Том 3, № 1 (2022)
- Год: 2022
- Выпуск опубликован: 24.04.2022
- Статей: 8
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/3449
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.31
Технические отчеты
Влияние COVID-19 на динамику изменений дозовой нагрузки на пациентов при проведении компьютерной томографии в медицинских организациях Москвы
Аннотация
Обоснование. Распространение новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19) в Москве привело к значительному увеличению числа компьютерных томографий органов грудной клетки, выполняемых пациентам в рамках диагностики и оценки эффективности проводимой терапии. Связанное с COVID-19 изменение структуры лучевой диагностики в Москве ведёт к изменениям в величине и структуре коллективной дозы облучения населения столицы, при этом сам процесс выглядит разнонаправленным. Отсутствие на текущий момент достоверной информации по изменению структуры лучевой диагностики и уровней облучения населения Москвы в связи с эпидемией COVID-19 и обусловило проведение данной работы.
Цель ― оценить влияние эпидемиологической обстановки на динамику изменений уровня дозовых нагрузок на пациентов при проведении компьютерно-томографических исследований в медицинских организациях Москвы за период 2017–2020 гг.
Материалы и методы. Собраны и проанализированы заполненные формы № 3-ДОЗ за 2017–2020 гг., полученные от медицинских организаций города Москвы различных форм собственности; данные формы № 30 за 2017–2020 гг. и данные единого радиологического информационного сервиса (ЕРИС) за 2020 г. Проведён анализ годовых коллективных и средних индивидуальных доз облучения пациентов по анатомическим областям тела.
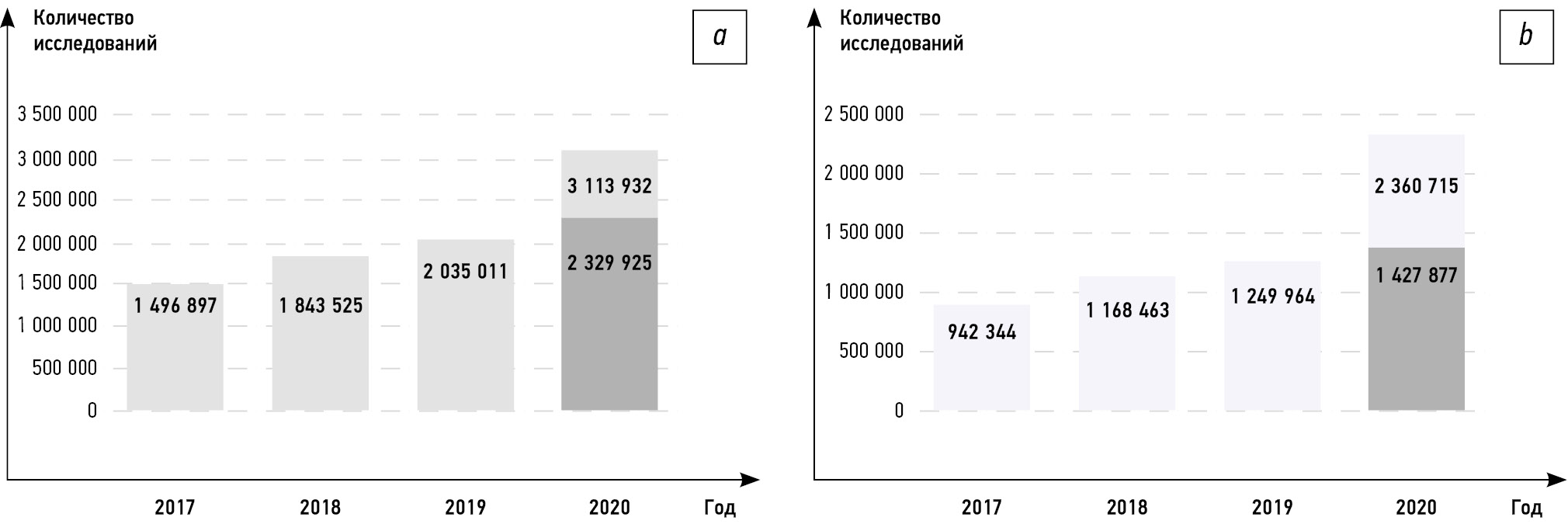
Результаты. Анализ данных учётных форм продемонстрировал существенный рост компьютерно-томографических исследований в Москве: реальное количество исследований оказалось на 31% больше ожидаемых. Количество исследований органов грудной клетки в 2020 г. увеличилось почти в 2 раза по сравнению с другими временными периодами. В совокупности всё это повиляло на рост значений средней эффективной дозы, которая в 2020 г. также выросла более чем в 2 раза.
