Vol 3, No 2 (2022)
- Year: 2022
- Published: 14.07.2022
- Articles: 7
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/3844
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.32
Original Study Articles
Safety and efficacy of percutaneous vesselplasty (Vessel-X) in the treatment of symptomatic thoracolumbar vertebral fractures
Abstract
AIMS: to assess radiological and clinical outcomes, in terms of safety and efficacy, of symptomatic vertebral fractures with and without posterior wall and\or both endplates involvement, treated with vesselplasty technique (Vessel-X, Dragon Crown Medical Co., Ltd Shandong, China).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively evaluated 66 Patients who underwent 92 vesselplasty procedures, performed for the treatment of symptomatic vertebral body fractures from March 19 to September 2020. We divided the fractures in two subgroups: 36 vertebral fractures with posterior wall and/or both endplates involvement, which we defined complex, while all the others were defined simple. Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) values has been registered 1 day before the procedure and at 1, 6 and 12 months follow-up. We also evaluated vertebral height restoration by comparing pre-interventional with post-interventional imaging.
RESULTS: 92 vertebrae were treated (58 lumbar, 34 thoracic), with 24 multilevel procedures. We observed a technical success rate of 100%, without major complications; a single case of asymptomatic paravertebral cement leak was reported. Both simple and complex subgroups registered a significative statistical difference in NRS and ODI between preoperative and at 1, 6 and 12 months (p <0.05). A significant statistical difference was demonstrated in vertebral height comparing pre-operative and post-operative data (p <0.05). No significant difference in vertebral height restoration was observed between simple and complex vertebral fractures groups.
CONCLUSIONS: Vesselplasty represents a safe and effective technique for the treatment of both simple and complex painful vertebral fractures, granting a significant reduction of symptoms, excellent cement leakage control and proper vertebral height restoration.
 98-107
98-107


Impact of body mass index on the reliability of the CT0–4 grading system: a comparison of computed tomography protocols
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The increased frequency of chest computed tomography utilization in the fight against COVID-19 has made usage of low-dose computed tomography necessary to reduce the radiation dose while preserving diagnostic quality. However, in the published literature, there were no data on the effect of body mass index on low-dose computed tomography accuracy in patients with COVID-19.
AIM: To assess the effect of patient body mass index on the level of agreement between radiologists interpreting standard-dose computed tomography and low-dose computed tomography in COVID-19-associated pneumonia using visual semiquantitative CT 0–4 scale.
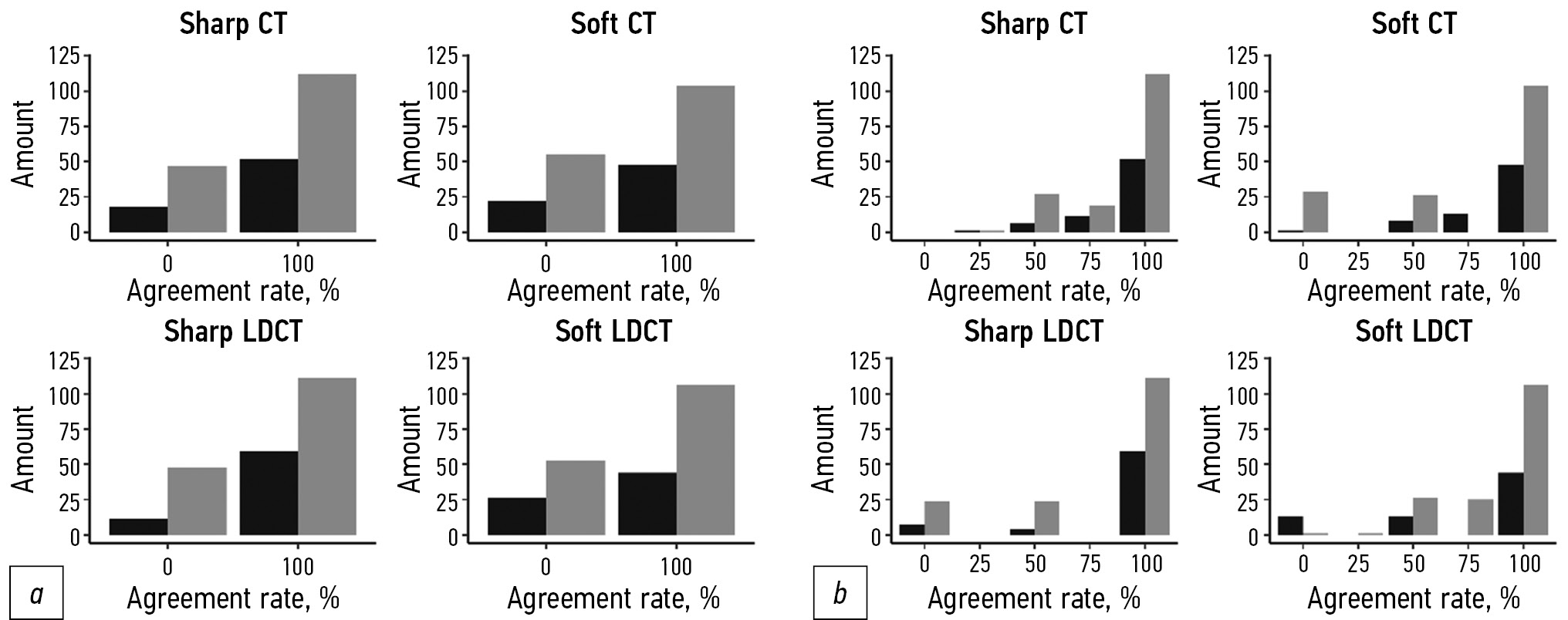
