Volume 5, Nº 4 (2024)
- Ano: 2024
- ##issue.datePublished##: 31.12.2024
- Artigos: 18
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/8464
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.54
Original Study Articles
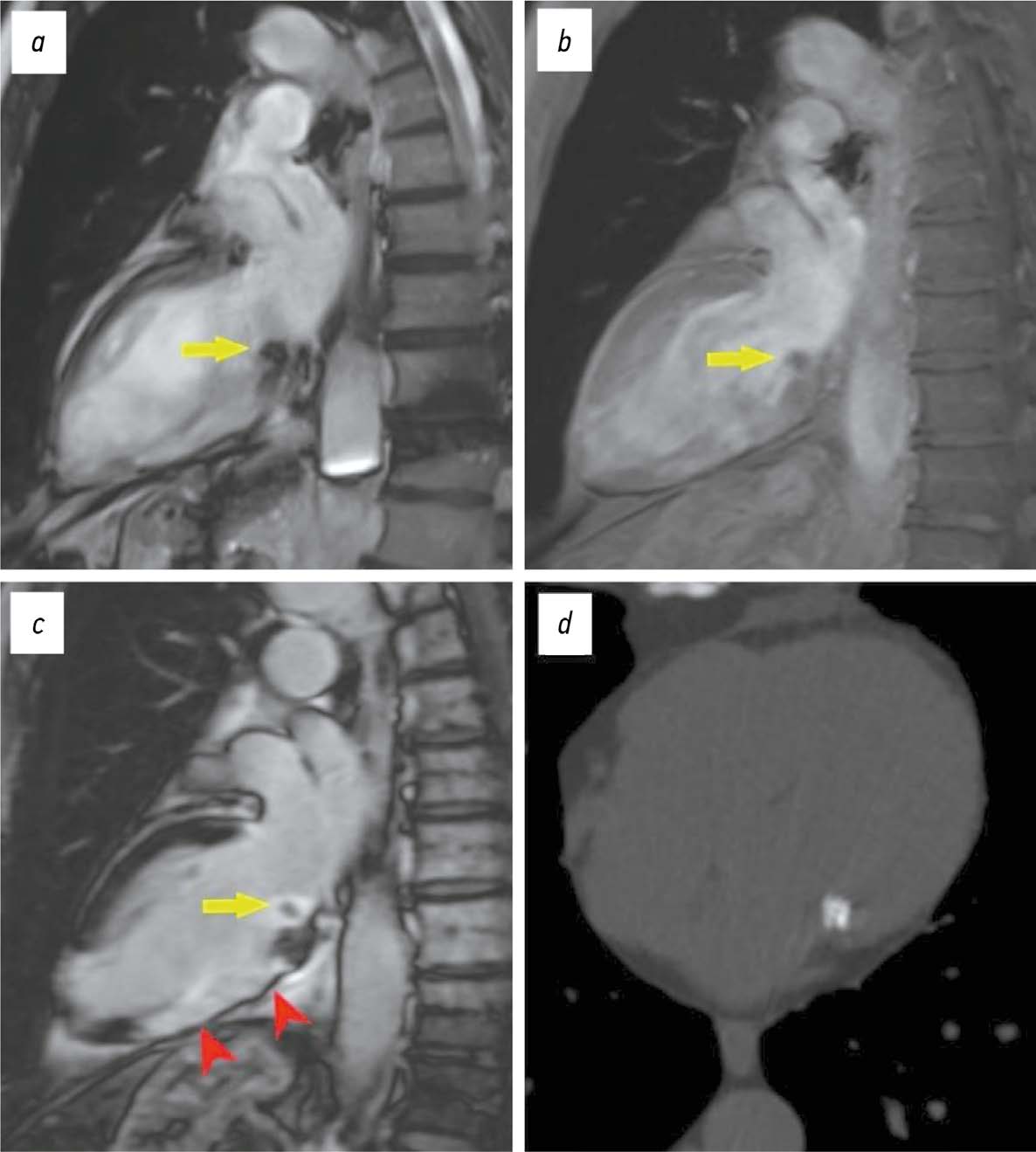
Potential use of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in differential diagnosis of cardiomyopathies due to light-chain amyloidosis and transthyretin amyloidosis
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Cardiac amyloidosis is a serious progressive disease with a high mortality rate. The differential diagnosis of cardiomyopathies due to amyloid light-chain (AL) amyloidosis and transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis is important for selecting the optimal treatment strategy.
AIM: The aim of this study was to evaluate the capabilities of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of cardiomyopathies due to AL and ATTR amyloidosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective analysis of the medical records of 25 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of amyloid cardiomyopathy was performed. Patients were divided into two groups according to the type of amyloidosis, with group 1 including patients with cardiomyopathy due to AL amyloidosis and group 2 including patients with cardiomyopathy due to ATTR amyloidosis. All patients underwent contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Volumetric and linear cardiac parameters, ventricular function, and late gadolinium enhancement patterns were assessed. Standard statistical methods were used, and differences were considered significant at p <0.05.