Заключение. Эпидемиологическая обстановка в 2020 г. оказала существенное влияния как на динамику изменений дозовой нагрузки на пациентов при проведении компьютерной томографии, так и на вклад определённых видов компьютерно-томографических исследований в зависимости от анатомической области. Анализ помог выявить ряд преимуществ и недостатков различных форм сбора данных.
 5-15
5-15


Краткие сообщения
Всероссийский рейтинг отделений лучевой диагностики: результаты конкурса 2020 года
Аннотация
Вопросы менеджмента качества медицинской помощи и организации работы отделений лучевой диагностики всегда актуальны и требуют постоянного контроля и аналитической экспертизы. Московское региональное отделение Российского общества рентгенологов и радиологов (МРО РОРР) с 2018 года проводит независимую оценку отделений лучевой диагностики во всех регионах России. Цель рейтинга ― выявить лидеров отрасли, а также распространить лучшие практики по всей стране. По результатам анкетирования выявлены положительные тенденции развития службы диагностической помощи по всей стране и критические точки, влияющие на качество работы медицинских организаций.
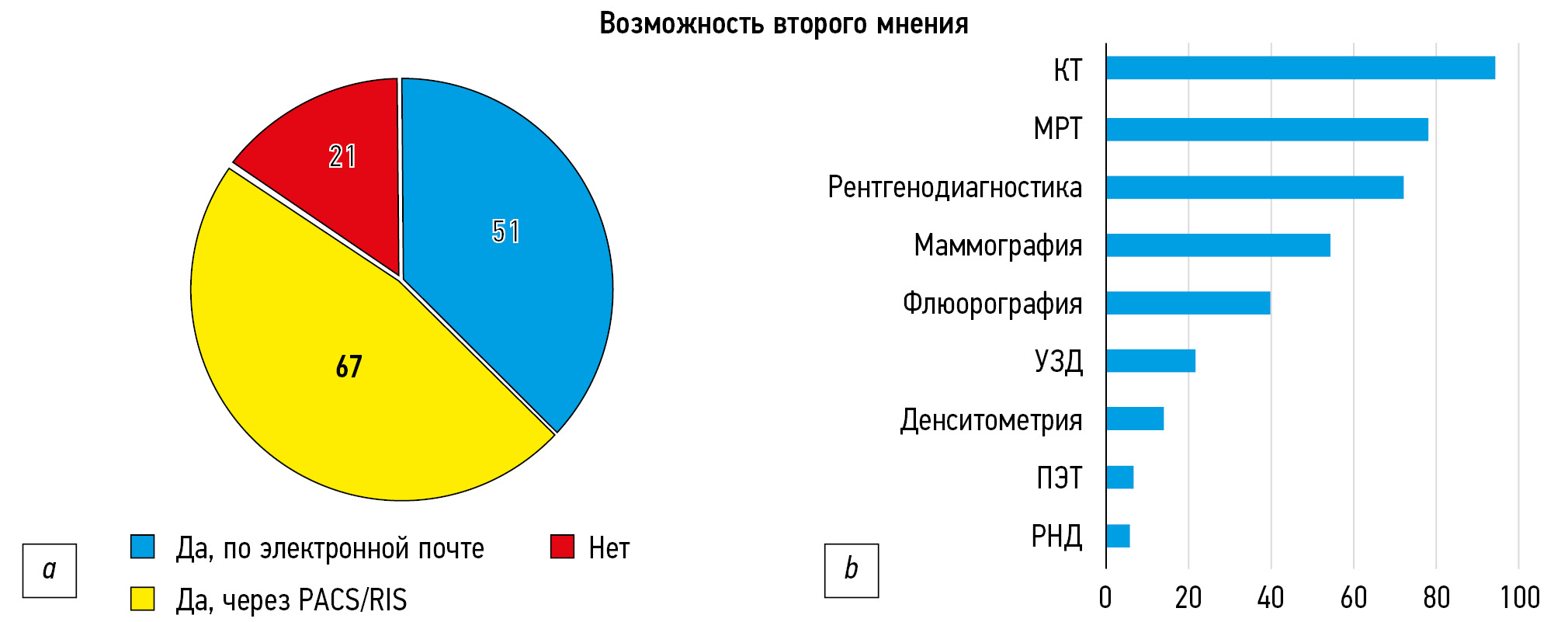
Представлен анализ функционирования 123 отделений лучевой диагностики в 2020 году. По окончании приёма заявок на участие в рейтинге был сформирован перечень из 163 медицинских организаций, расположенных в 15 городах 7 федеральных округов. Процедура оценки была разбита на три этапа. На первом этапе состоялось онлайн-анкетирование: каждой из организаций-участников было предложено ответить на вопросы по устройству работы отделения, оснащённости, перечню и особенностям выполнения диагностических исследований, а также работе с пациентами. Во время второго этапа проводился клинический и технический аудит набора анонимизированных исследований с заключениями. Следует отметить, что техническому аудиту уделялось особое внимание, поскольку ряд медицинских организаций нарушал методику проведения исследований. Третий этап включал проверку информации о медицинских организациях в открытых источниках. Во время первого и второго этапов начислялись баллы, на основании которых были выбраны финалисты, лидеры и победители рейтинга.