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this retrospective multicenter study, each participant underwent two consecutive chest scans at a single visit using standard-dose and low-dose protocols. Standard-dose and low-dose computed tomography with pulmonary and soft tissue kernels were interpreted using a visual semiquantitative CT 0–4 grading system. Data for each protocol were grouped by body mass index value (threshold value for pathology was equal to 25 kg/m2). Agreement was calculated based on binary and weighted classifications. One-way ANOVA analysis of variance was used to assess the presence of statistically significant differences in the mean for the groups.
RESULTS: Two hundred thirty patients met the established inclusion criteria for the study. The experts processed 4 studies for each patient: standard-dose and low-dose computed tomography with pulmonary and soft tissue kernels. The proportion of normal-weight patients was 31% (71 subjects), and the sample’s median body mass index was 27.5 (18.3; 48.3) kg/m2. There were no statistically significant differences in intergroup pairwise comparisons for both the binary and weighted classifications (p values were 0.09 and 0.12, respectively). The group of overweight patients was further subdivided according to the degrees of obesity; however, the results were invariant to this division (no statistically significant differences: for the most different body mass index groups “normal” and “3rd degree obesity” p-value 0.17).
CONCLUSION: Body mass index does not affect chest standard-dose and low-dose computed tomography interpretation in COVID-19 using the visual semiquantitative CT 0–4 grading system.
 108-118
108-118


Reviews
Left atrial longitudinal strain analysis in diagnostic of cardiotoxicity
Abstract
A wide range of extremely effective chemotherapy drugs has a negative effect on the cardiovascular system, leveling oncological treatment success. Early diagnosis of cardiotoxicity is very important, allowing timely application of preventive and therapeutic measures. Left ventricular ejection fraction evaluation using echocardiography is the basic non-invasive instrumental method to assess cardiac function and the main guideline in cardiac dysfunction diagnosis during chemotherapy. However, if dysfunction is subclinical, the ejection fraction can remain normal for a long time, and also has a pronounced inter-operator variability and dependence on volumetric load. Specialists are constantly in search of optimal echocardiographic parameters that allow early-stage cardiac dysfunction diagnosis. Analysis of the global longitudinal deformation of the left atrium seems to be a promising method for these purposes. A large amount of accumulated data suggests that the left atrium is not just a conduit chamber, but a reflection of the filling pressure of the left ventricle, being a sensitive marker of its systolic and diastolic dysfunction. This review presents an analysis of currently available studies on applying the methodology for assessing global longitudinal deformation of the left atrium in cardiac dysfunction diagnosis in the use of cardiotoxic drugs.
