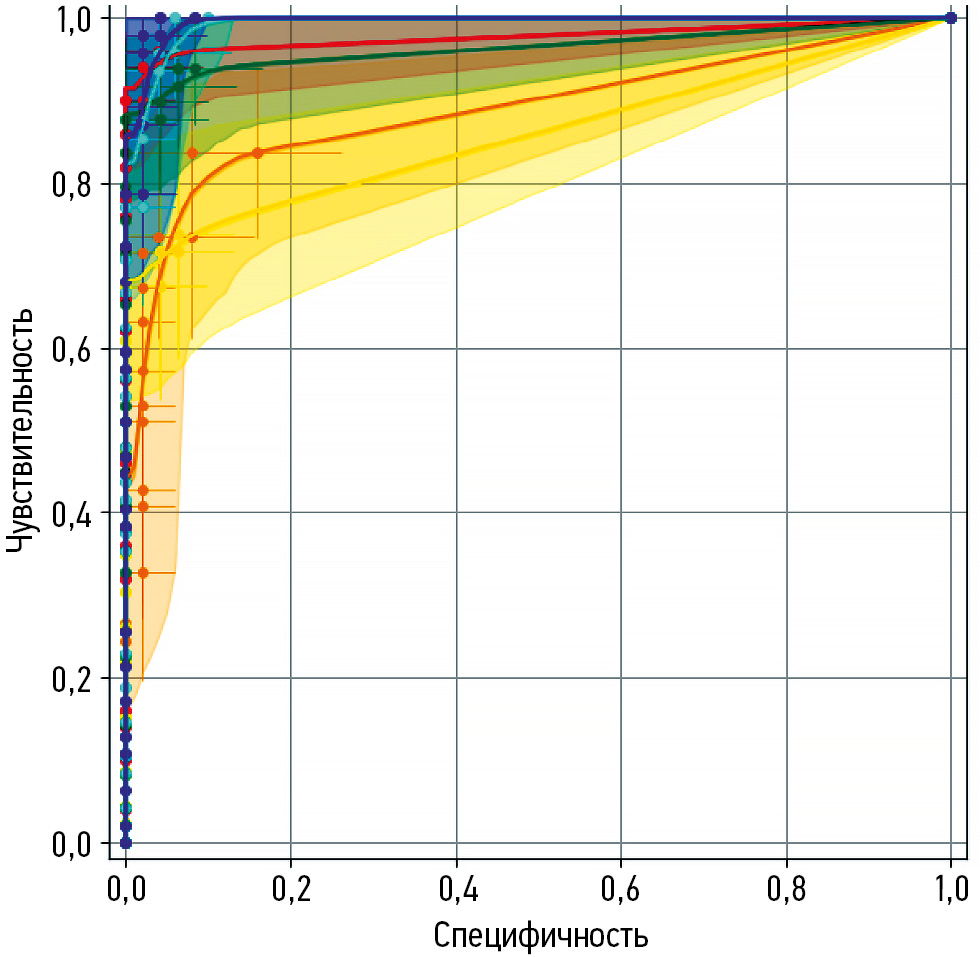
Application of artificial intelligence technologies in detecting adrenal neoplasms on computed tomography scans
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Adrenal neoplasms are a common incidental finding on computed tomography, which remains the primary imaging method used to make a presumptive diagnosis of the lesion’s nosological type. Artificial intelligence-based software solutions for detecting adrenal neoplasms on computed tomography scans have been actively developed and implemented.
AIM: This study aimed to assess the diagnostic effectiveness of artificial intelligence-based software in identifying adrenal neoplasms on computed tomography images of the chest and abdominal organs available as of the first quarter of 2024.
