Volume 2, Nº 4 (2021)
- Ano: 2021
- ##issue.datePublished##: 30.12.2021
- Artigos: 8
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/3397
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.24
Historical Articles
The 25 years development of the Moscow Center for Diagnostics: through an eyewitness
Resumo
Today, on the eve of the 25th anniversary of the leader in the Moscow radiological service, Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Healthcare Department (used to be the Research and Practical Center of Medical Radiology until 2019), the bright quarter-century history of this institution comes to life in our me-mory, day after day has passed by since the opening of the Center, our weekdays, scientific breakthroughs, and celebrations.
We would like to present to our readers a brief history of one of the aspects of the Center’s complex activities, the development of professional education of radiologists. We observe a period from its launching to its recognition as the authority in radiology. The Education Department of the Moscow Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies is currently appointed by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation as an expert to participate in addressing the current challenges of professional training and certification in diagnostic radiology.
The article is devoted to well-known scientists and teachers, professors, and leading specialists in the industry, who are actively involved in the development of continuing education of radiologists and other specialists in diagnostic radiology at different stages of the center’s existence. Specialists of the Training Center strive for the compliance of the provided professional training following the Bologna Declaration (1999), thereby creating conditions for Russian professionals to obtain European diplomas.
 421-430
421-430


Original Study Articles
Use of magnetic resonance imaging features as radiomic markers in pre-operative evaluation of extra-axial tumor grade
