Том 3, № 4 (2022)
- Жылы: 2022
- ##issue.datePublished##: 30.12.2022
- Мақалалар: 7
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/4133
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.34
Original Study Articles
Substantiation of a new approach to the criteria for assessing the radiation dose of patients during computed tomography
Аннотация
BACKGROUND: In accordance with the requirements of the IAEA basic safety standards and the International Commission on Radiation Protection, comparing the radiation dose for patients undergoing computed tomography (CT) in diagnostic and treatment clinics with national or international DRLs is important for controlling medical radiation doses. The search for ways to improve DRLs calculations determines the relevance of such studies.
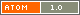
AIM: To analyze the dependence of effective doses (EDs) in CT of different body parts on patient’s weight and to calculate the standard ED for the patient (70 and 80 kg).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: CT acquisition protocols in 209 patients were single phase (SP) CT, while 114 patients underwent multi-phase (MP) CT. ED was calculated according to the normalized coefficients for each body area. The values of standard ED was calculated by data approximation using linear function of ED relatively body weight for each type CT scanner and body area scanned.
RESULTS: The increase in ED following a CT examination was proportional to the body weight of patients. For SP and MP CT scans, the standard EDs were calculated according to all body areas. The mean ED, median ED, and DRLs (mSv) in these groups was slightly higher than standard ED (mSv) if the criterion was 70 kg and were close to standard ED if the criterion was 80 kg. These values give a basis for improving the guidelines concerning the recommended limits of radiation doses for CT in individual patients according to indications and body parts studied.
CONCLUSIONS: In the study, a methodology for assessing and comparing the dose of CT-radiation at two hospitals in the two CT scanners, considering weight of a standard patient, is described. Our results show that the calculation and analysis of the standard ED of CT-examining areas of the body instead of mean ED and median ED help to compare the radiation exposure in different medical facilities more properly. Given the recent sharp increase in the number of CT studies, not exceeding the standard ED for patients with CT will reduce the long-term consequences in the form of oncological pathology among the population.
 344-361
344-361


Possibilities and limitations of using machine text-processing tools in Russian radiology reports
Аннотация
BACKGROUND: In radiology, important information can be found not only in medical images, but also in the accompanying text descriptions created by radiologists. Identification of study protocols containing certain data and extraction of these data can be useful primarily for clinical problems; however, given the large amount of such data, the development of machine analysis algorithms is necessary.
AIM: To estimate the possibilities and limitations of using a tool for machine processing of radiology reports to search for pathological findings.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: To create an algorithm for automatic analysis of radiology reports, use cases were selected that participated in the experiment on the use of innovative technologies in the computer vision for the analysis of medical images in 2020. Mammography, chest X-ray, chest computed tomography (CT), and LDCT, were among the use cases performed in Moscow. A dictionary of keywords has been compiled. After the automatic marking of the reports by the developed tool, the results were assessed by a radiologist. The number of protocols analyzed by the radiologist for training and validation of the algorithms was 977 for mammography, 4,804 for all chest X-ray scans, 4,074 for chest CT, and 398 for chest LDCT. For the final testing of the developed algorithms, test datasets of 1,032 studies for mammography, 544 for chest X-ray, 5,000 for CT of the chest, and 1,082 studies for the LDCT of the chest were additionally labeled.
RESULTS: The best results were achieved in the search for viral pneumonia in chest CT reports (accuracy 0.996, sensitivity 0.998, and specificity 0.989) and breast cancer in mammography reports (accuracy 1.0, sensitivity 1.0, and specificity 1.0). When searching for signs of lung cancer by the algorithm, the metrics were as follows: accuracy 0.895, sensitivity 0.829, and specificity 0.936, when searching for pathological changes in the chest organs in radiography and fluorography protocols (accuracy 0.912, sensitivity 1.000, and specificity 0.844).
CONCLUSIONS: Machine methods with high accuracy can be used to automatically classify the radiology reports of mammography and chest CT with viral pneumonia. The achieved accuracy is sufficient for successful application to automatically compare the conclusions of physicians and artificial intelligence models when searching for signs of lung cancer in chest CT and LDCT, pathological findings in chest X-ray.