 119-130
119-130


Technical Reports
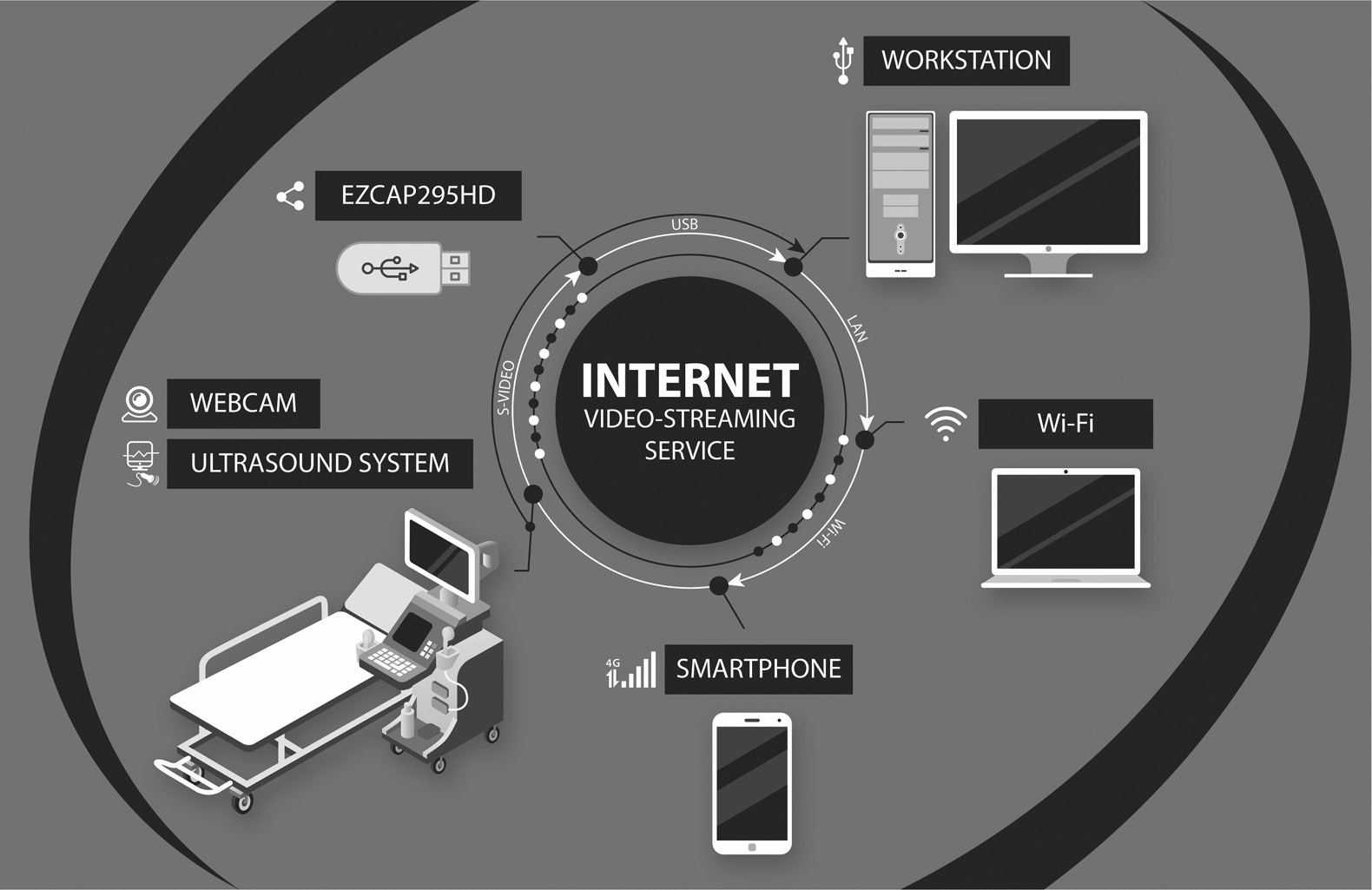
Streaming technology: from games to tele-ultrasound
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Due to the gaming industry’s rapid development, a large number of technical tools and technologies with unique characteristics have emerged. One of these technologies, which can be potentially used in medical diagnostics, is streaming (online streaming). By connecting an ultrasound scanner to a video capture system, it is possible to significantly expand the diagnostic device’s functionality.
AIM: To investigate the possibility of applying the gaming industry’s information technology in telemedicine, like tele-ultrasound.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this study, an ultrasound video image was captured using a video capture system developed for gamers. The video was obtained during brachycephalic arteries ultrasound in the following modes: greyscale B-mode, color duplex, and pulse Doppler mode. The examination was broadcast to a video streaming service in real time.
RESULTS: An expert sonologist obtained optimal video image parameters and determined the minimum required video streaming settings for an adequate remote evaluation. The following video capture workstation settings are recommended: video, 1280×720; 24 fps; H.264 encoder; bitrate, at least 350 Kbps.
CONCLUSIONS: Using technical and software tools developed for video game streaming to provide tele-ultrasound is possible.
 131-140
131-140


Case reports
“Superior Pectus Carinatum” (Currarino–Silverman Syndrome) in a 66-year-old woman: a case report
Abstract
The premature fusion of some of the sternal ossification centers and the obliteration of the manubrio-sternal joint caused a rare deformity called Currarino–Silverman syndrome. Patients present an abnormally short sternum with a forward angulation at the manubrio-sternal junction. Cardiopulmonary diseases and spinal deformities are the most frequent related disorders. It was also described as a component of Turner’s and Noonan’s syndromes.