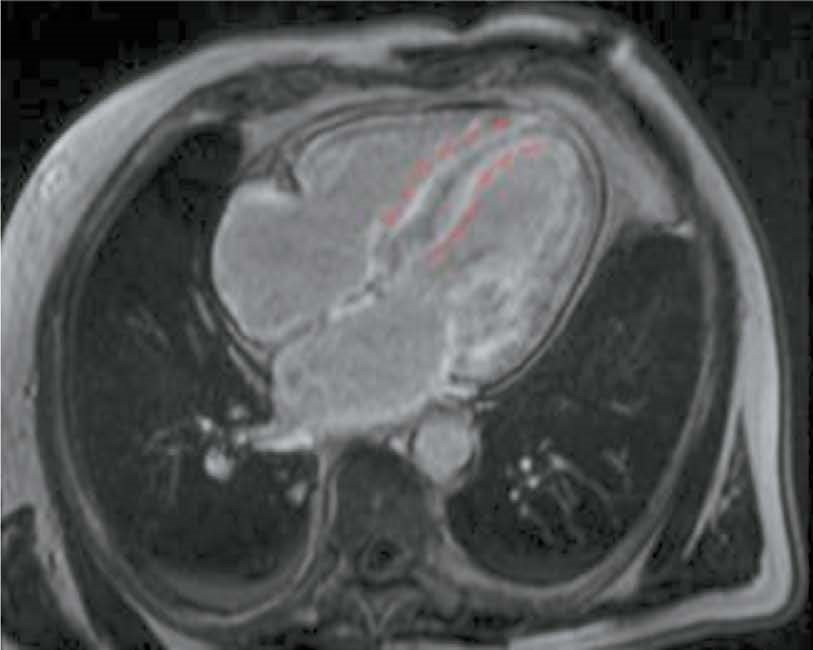
RESULTS: Group 2 showed a more significant thickening of the myocardial walls compared to group 1 (interventricular septum: 18 [17; 18] vs. 14.5 mm [12.8; 16.0], p <0.01, posterior wall of the left ventricle: 14 [13; 17] vs. 10.5 mm [10; 12.3], p <0.01). The indexed mass of the left ventricle myocardium was 110 [92; 125] in group 2 and 85 mm [69.3; 91.8] in group 1 (p <0.01). In group 2, late gadolinium enhancement with a transmural left ventricle pattern was more frequently observed in the basal and mid-lower-lateral segments, whereas in group 1, a subendocardial pattern of late gadolinium enhancement was more frequent in the mid-anterior and lower-lateral segments (p <0.05). In addition, frequency of simultaneous contrast enhancement in the subendocardial layers of the interventricular septum on the left ventricle and right ventricle sides was higher in group 2 (100% of cases vs. 50%, p <0.01). Late gadolinium enhancement of the right ventricle was also more common in group 2 (100 vs. 58%, p <0.05), especially in the interventricular septum and inferior wall area (p <0.05). Semi-quantitative assessment of LGE using the Query Amyloid Late Enhancement (QALE) showed greater contrast enhancement in group 2: 13 [12; 14] vs. 10.5 [1.75; 12], p <0.01), and a score greater than 13 differentiated between cardiomyopathy due to AL amyloidosis and ATTR amyloidosis with a sensitivity of 69% and a specificity of 83%.
CONCLUSIONS: Cardiac MRI identifies typical features of cardiomyopathies due to AL amyloidosis and ATTR amyloidosis for their differential diagnosis. Further research is needed to confirm diagnostic accuracy of the patterns identified.
 668-681
668-681


Potential use of radiomics analysis of cine-mode cardiac MRI to detect post-infarction lesions in the left ventricular myocardium
Resumo
BACKGROUND: The size and location of an infarct lesion and its clear differentiation from normal tissue are important for clinical diagnosis and precision medicine. This paper is based on the study of radiomic attributes for differentiation of infarct and non infarct tissue using non contrast enhanced cine mode cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data.
AIM: The aim of the study was to evaluate the potential use and informative value of radiomics analysis to identify post-infarction lesions in the left ventricular myocardium in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) using non-contrast-enhanced cine-mode cardiac MRI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Results of contrast-enhanced cardiac MRI were evaluated in 33 patients following surgical treatment for ICM. Texture analysis was performed on 66 lesions in cine-mode cardiac MRI images, and 105 texture attributes were determined for each lesion. Cardiac MRI was performed according to a standard technique using a Vantage Titan 1.5 T MRI scanner (Toshiba). For texture analysis, 3D Slicer version 5.2.2 (Pyradiomics) was used.