По итогам оценки всех этапов 31 организация вышла в финал,6 попали в группу лидеров и 5 стали победителями, при этом 45% финалистов относились к Центральному федеральному округу. Прослеживается наибольшая заинтересованность аудита работы в муниципальных и частных медицинских учреждениях, нежели ведомственных и федеральных. Помимо перечня победителей собрана некоторая база данных, которая может представлять собой срез состояния службы лучевой диагностики в Российской Федерации.
Проведение подобных конкурсов направлено в первую очередь на повышение качества и безопасности проведения рентгенологических исследований. Методика проведения конкурса совершенствуется каждый год.
 43-54
43-54


Клинические случаи и серии клинических случаев
Полиоссальная фиброзная дисплазия: результаты визуализации спорного случая
Аннотация
Фиброзная дисплазия — редкое опухолеподобное доброкачественное врождённое заболевание костей, которое, по всей вероятности, связано с мутациями гена GNAS и характеризиуется широким спектром клинических проявлений, начиная от изолированных монооссальных и полиоссальных форм и заканчивая другими внескелетными проявлениями (синдром МакКьюна–Олбрайта). В результате этих изменений отмечается увеличение хрупкости костей, повышается риск возникновения переломов.
В данной статье описана пациентка в возрасте 65 лет, поступившая в наше рентгенологическое отделение с жалобами на боли в шее и спине. Ранее у больной были диагностированы поражения костей шейного и грудного отделов с подозрением на метастазы. В нашем отделении у пациентки предварительно диагностировали фиброзную дисплазию, что впоследствии было подтверждено данными ренгенографии, компьютерной и магнито-резонансной томографии. Окончательный диагноз поставлен по результатам биопсии костей.