 374-383
374-383


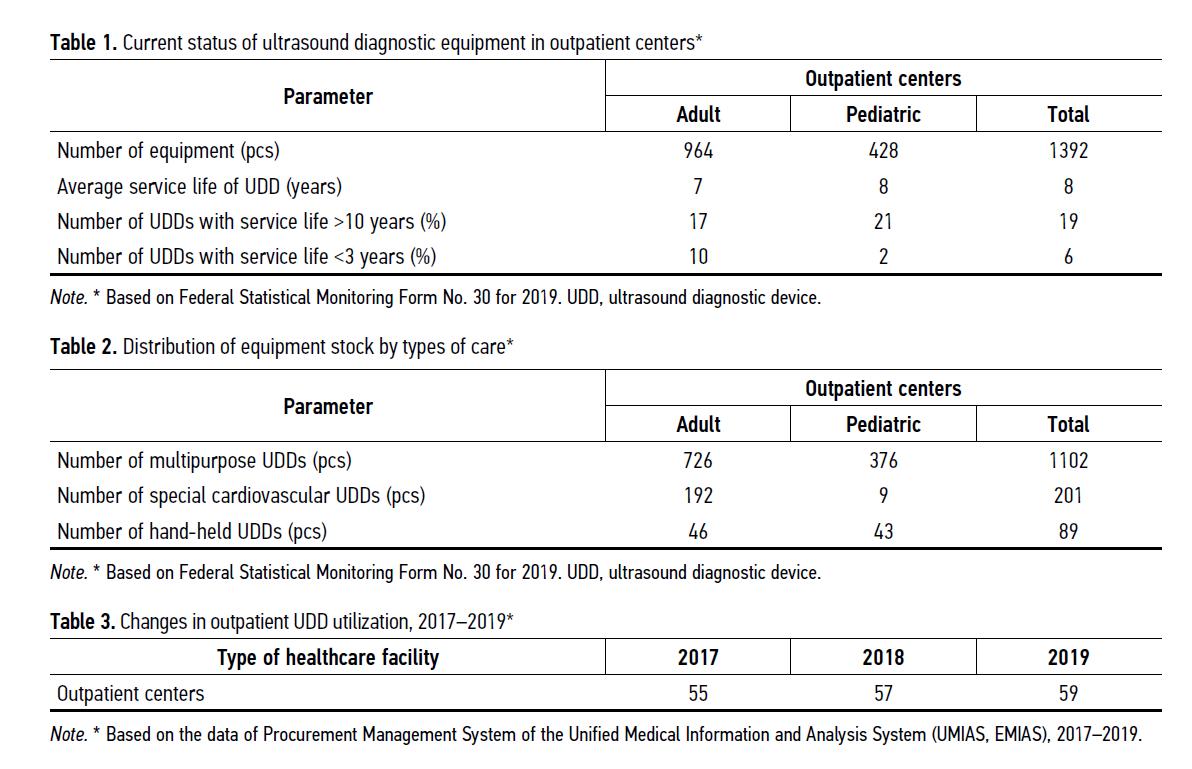
Minimum standard for equipping Moscow clinics with ultrasound diagnostic devices
Аннотация
BACKGROUND: A variety of ultrasound equipment and a lack of generally accepted classifications lead to inefficient equipment of medical organizations, incorrectly selected types of device, sets and probes’ characteristics, as well as a level of study quality. A systematic approach to equipping similar medical organizations with ultrasound devices will ensure the availability and improve the quality of primary medical care in outpatient centers.
AIM: To develop a calculation algorithm and recommendations for the minimum standard for equipping regional outpatient medical facilities of the state healthcare system based on the Moscow example.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In conducting the study, we used software for statistical and comparative analysis based on the data of the Material Support Management System of the Unified Medical Information and Analytical System (MSMS UMIAS), Form No.30 of Federal Statistical Observation, as well as a number of assigned population to the outpatient center (hereinafter referred to as the OC), technical data, and reviews of modern ultrasound diagnostic devices.