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Extra-axial tumors are one of the tumor groups with difficult primary differential diagnostics. Detection and standardization of radiomic markers are one of the main problems of our time.
AIM: To detect radiomic markers for preoperative assessment of extra-axial tumor grade.
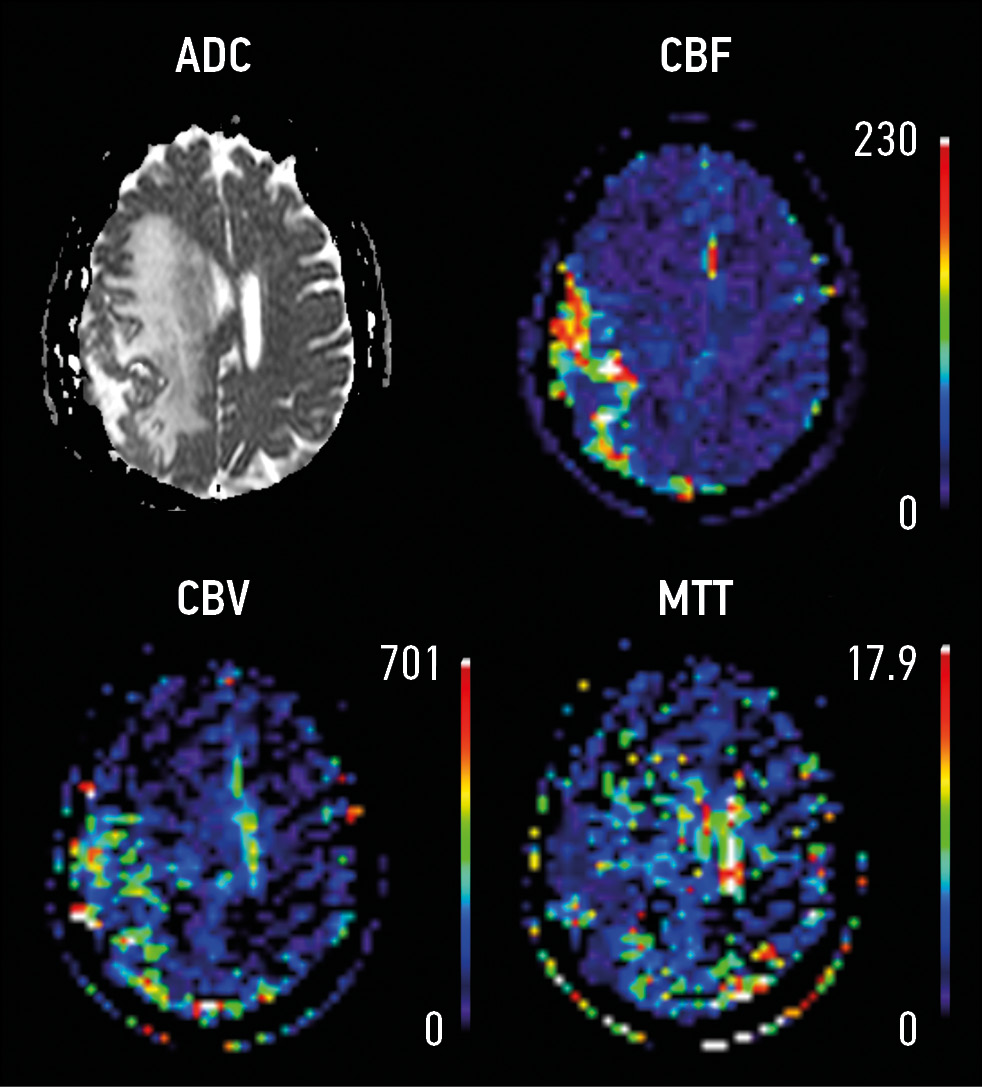
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study retrospective analyzed the magnetic resonance imaging (1.5 T) data of 156 patients with extra-axial tumors. Patients were divided into 2 groups: Group 1 (n=106) with perifocal changes and Group 2 (n=50) with extra-axial tumors without perifocal changes. Diffusion and perfusion sequences were included in the scanning protocol. The areas of interest include (1) the lesion and (2) the area of perifocal changes. Measurements were made from the lesion and the area of perifocal changes on ACD and DSС maps, DCE was analyzed.
RESULTS: The maximum lesion size in Group 1 was 2.2 cm (1.4; 4.3), whereas in 1.2 cm in Group 2 (0.9; 3.5). In Group 1, the diffusion restriction from the lesion was detected in 42 patients (39.6%), whereas 7 (14%) in Group 2. The maximum size of perifocal changes in Group 1 was 2.85 cm (1.5; 4.7). Diffusion restriction was detected in 52 (49.1%) cases. In Group 1, patients with verified meningioma multivariable linear regression analysis showed 3.3-times increase of rCBF of the maximum size of the lesion from the area of perifocal changes (βcoef. 3.3, CI: 1.27; 5.28), p=0.003; however, it demonstrated a 4-time decrease of rCBF (βcoef. 4 CI: -7.46; -0.71), p=0.02.
CONCLUSIONS: Perfusion and diffusion methods combined with anatomical sequences show potential use as radiomic markers for diagnostic assessment and treatment of extra-axial tumors. Further detection of radiomic functional markers from the area of perifocal changes has potential.