METHODS: Artificial intelligence-based software was tested in two modifications: a single-purpose service designed to detect adrenal neoplasms and comprehensive artificial intelligence service for analyzing non-contrast computed tomography image series of the chest and abdominal organs (including contrast-enhanced studies). Two datasets were used: dataset 1 included abdominal computed tomography scans, and dataset 2 comprised chest computed tomography scans. Each dataset consisted of 100 anonymized computed tomography studies of patients with (n = 50) and without (n = 50) adrenal neoplasms. The diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based software was determined by calculating the following statistical metrics: area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
RESULTS: Testing of the artificial intelligence-based software on datasets with signs of adrenal neoplasms demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy metrics that exceeded the declared performance values. AUC ranged from 0.858 to 0.995 (the highest value was achieved by the artificial intelligence single-purpose service-2 for analyzing abdominal computed tomography images); specificity ranged from 0.920 to 1.000 (the highest value was achieved by the artificial intelligence comprehensive service-2 for analyzing chest computed tomography images); and sensitivity ranged from 0.739 to 1.000 (the highest values were achieved by the artificial intelligence single-purpose and artificial intelligence comprehensive service-2 for analyzing abdominal computed tomography images).
CONCLUSION: Artificial intelligence-based software for detecting adrenal neoplasms showed high diagnostic accuracy across all the evaluated metrics. Therefore, such systems may be effective for identifying adrenal neoplasms on chest and abdominal computed tomography scans of the chest and abdominal organs.
 464-476
464-476


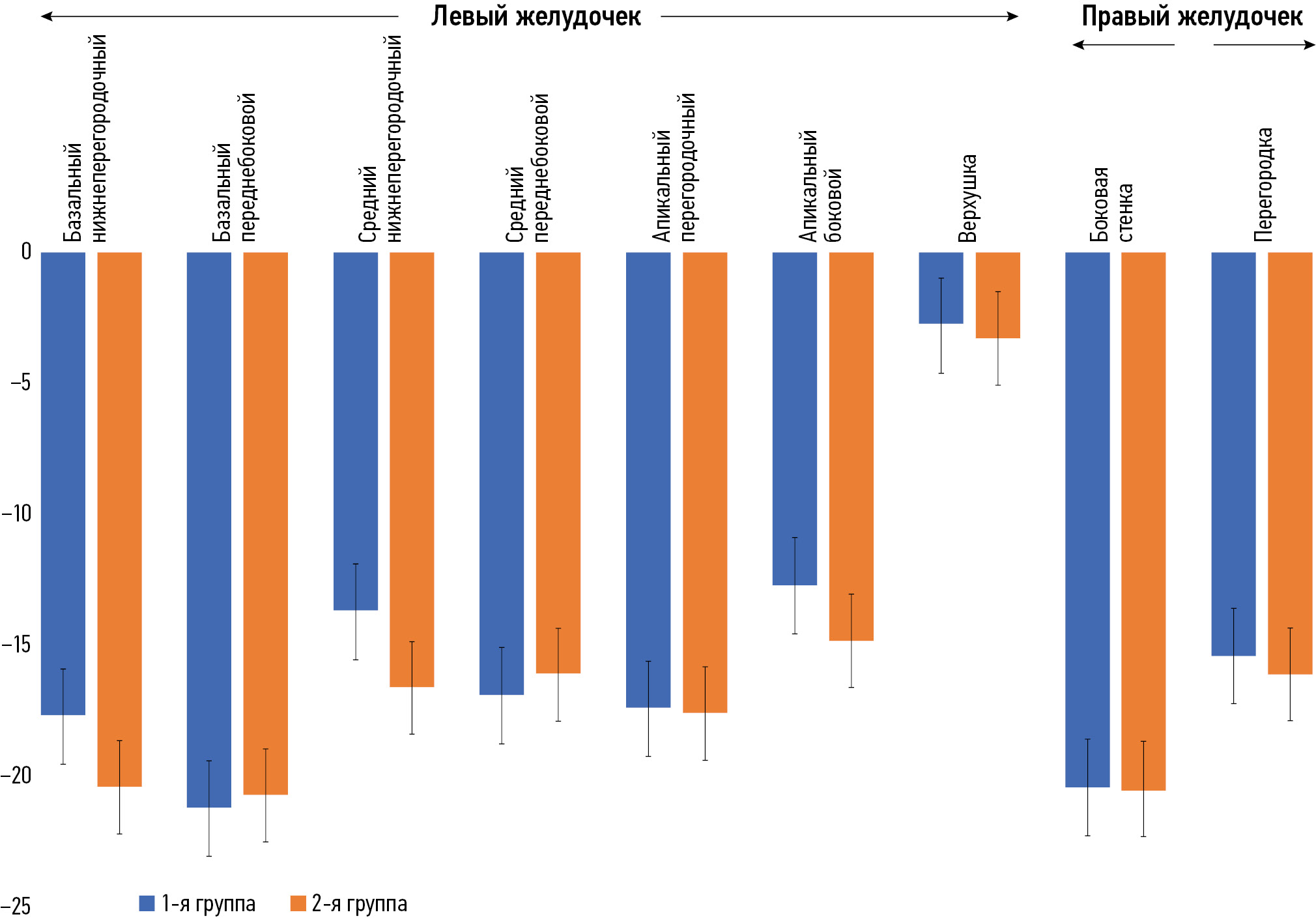
Role of myocardial strain parameters in assessing indications for pulmonary valve replacement in children after tetralogy of Fallot repair: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Radical repair of tetralogy of Fallot significantly improves patients’ survival and quality of life. However, in the long-term postoperative period, most patients develop progressive pulmonary