Таким образом, фиброзная дисплазия в основном поражает кости, при этом нормальная костная ткань замещается диспластической фиброзной тканью. В зависимости от количества поражённых костей и сопутствующих эндокринных изменений выделяют три формы заболевания: монооссальную, полиоссальную и синдром Олбрайта. Дифференциальный диагноз среди прочего включал множественную миелому. Выбрана оптимальная тактика лечения.
 55-63
55-63


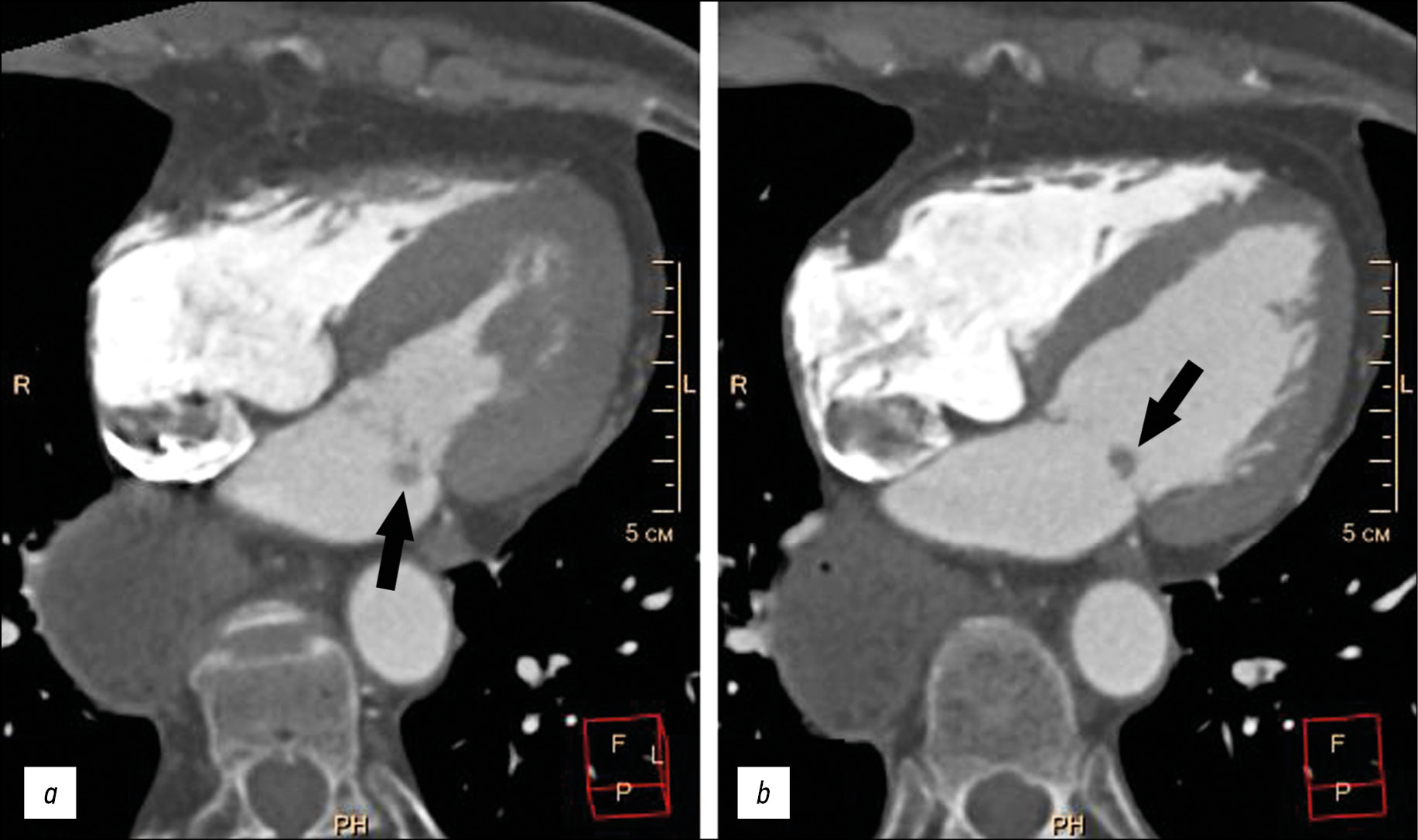
Миксома створки митрального клапана
Аннотация
Первичные опухоли сердца являются крайне редким заболеванием, распространённость их в популяции, по разным данным, составляет 0,0017–0,03%.