 431-440
431-440


Case reports
Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum in a young male patient: a case report
Resumo
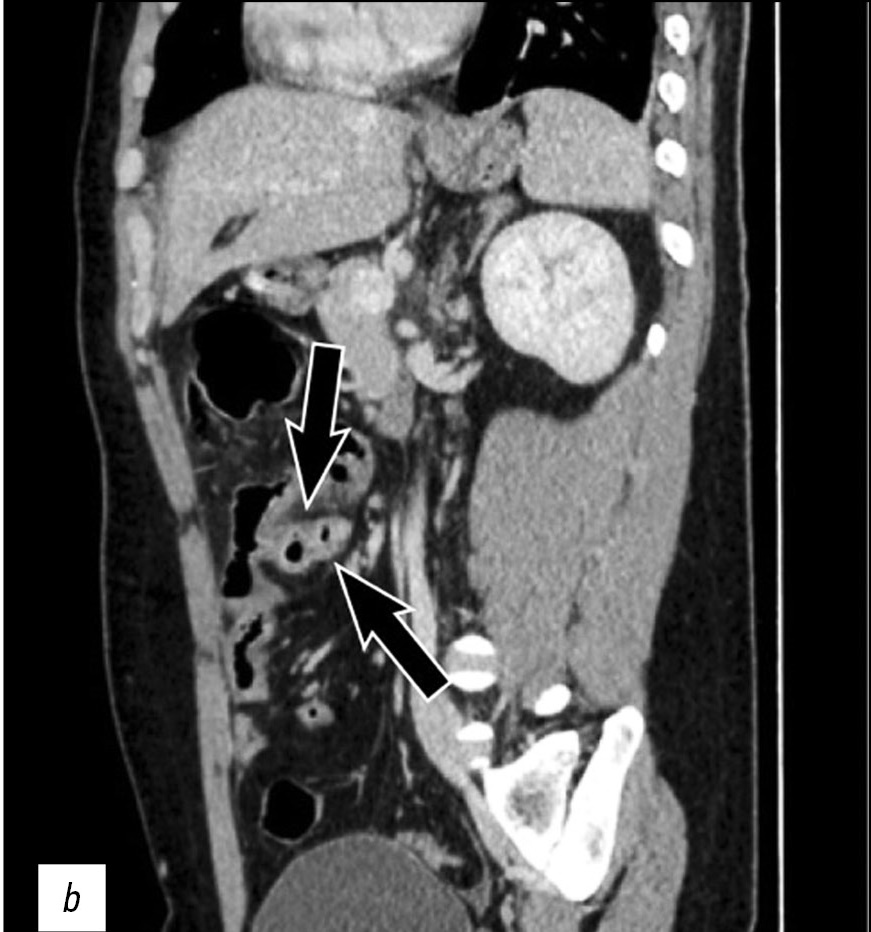
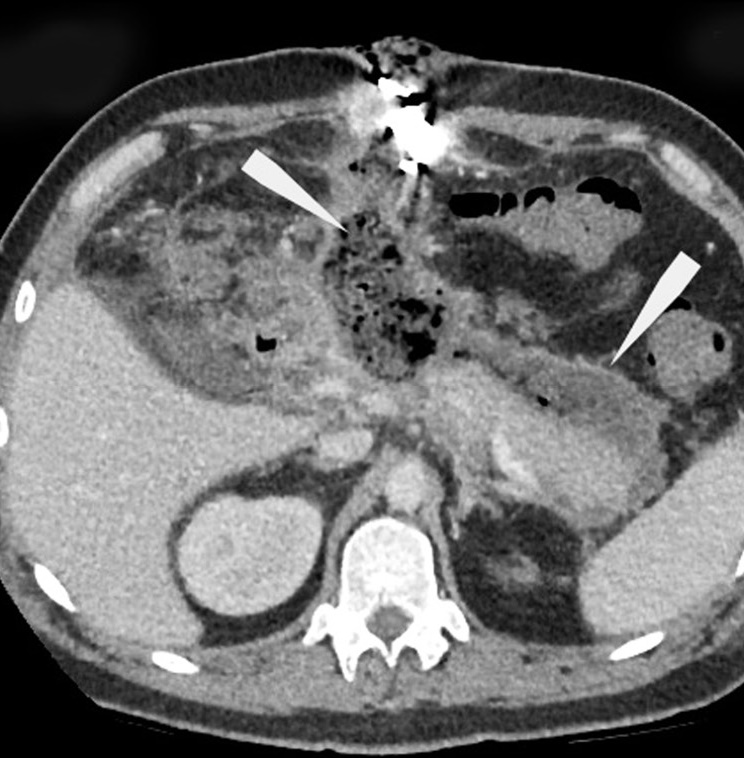
The case of a 26-year-old male patient with perforation of Meckel’s diverticulum, a rare complication of the most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract, is reported in this article. This congenital condition can remain asymptomatic for a long time, and it can get complicated with diverticulitis, enteroliths, neoplasms, and rarely perforation, as in this case.