RESULTS: The developed minimum standard for equipment considers the following factors: 1) need to provide medical care to children and adult populations separately; 2) compliance with modern diagnostic technologies; 3) ensuring the territorial availability of diagnostics under the condition of efficient equipment operation.
CONCLUSIONS: Standardization of equipment of outpatient medical facilities with ultrasound diagnostic devices contributes to improving the quality of diagnostics and the availability of providing required examinations to the assigned population, reducing the waiting time for examinations, reducing the shortage of necessary equipment, expanding the range of medical services provided to the city population, and minimizing duplicate studies at subsequent stages of medical care.
 362-372
362-372


Case reports
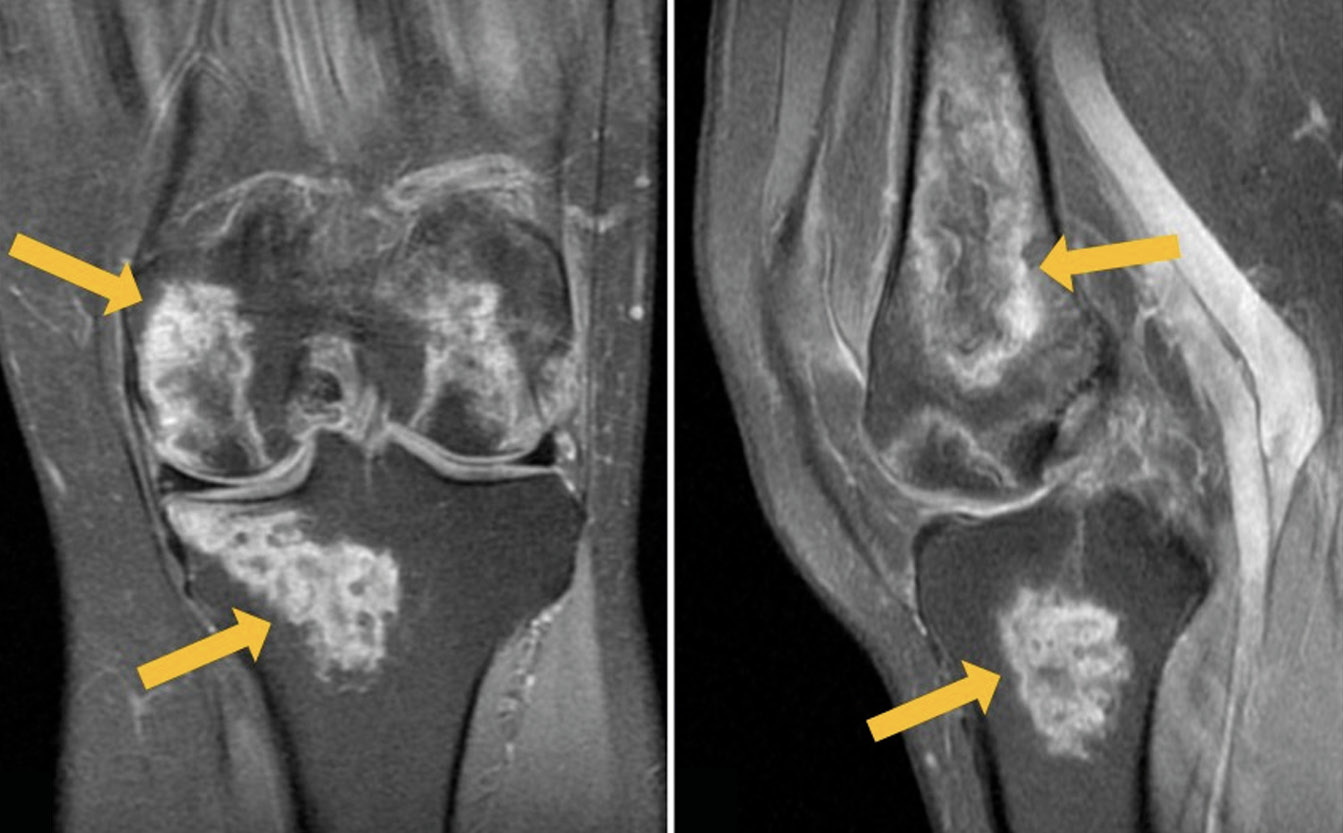
Rare localization of avascular necrosis during treatment of COVID-19 with glucocorticosteroids
Аннотация
The development of bony avascular necrosis induced by glucocorticoid treatment of COVID-19 is a common adverse effect, with femoral head being the most commonly affected. Timely detection of avascular necrosis is important in the prevention of osteoarthrosis and other complications.