В большинстве случаев опухоли сердца имеют доброкачественный характер, более половины подобных образований представлены миксомами сердца. Миксома, поражающая створки клапанов сердца, является редчайшей патологией. Впервые подобный вариант изменений был описан в 1934 году. Наиболее часто миксомы сердца локализуются на уровне межпредсердной перегородки в непосредственной близости от овальной ямки. Одним из типичных признаков миксом является узкая ножка и неровная поверхность, что обусловливает риск эмболии. Эхокардиографическое исследование и магнитно-резонансная томография на настоящий момент являются методами выбора при подозрении на объёмное образование сердца. При подобной нетипичной локализации опухоли обязательна дифференциальная диагностика с вегетациями на клапанах сердца и папиллярной фиброэластомой.
Представлен случай пожилой пациентки с жалобами на одышку, колющие боли в левой половине грудной клетки, аритмии, в анамнезе которой имелась аспирационная пневмония, экстирпация пищевода с эзофагогастропластикой желудка. При обследовании у пациентки выявлены пароксизмальная форма фибрилляции предсердий (вне пароксизма), хроническая сердечная недостаточность, артериальная гипертензия. Клинические данные больной были нехарактерны для инфекционного эндокардита с вегетациями на клапанах. Благодаря эхокардиографическому исследованию и мультиспиральной компьютерной томографии с болюсным контрастным усилением на атриальной поверхности задней створки митрального клапана обнаружено дополнительное объёмное образование размерами 5–9 мм, округ-лой формы, с чёткими неровными контурами, смещаемое вместе со створкой клапана в полость левого желудочка в систолу предсердий. Оптимальная визуализация образования