A preoperative radiological assessment is of fundamental importance for proper diagnostic and therapeutic management of the patient. In this article, we present the typical tomographic imaging features of this infrequent complication to assist radiologists in detecting it.
 465-470
465-470


Encapsulated necrotic pancreatitis
Resumo
This study presents a rare clinical case of encapsulated necrotic pancreatitis, which was a complication of acute pancreatitis that arose against the background of alimentary disorders. The aspects of the semiotics of radiation diagnostic methods in the follow-up control of these pathologies were presented.
This case is notable for the manifestation of diseases upon hospital admission, as in the classical edematous form of acute pancreatitis, with a further increase in negative dynamics. This demonstrated the possible stepwise disease development, accompanied by a series of follow-up computed tomography between the clinical and morphological phases of acute pancreatitis and before the formation of pancreatic necrosis, which was complicated by sequestration of the pancreatic body with peripancreatic abscess formation. Afterward, the therapeutic paradigm was changed, and the place of the conservative approach was taken by active surgical tactics, followed by repeated manipulations and follow-up computed tomography and magnetic resonance until the improvement of the patient’s condition.
 471-480
471-480


Osteopoikilosis in the ribs, pelvic region and spine: a case report
Resumo
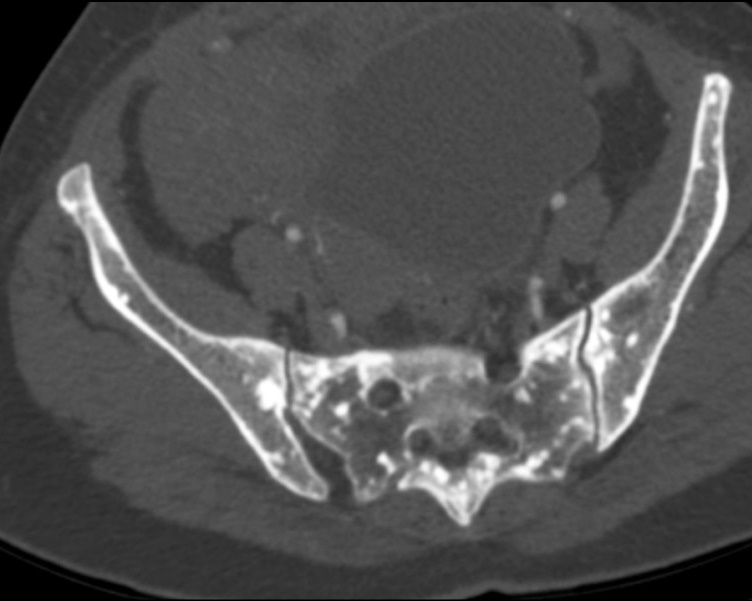
Osteopoikilosis is a rare inherited benign bone dysplasia incidentally found on radiological exams. It is characterized by a specific radiological pattern: diffuse, round or oval, symmetrically shaped sclerotic bone areas distributed throughout the skeleton. It is essential to do a correct diagnosis because these lesions could be easily confused with bone metastasis.
We reported a case of an osteopoikilosis patient presenting to our clinic with transient loss of consciousness and without any numbness, tingling and weakness in the legs or other parts of the body. The computed tomography scan showed multiple small sclerotic foci bone islands, scattered throughout the thoracic and lumbar spine, ribs, pelvic bone, sacrum and bilateral proximal femur. No significant increase in the activity was detected in technetium-99m whole-body bone scintigraphy. The patient was diagnosed with characteristic radiological findings of osteopoikilosis and was followed up.