We present a clinical case of a 54-year-old patient hospitalized for novel coronavirus infection with complaints of severe pain in both knees 2 weeks after the disease onset. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed pronounced changes in both knees, corresponding to avascular necrosis. The results of conservative therapy, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bisphosphonate bone resorption inhibitors, produced a pronounced positive result. At follow-up examination 3 months later, there was no pain, but the knee joints still had slight restrictions of movement. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a significant decrease in the previously detected changes.
The side effects of glucocorticoids (impaired glucose tolerance, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, gastrointestinal erosive ulcers, sleep disorders, etc.) are widely known, but knee osteonecrosis caused by steroid intake rarely comes to the attention of clinicians. This clinical case emphasizes the complex nature of osteonecrosis pathogenesis and demonstrates a wide range of complications in corticosteroid therapy.
 384-392
384-392


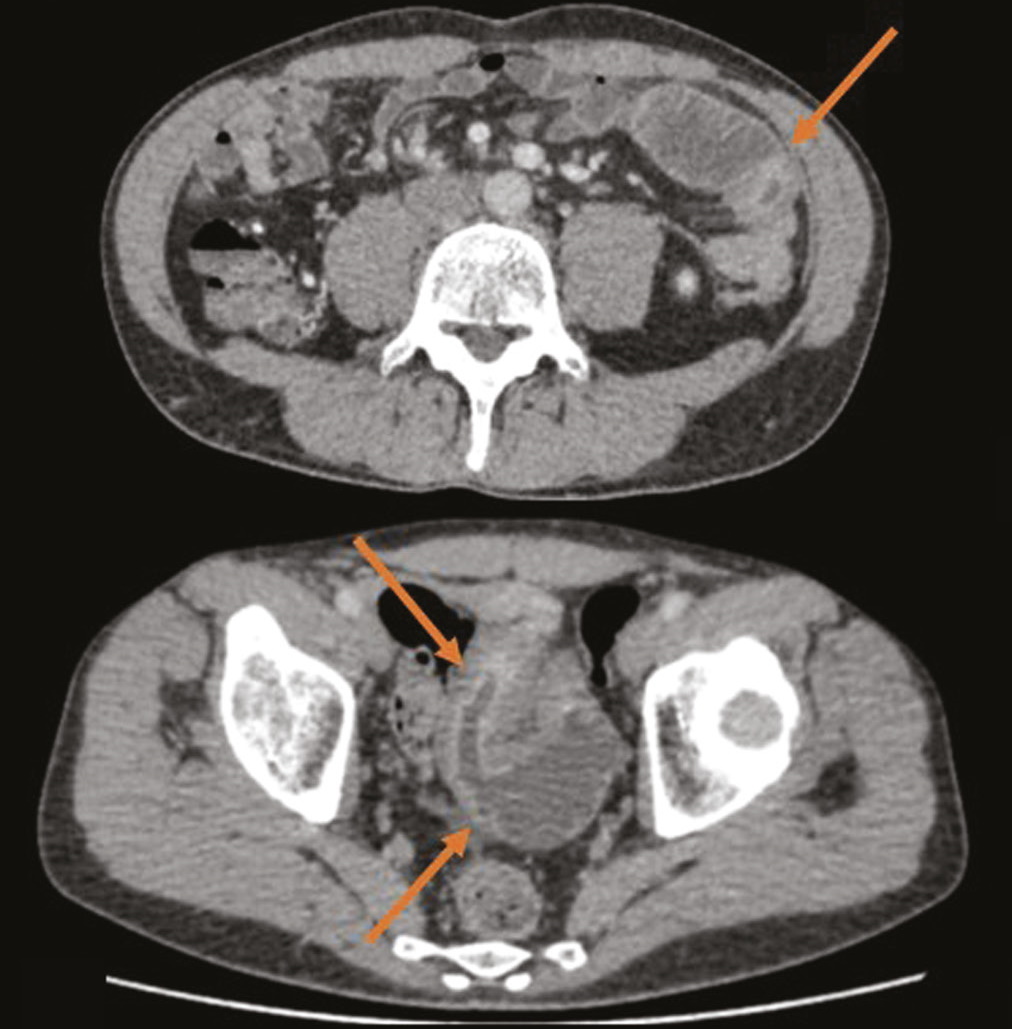
Latent course of Crohn’s disease: the role of tomographic imaging in diagnosis
Аннотация
Crohn’s disease with localization in the upper gastrointestinal tract, terminal ileum, or colon is diagnosed based on visualization of the lesion area using endoscopic methods and histological examination. In cases of damage to the small intestine, when endoscopy methods are not informative enough and the use of videocapsular endoscopy has a number of contraindications, it is advised to use radiation diagnostic methods, such as multispiral computed tomography and/or magnetic resonance enterography, to make a diagnosis.