получена в режиме Fiesta-CINE в модифицированных двух- и четырёхкамерных проекциях. Пациентке выполнено удаление образования с шовной пластикой митрального клапана в условиях искусственного кровообращения. При гистологическом исследовании образования получена характерная морфологическая картина миксомы. Послеоперационный период протекал без осложнений.
 64-70
64-70


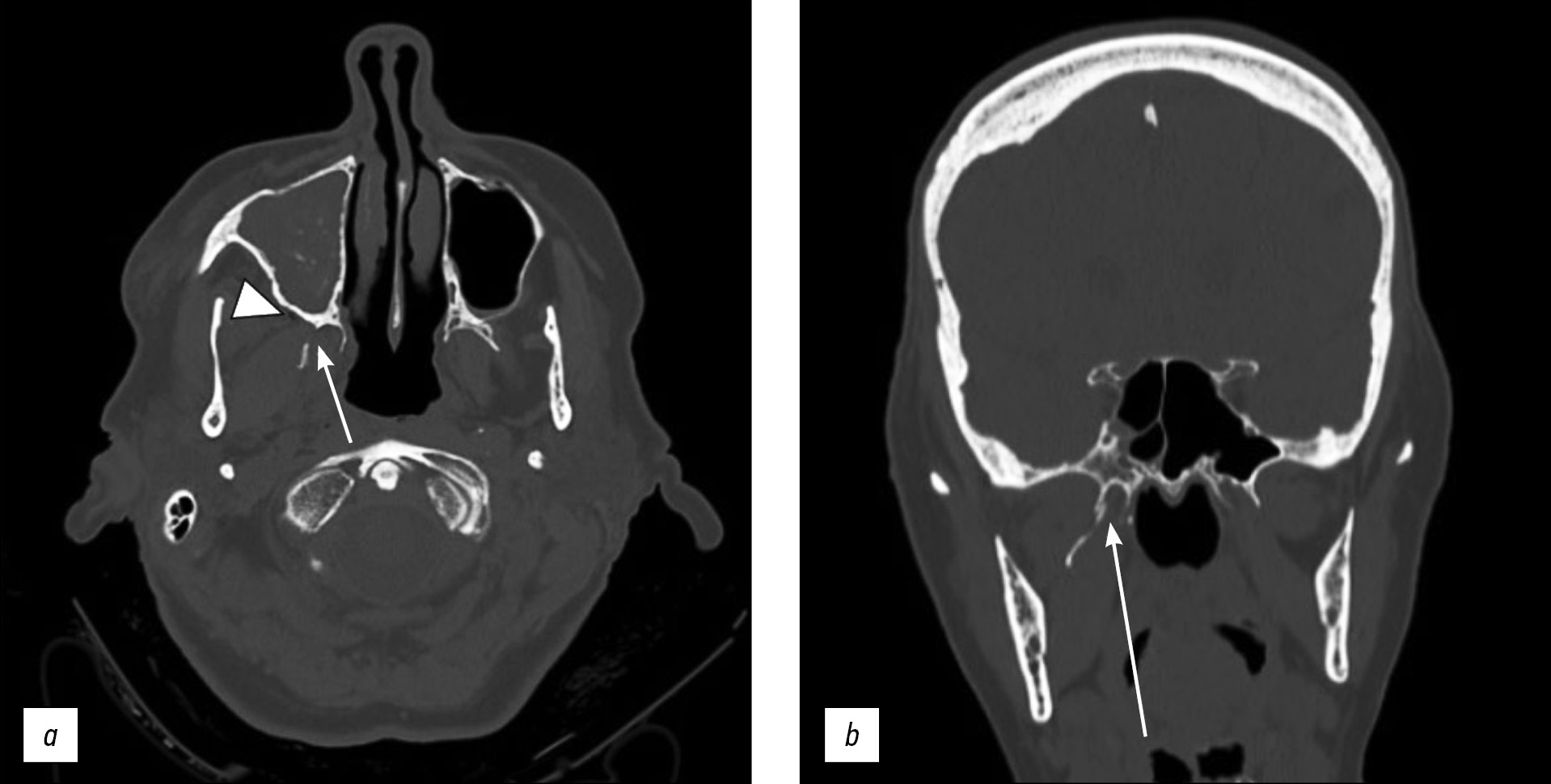
Односторонний изолированный перелом крыловидного отростка клиновидной кости: клинический случай
Аннотация
Переломы крыловидного отростка часто сочетаются с переломами по типу Ле-Фор и могут наблюдаться при других переломах лицевых костей, таких как переломы стенок лобных пазух и носо-глазнично-решётчатые переломы. Изолированные переломы крыловидного отростка встречаются крайне редко.
В отличие от переломов по типу Ле-Фор, которые необходимо лечить хирургическим путём с фиксацией нестабильных отломков для восстановления формы и функции и стабилизацией крыловидного отростка, изолированные переломы пластинок крыловидного отростка не требуют хирургического лечения.
В статье описывается редкий случай изолированного одностороннего перелома крыловидного отростка у 71-летней пациентки с черепно-мозговой травмой и гематомой у основания правой глазницы, полученными в результате потери сознания.
Компьютерная томография показала односторонний перелом пластинки крыловидного отростка справа с признаками эмфиземы в жевательно-челюстном пространстве с ипсилатеральной стороны. Кроме того, у пациентки выявлен перелом медиальной стенки вехрнечелюстной пазухи справа с признаками гемосинуса. Переломы основания черепа или повреждения твёрдой мозговой оболочки не обнаружены. Пациентка получала консервативное лечение.