 481-487
481-487


Reviews
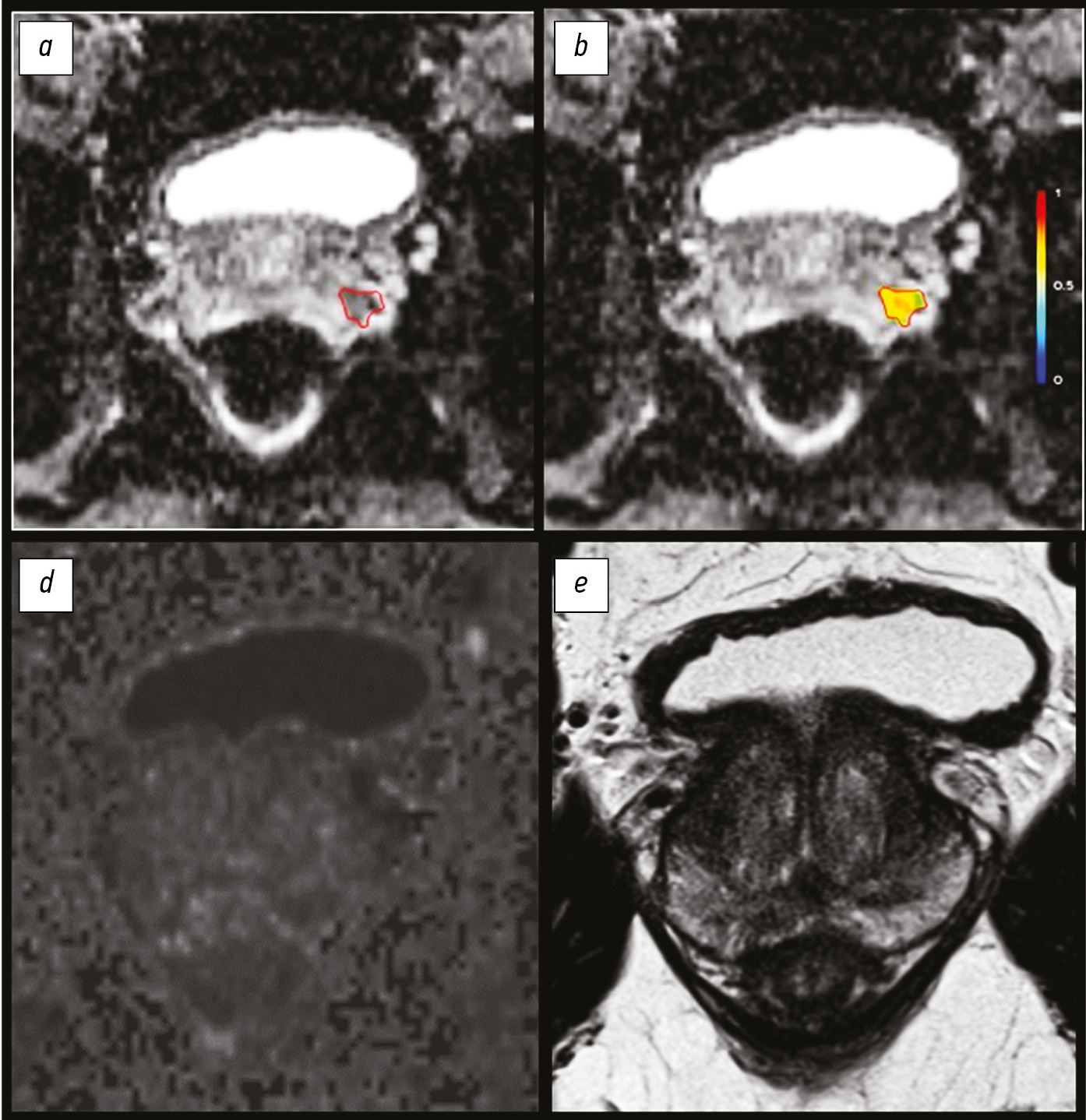
Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics in prostate cancer radiology: what is currently known?
Resumo
Diagnostic and treatment approaches in prostate cancer rely on a combination of magnetic resonance imaging and histological data.