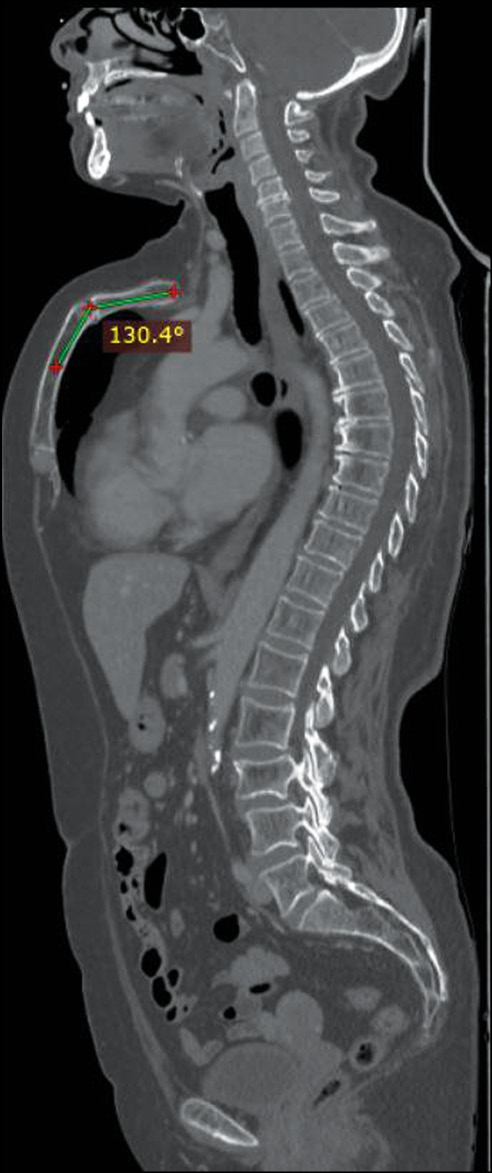
Herein, we present the case of a 66-year-old woman who presented to our clinic for follow-up computed tomography after surgery and chemotherapy for breast cancer with frequent episodes of dyspnea, wheezing, bronchitis, and mild dyspnea annually, which was more frequent during childhood. Computed tomography showed the absence of metastatic lesions and other accompanying diseases, except for a rare deformity of the anterior chest wall, the so-called, a “superior” pectus carinatum, a chondromanubrial deformity with a dorsal-open angle of 130º, and a sternum body length of 9 cm, which is not depressed in the lower third.
 141-148
141-148


Computer tomography of uro-lymphatic fistulas associated with renal colic
Abstract
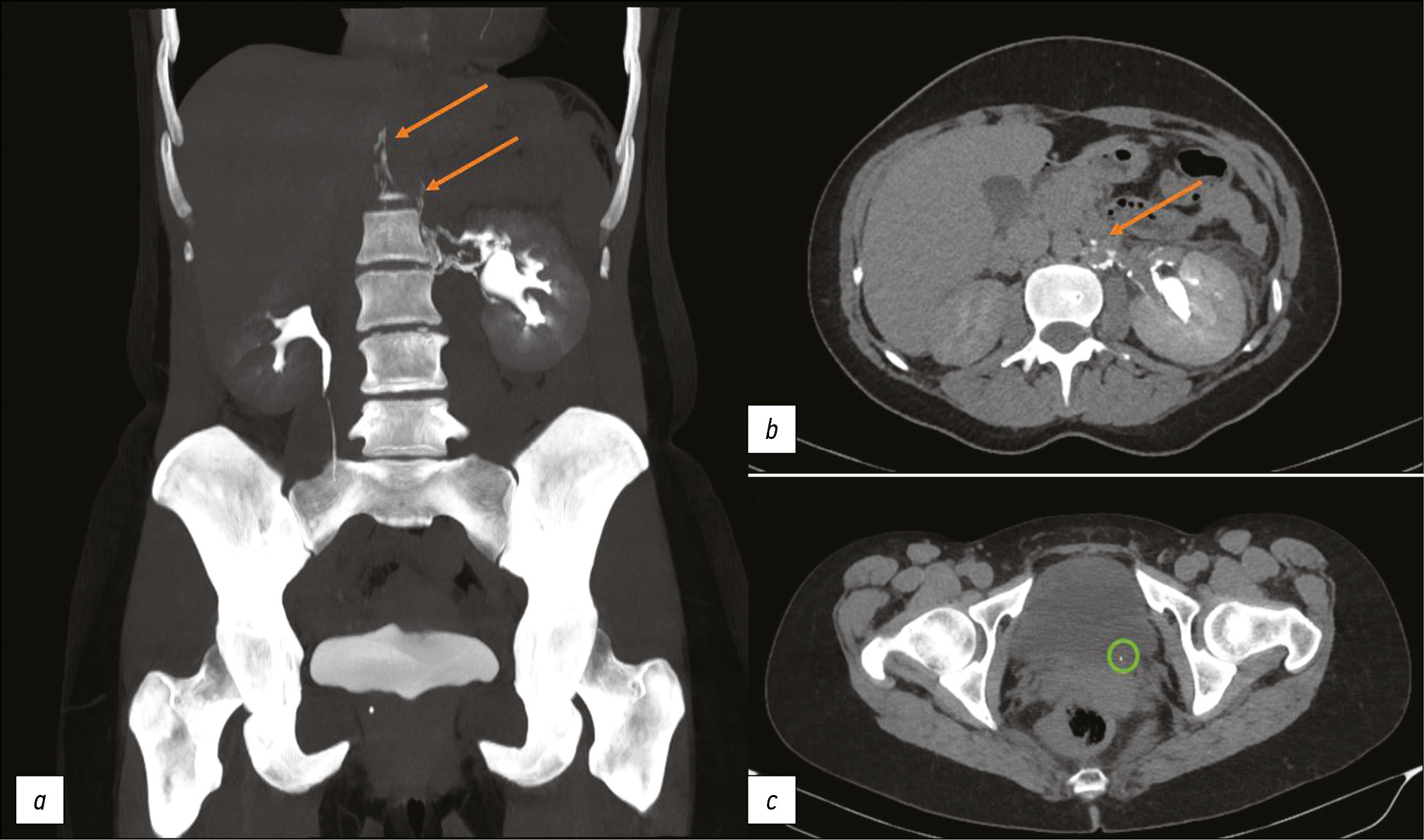
This article presents two clinical observations of uro-lymphatic fistulas diagnosed by computed tomography. In both cases, the patients were admitted with symptoms of renal colic. Uro-lymphatic fistulas are a rare condition caused by the formation of a connection between the urinary and lymphatic systems, which is caused by, as a rule, lymphatic vessel obstruction due to parasitic infestation. Other causes may be radiation therapy, retroperitoneal trauma, and tumor sprouting. In the era before antibiotics, infectious processes such as xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis and renal tuberculosis were common. Cases of uro-lymphatic fistulas formed against urolithiasis background are presented below. In the clinical cases presented, urine directly entered the lymphatic vessels through a uro-lymphatic fistula detected on contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Uro-lymphatic fistulas caused by impaired urine outflow due to blocked urinary tract are rarely detected since abdominal ultrasound is the diagnostic method of choice in renal colic. In the vast majority of cases, uro-lymphatic fistulas are treated conservatively and do not require surgical intervention. As a rule, the formed fistulas cease to exist when its root cause is successfully treated.
 149-155
149-155


Correspondence
Features of conducting ethical review of research on artificial intelligence systems on the basis of the research and practical clinical center for diagnostics and telemedicine technologies of the Moscow Health Care Department, Moscow, Russian Federation