 71-77
71-77


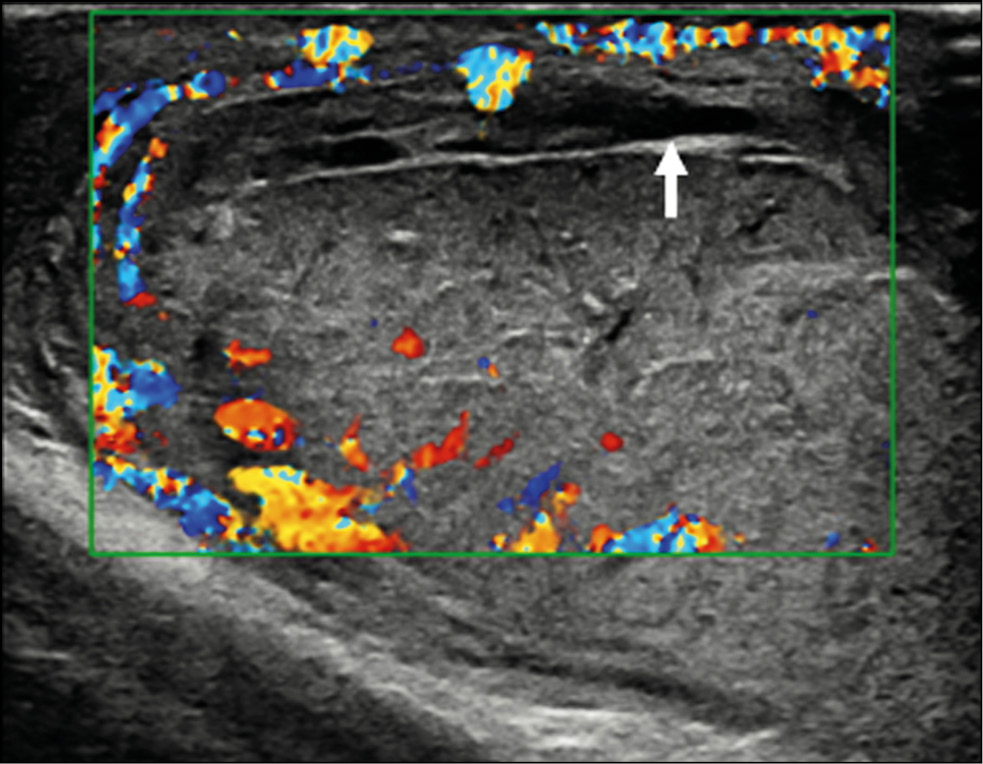
Разрыв яичка у молодого пациента: диагностическая ценность ультразвукового исследования с контрастным усилением
Аннотация
Разрыв яичка, возникший в результате тупой травмы мошонки, характеризуется повреждением белочной оболочки, что приводит к экструзии семенных канальцев.
Методы визуализации, в частности ультразвуковое исследование, играют важнейшую роль в оценке травмы мошонки и позволяют определить дальнейшую тактику ведения пациента — консервативное лечение или хирургическое вмешательство. Ультразвуковое исследование в стандартном В-режиме и цветовое допплеровское картирование являются основными методами визуализации при оценке травмы яичка, однако малоинформативны в отношении степени его повреждения. Наиболее важной информацией для хирурга являются целостность или разрыв белочной оболочки и степень повреждения жизненно важных тканей яичка. О последнем сложно судить, исходя лишь из данных стандартной ультрасонографии, по причине гиперваскуляризации яичка, возникающей вследствие отёка, нарушающего сосудистый кровоток. В случае сомнительных результатов цветового допплеровского картирования необходимо прибегать к другим современным методам визуализации, в частности к ультразвуковому исследованию с контрастным усилением, позволяющим определять жизнеспособность травмированного яичка.
В данной статье описывается клинический случай тупой травмы яичка у 15-летнего футболиста.