We present a clinical case of ambiguous clinical manifestations of Crohn’s disease with small intestine and rectal involvement. Tomographic imaging was used to confirm the diagnosis. A 44-year-old patient presented with complaints of non-pronounced abdominal pain, dyspepsia. The lab panel showed indirect signs of malabsorption, an increase in fecal calprotectin. An endoscopic examination with histological verification revealed a picture of proctitis. After performing computed tomography and/or magnetic resonance enterography multiple lesions of the small intestine were revealed. This clinical case demonstrates an atypical clinical picture of Crohn’s disease with jejunal, iliac, and rectal lesions.
The patient had no characteristic complaints; the results of endoscopic and morphological studies were not informative. Imaging by means of computed and magnetic resonance tomography has played a crucial role in the diagnosis and successful treatment.
 394-402
394-402


Editorials
How to create a modern medical center in the current conditions?
Аннотация
A modern multidisciplinary clinic is not only a medical facility, but also an engineering and often biotechnical facility. The technological complexity of the object depends on the planned (bio) medical profiles and functionality, the need for scalability and upgradability, as well as many other factors.
When viewed from the outside, the creation, from an idea to commissioning, of a modern specialized or multidisciplinary medical center does not look prohibitively complicated, and its stages (pre-project surveys, medical and technical specifications, draft design, design stages, construction, equipping, and entering the planned production power) are seen as understandable and achievable. However, our own experience of direct participation and analysis of the implementation of various specialized medical centers in our country indicates the presence of a lot of false prejudices, mistakes, outdated principles, and other problems in practice.
In the article, we analyze, explain, and systematize typical misconceptions and vices when creating an oncology center, but the same problems arise when creating any multidisciplinary medical center. We believe that our experience will be useful for familiarization not only to designers, technologists and architects, but also to doctors, healthcare organizers, as well as to all specialists involved in the creation of modern medical centers.
 404-412
404-412


Correspondence
Innovative strategic session in the scientific activity of the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine
Аннотация
Sometimes, you need to go beyond the possible and ordinary in order to create something new. Human potential is limitless, and the world of technological possibilities opens up new horizons and helps to achieve the most difficult goals.
A real scientist should think out of the box and go beyond the rules. Sticking with what we know today and being not open to new knowledge hinders our scientific progress. It is quite difficult, if not impossible, to get rid of bias. Similar to how it is almost beyond our possibilities to pull yourself out of the “rut” of the rules without a help.
However, we tried to do impossible possible at our “Science Week.” The last week of July at the Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Healthcare Department was highlighted by this outstanding extraordinary event. During this week, the importance of scientific discoveries for both an individual and whole society was demonstrated. In fact, it was a platform for discussing advanced technologies, challenges, and solutions. For 4 days, the scientists of the Center presented their reports and defended their ideas. Their colleagues took part in the discussion and asked questions about the application and implementation of their initiatives.
 414-420
414-420