This study aimed to introduce the basics of the current diagnostic approach in prostate cancer with a focus on texture analysis.
Texture analysis evaluates the relationships between image pixels using mathematical methods, which provide additional information. First-order texture analysis of features can have greater clinical reproducibility than higher-order texture features. Textural features that are extracted from diffusion coefficient maps have shown the greatest clinical relevance. Future research should focus on integrating machine learning methods to facilitate the use of texture analysis in clinical practice.
The development of automated segmentation methods is required to reduce the likelihood of including normal tissue in the area of interest. Texture analysis allows the noninvasive separation of patients into groups in terms of possible treatment options. Currently, few clinical studies reported on the differential diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer, including the Gleason and International Society of Urological Pathology grading. Large prospective studies are required to verify the diagnostic potential of textural features.
 441-452
441-452


The Russian regulatory documents on the organization and functioning of offices and departments of magnetic resonance imaging
Resumo
Diagnostic studies that are conducted using any medical equipment require comprehensive control, which is provided by several regulatory documents. Particular attention is paid to X-ray imaging methods, but in the field of magnetic resonance imaging, one can notice both the lack of attention and the multidirectional efforts for its normalization.
Understandably, this diagnostic method is not based on the use of ionizing radiation, and magnetic fields have some effect on human health, especially on personnel who work in magnetic resonance imaging rooms at all times. They are safe for patients who come to the diagnostic procedure from time to time and those without foreign metal (steel implants) or electronic (pacemakers and neurostimulators) objects in their bodies.
However, ignorance and non-compliance with both advisory and mandatory requirements can significantly increase the risk of harm to patients or staff, as well as lead to a decreased quality of imaging and diagnostics. A separate feature of the field of magnetic resonance imaging regulation in the past decades includes more than a dozen of different standards, sanitary norms, rules, letters, and recommendations that have been published or revised, of which a significant part complement or duplicate each other, or completely contradict each other. Therefore, the need to ensure the compliance of the magnetic resonance imaging room/department with the requirements of regulatory documents is greatly complicated.
This study provides an overview of the regulatory documentation in force in Russia related to the organization and functioning of a magnetic resonance imaging room/department, highlights the aspects that are most important from the point of view of the safe and high-quality operation, and formulates the steps necessary to modernize the system, both from the point of view of the quality of diagnostics and the safety of magnetic resonance imaging studies.
 453-464
453-464


Editorials
The increasing role of functional visualization modalities for navigation of external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy in prostate cancer
Resumo
Brachytherapy is successfully used in the treatment of malignant neoplasms in males and females and rare cases in children, as an independent method (with localized prostate cancer) or adjuvant with remote focal radiation therapy (with cancer of the cervix, anal canal, head and neck, breast, etc.).
The expansion of diagnostic capabilities (the advent of computer and magnetic resonance imaging) due to three-dimensional imaging has given brachytherapy an important technological advantage over other methods. Many options are available for combining brachytherapy with remote radiation or systemic antitumor therapy in the first line, as well as in a single mode for localized tumor recurrence in a previously irradiated area.
Intrastates (hollow tubes) for intra-tissue high-dose brachytherapy are administered during surgery and encapsulated (closed) radioactive micro-sources for low-dose brachytherapy are directly administered (percutaneously).
A distinctive feature of brachytherapy is a sharp drop in the dose outside the tumor focus, which minimizes the risk of irradiation of surrounding organs and tissues.
The main advantage of brachytherapy in comparison with remote radiotherapy is a higher radiation dose gradient at the tumor border (from all sides). Moreover, clarifying the boundaries of uncertainty when irradiating the target is unnecessary. When the tumor changes during treatment, the sources fixed in the tumor synchronously change their position.
In addition to the advantages in efficiency and safety, the total financial costs of brachytherapy are significantly lower than other radiotherapy options.
 488-497
488-497