 78-85
78-85


Обзоры
Рекомендации CARE для описания случаев: разъяснения и уточнения
Аннотация
Обоснование. Доступное и понятное описание клинических случаев помогает выявлять самые ранние данные о возможной пользе, неблагоприятном влиянии и расходовании ресурсов; предоставляет информацию для клинической научной работы и разработки рекомендаций для клинической практики; интегрируется в медицинское образование. Авторы с большей вероятностью подготовят высококачественные описания случаев, если они будут следовать определённым правилам написания таких публикаций. В 2011–2012 гг. группа клиницистов, учёных и редакторов журналов разработала рекомендации для точного представления информации при описании случаев, итогом которых стало Положение и проверочный перечень CARE (CAse Report ― описание случаев), представленных в 2013 г. на Международном конгрессе по экспертному рецензированию и биомедицинским публикациям, поддержанных многочисленными медицинскими журналами и переведённых на девять языков.
Цель этого разъясняющего и уточняющего документа ― более широко внедрить и распространить использование проверочного перечня CARE при подготовке и опубликовании описаний случаев.
Схема (дизайн) статьи и контекст. К каждому пункту проверочного перечня CARE даны пояснения и прилагаются примеры из публикаций. Объяснения и примеры в данном документе помогают авторам подготовить высококачественное описание случая, а редакторам, экспертам-рецензентам и читателям ― критически проанализировать его.
Результаты и выводы. Данная статья вместе с Положением и проверочным перечнем CARE от 2013 г., с которым можно ознакомиться на веб-сайте CARE (www.care-statement.org) и веб-сайте группы EQUATOR (www.equator-network.org), служит способом улучшить полноту и прозрачность описания случаев.
Источник. Данная статья является переводом оригинальной публикации «CARE guidelines for case reports: explanation and elaboration document» в Journal of Clinical Epidemiology (doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.04.026), созданным с разрешения правообладателя (Elsevier Inc.), под руководством научного редактора и переводчика профессора, д.м.н. Е.Г. Старостиной (Москва, Россия).
 16-42
16-42


Редакционные статьи
Междисциплинарный банк данных в онкоэндокринологии: радиойодрефрактерный дифференцированный рак щитовидной железы
Аннотация
Высокие достижения в персонализированной доказательной медицине, и онкологии в развитых странах связаны с развитием клинических карцер-регистров пациентов (SEER, NCDB и др.), которые представляют собой мультимодальные и междисциплинарные банки данных. Они являются матрицей данных для развития аналитических и прогностических инструментов в изучении особенностей диагностики, клинического течения болезней, ответа на терапию, оценки влияния прогностических факторов и пр. С точки зрения медицинских цифровых банков данных, избыточность и дублированность данных не так критичны, как неполнота или противоречивость информации при принятии медицинских решений.
Цель статьи — анонс мультимодального банка данных пациентов с радиойодрефрактерным дифференцированным раком щитовидной железы, который, по сути, является современным междисциплинарным цифровым медицинским регистром.
Наряду с демографическими и нозологическими данными, характерными для эпидемиологических регистров, в мультимодальных банках данных учитываются ключевые клинические и параклинические данные: результаты лабораторных, морфологических и инструментальных методов исследования, различные методы визуализации (ультразвуковое исследование; компьютерная и магнитно-резонансная томография; однофотонная эмиссионная компьютерная томография, совмещённая с компьютерной томографией; позитронно-эмиссионная томография, совмещённая с компьютерной томографией). В мультимодальных банках данных представлены результаты молекулярно-генетического профиля опухоли, клиническая польза которого в выборе тактики лечения сегодня не подвергается сомнению. Все эти данные накапливаются в мультимодальных банках данных с отметкой о времени выполнения, результатах пересмотра (второе мнение), учёта стандартизированных качественно-количественных параметров (факторов), потенциально влияющих на клиническое течение, ответ на лечение, развитие осложнений и исход.
 86-93
86-93