Abstract
Ethical issues occupy a special place when conducting clinical trials of medicines, where it is impossible to predict in advance and accurately the effectiveness and safety of a new drug on the human body. Currently, during clinical trial examination, attention is paid to patients’ quality of life, and issues of compliance with patients’ rights, as well as compliance with the rules of good clinical practice and current legislation. Thanks to technological development, the number medical studies and devices using, among other things, specialized medical technologies and software is increasing.
Automation, development, improvement, and structuring of the processes involved cause an increase in the use of technical devices that use not only programs but also systems in their work. Artificial intelligence system software have a special place in medical science development.
Artificial intelligence, which was the field of science fiction 50–80 years ago, is now firmly embedded in our everyday life. By introducing artificial intelligence’s capabilities into medical software, using it as part of medical equipment, and developing medical devices with artificial intelligence systems, we get a product that requires careful study and further development, which includes a complex of works on conducting scientific research, and registration and maintenance of such systems and complexes. All work is regulated by legislation in the field of circulation of medical devices and requires a deep systematic and scientific approach, including involving ethics to monitor compliance with the rights and safety of study participants and their medical data.
The Ethics Committee is an independent body that monitors compliance with the rights and requirements of legislation and conducts ethical and scientific examination of research documentation. Ethical issues when planning any research involving a person or his/her data should be discussed and considered in detail. The ethics committees should be contacted not only at the stage of approving research materials, but also when planning the design and developing research documentation and materials for patients, as well as regularly at all stages of the study.
 156-161
156-161