valve insufficiency. Pulmonary regurgitation gradually increases the volume load on the right ventricle, causing dilation, impaired systolic and diastolic function, and higher risk of arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. In turn, pulmonary valve replacement decreases afterload and improves myocardial function. Nevertheless, the optimal timing of valve replacement in asymptomatic patients after tetralogy of Fallot repair remains unclear.
AIM: This study aimed to evaluate myocardial strain parameters as potential criteria for determining the need for pulmonary valve replacement.
METHODS: This single-center retrospective (medical record-based) cross-sectional study included data from patients treated at the departments of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Cardiology within the National Research Cardiac Surgery Center (Astana, Kazakhstan). Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was performed between December 2011 and June 2020 in patients who had undergone radical tetralogy of Fallot repair. Because a threshold value of right ventricular end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) between 150 and 170 mL/m2 indicates a need for pulmonary valve replacement in asymptomatic patients, the sample was divided into two groups based on RVEDV: group 1, RVEDV <150 mL/m2, and group 2, RVEDV ≥150 mL/m2. The prognostic value of myocardial strain parameters in decision-making for timely pulmonary valve replacement was assessed.
RESULTS: The study included 69 patients aged 3–18 years (11 ± 4 years) who had undergone radical tetralogy of Fallot repair. Circumferential strain in the basal anteroseptal segment of the left ventricle significantly differed between groups 1 (n = 52) and 2 (n = 17): −23.2 ± 5.8% vs −16.7 ± 8.4% (p = 0.003). Moreover, in the basal inferior segment of the left ventricle, significant differences were observed: −10.8 ± 5.2% in group 1 and −7.8 ± 6.8% in group 2 (p = 0.014). The right ventricular end-systolic volume in group 1 was approximately twice as low as in group 2: 56.9 ± 19.1 vs 103.9 ± 111.9 mL/m2 (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION: The findings indicate the diagnostic value of myocardial strain parameters and their potential as additional criteria for evaluating indications for pulmonary valve replacement.
 440-451
440-451


Technical Reports
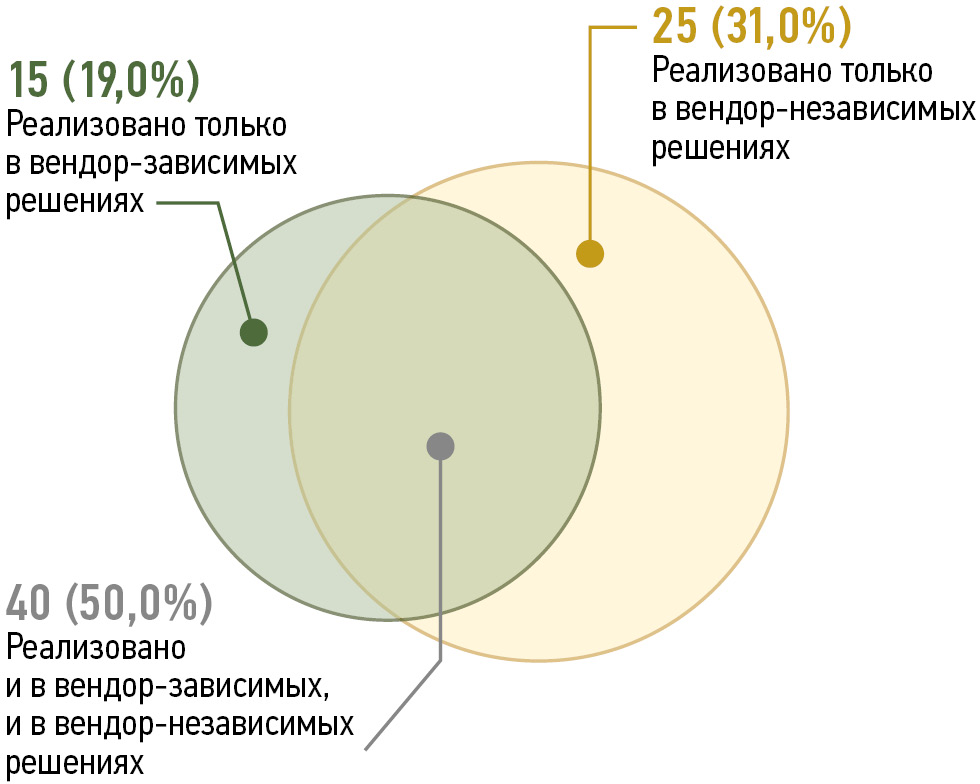
Automated radiology workstation: comparing two approaches for selecting radiodiagnostic solutions (technical report)
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Patient examinations generate large amounts of data on various diseases, which are virtually impossible to process manually. Currently, automated radiology workstations incorporate clinical decision–support systems that facilitate image analysis. At present, two options are used: built-in vendor-dependent and vendor-independent software solutions. Both have broad functionality, but they also have their advantages and drawbacks. Therefore, the choice of the best clinical decision–support system depends on the healthcare organization.
AIM: This study aimed to compare two approaches for selecting radiodiagnostic solutions for automated radiology workstations in Moscow.
METHODS: The study conducted a two-stage, cross-sectional survey between September 2023 and March 2024. Data on vendor-independent software were obtained from participants of the Experiment on the use of innovative computer vision technologies for analysis of medical images in the Moscow healthcare system. Conversely, data on vendor-dependent solutions was collected from the manufacturers’ websites. Furthermore, a survey of 40 radiologists was performed to evaluate the relevance of software functions.
RESULTS: At the time of the survey, the vendor-independent software demonstrated slightly more functions than the vendor-dependent solutions. The greatest differences were observed in the functionality of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging modalities, whereas the functionality for X-ray imaging and mammography was nearly identical. The survey of radiologists showed that 6 of 17 functions were unique to built-in vendor-dependent software. However, <40% of the radiologists actually needed these functions, whereas the shared functions were relevant for >50% of the respondents.
CONCLUSION: Vendor-independent and built-in vendor-dependent software solutions share only half of their functions. Thus, in choosing between these two options, healthcare facilities should consider their specialization and their radiologists’ requests. Moreover, approximately two-thirds of the built-in vendor-dependent software functions used by radiologists in Moscow can be implemented using vendor-independent solutions. Therefore, the choice of software should be based on the facility’s technical capacity and economic feasibility.
 477-486
477-486


Short communications
Evaluation of the radiation dose from dental cone-beam computed tomography: short communication
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Dental cone-beam computed tomography offers several advantages, including superior image quality, an acceptable size, and a lower radiation dose compared to conventional CT scanning. Moreover, cone-beam computed tomography is more suitable for dentists to acquire and analyze images, and it provides greater comfort for patients due to technological advancements. Cone-beam computed tomography generates three-dimensional images of the head and neck and is utilized across various dental fields, including dental surgery, endodontics, trauma, implant dentistry, head and neck lesions and diseases, and orthodontics.
AIM: To evaluate seven tissue doses using three scan protocols on a cone-beam computed tomography scanner KaVo OP 3D Pro, and to investigate the effect of resolution options on the effective dose.
METHODS: Three protocols were employed in this study. Three voxel size settings were assessed: 420 μm, 380 μm, and 320 μm. The field of view and tube voltage were kept constant at 13 cm × 15 cm and 90 kV, respectively. Other were, scan time (8–27 seconds) and dose range (50–350 μSv). The absorbed and effective doses were calculated for each cone-beam computed tomography scan protocol.
RESULTS: In the throat, the highest dose was absorbed by tissue-2 (7.719 mGy). In the teeth, the highest dose was absorbed by tissue-3 (16.326 mGy). In the cheek, the maximum dose was absorbed by tissue-3 (25.053 mGy). In the eyes, the highest dose was absorbed by tissue-3 (12.962 mGy). In the forehead, the highest dose was absorbed by tissue3 (8.465 mGy). In the mid-skull, the highest dose was absorbed by tissue-3 (20.904 mGy). In the occipital region, the highest dose was absorbed by tissue-2 (7.8 mGy). Regarding effective doses, protocol-3 generally resulted in higher values, except in the throat and occipital regions, where tissue-2 absorbed more.
CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates that changes in cone-beam computed tomography exposure parameters influence the effective dose. Adjusting resolution settings results in variations in effective doses, highlighting the significance of selecting appropriate exposure factors, such as voxel size or resolution options. Dentists must carefully consider imaging parameters, as these decisions have a direct impact on patient exposure.
 487-495
487-495


Reviews
Experience of using machine learning to optimize renal replacement therapy: a review
Abstract
This review examined studies on the use of machine learning tools to optimize renal replacement therapy.
Publications were searched using the databases eLibrary, PubMed, and Scopus. The TITLE and ABSTRACT fields were used to select the metadata for the following queries: artificial intelligence AND (dialys* OR hemodialys*) and machine learning AND (dialys* OR hemodialys*). The use of different word forms for key concepts was considered, and the period of publications was not limited. The primary search yielded 669 full-text articles. Three independent experts (i.e., two nephrologists and one machine learning specialist) manually selected articles. Article selection focused on the use of machine learning algorithms, solution of a specific issue of optimization of dialysis therapy, and availability of a model specifically developed for patients on dialysis and not intended for other clinical tasks.
Review of articles revealed that predicting dialysis adequacy is the most common dialysis-related task wherein machine learning tools are used. Dialysis adequacy refers to the effective removal of nitrogenous waste products. Post-procedural complications are a potential indirect sign of dialysis inadequacy, the risk of which is what artificial intelligence models are trained to identify. They are also used as basis for selecting therapy for renal anemia and phosphorus–calcium metabolism disorders, as various factors should be considered in these cases, including changes over time. Several studies of machine learning are aimed at predicting survival of patients on dialysis and determining the optimal time to initiate renal replacement therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease. A comprehensive review of the articles showed several limitations, including small sample sizes, insufficient testing during the preliminary preparation and analysis stages, and low reproducibility of many studies. The most relevant studies described the clinical implementation of systems based on machine learning algorithms after testing them on different patient populations.
 497-509
497-509


Correspondence
Visual images in radiography: pareidolia as a useful tool for physicians and artificial intelligence
Abstract
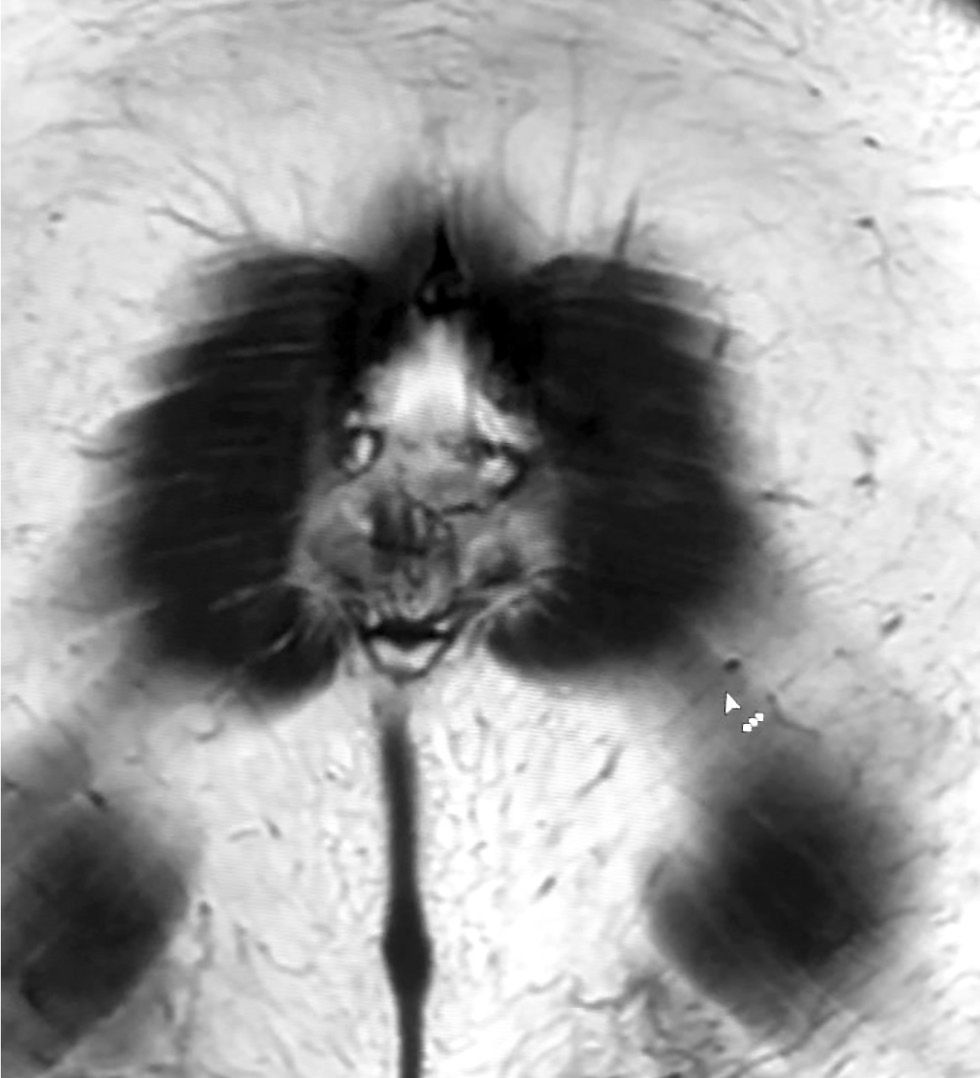
This article explored the role of pareidolia in radiography and its potential in improving diagnosis and medical personnel training. Pareidolia is the phenomenon of perceiving familiar patterns in random objects, such as faces on the moon’s surface and animal figures in clouds. In radiography, pareidolia can manifest as recognizable patterns in medical images. This enables radiographers to identify abnormalities and improve their diagnostic skills.
This work aimed to evaluate pareidolia caused by the interpretation of X-ray images and determine its potential applications.
From June to December 2023, a competition was held to create a dataset of pareidolic illusions. Thirty-one individuals participated, including medical imaging specialists who had access to radiographic images. Images from nine additional participants were obtained outside the competition. Overall, 71 images were received. Participants uploaded images using a form on Yandex Forms. Data quality was ensured by clearly defined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Data analysis revealed that people most frequently perceive human faces, animal snouts, and the heart symbol. These findings indicate the possibility of further research. This article discusses the potential applications of pareidolia in developing neural networks for automated medical image analysis and in educational activities that stimulate creative thinking and association.
Moreover, the article emphasizes the importance of ongoing research in this area to develop effective diagnostic tools and educational programs by expanding the evidence base.
 510-521
510-521