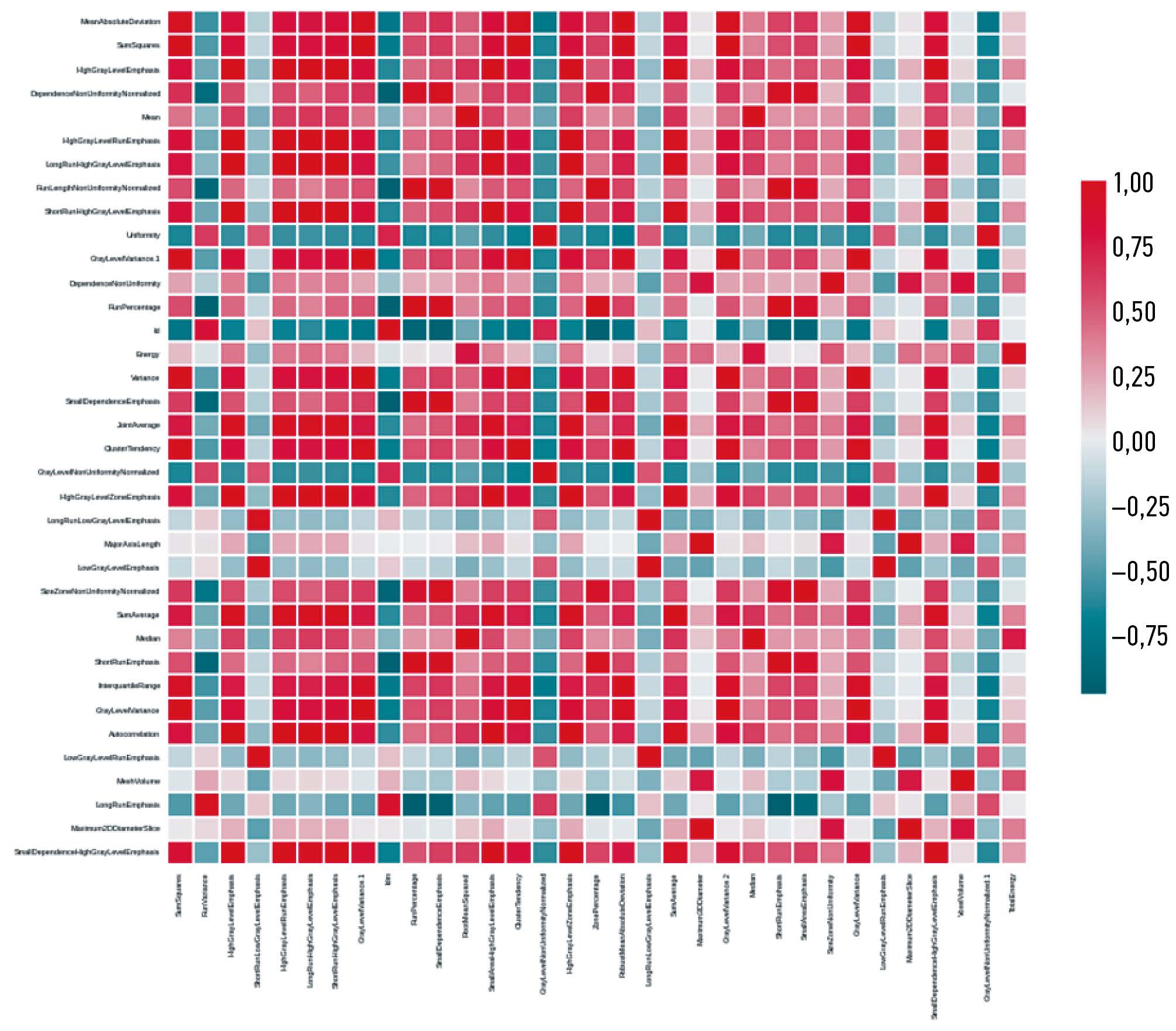
RESULTS: During the study, attribute collinearity diagrams were plotted, zero-significance attributes were identified, and attribute significance was determined using a gradient boosting algorithm, and the cumulative significance of attributes was estimated as a function of their total number. By identifying low-significance attributes, the least significant parameters that did not affect the overall significance level were determined. When single-valued attributes were extracted, no corresponding attributes were found. Based on the analysis results, an ROC curve was constructed for Lasso logistic regression (Se=57.14%, Sp=71.43%, AUC=0.76). The main result of this study was to determine radiomic attributes that characterized lesions corresponding to post-infarction cardiosclerosis and intact left ventricular wall based on cine-mode cardiac MRI images.
CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrated that radiomics analysis of non-contrast-enhanced cine-mode cardiac MRI images is a promising approach to identify lesions corresponding to myocardial infarction and intact wall. This method may potentially be used to identify lesions of post-infarction cardiosclerosis in patients with ICM without contrast enhancement.
 682-694
682-694


Evaluating the performance of artificial intelligence based software for digital mammography characterization
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Digital screening mammography is a key modality for early detection of breast cancer, reducing mortality by 20–40%. Many artificial intelligence (AI)-based services have been developed to automate the analysis of imaging data.
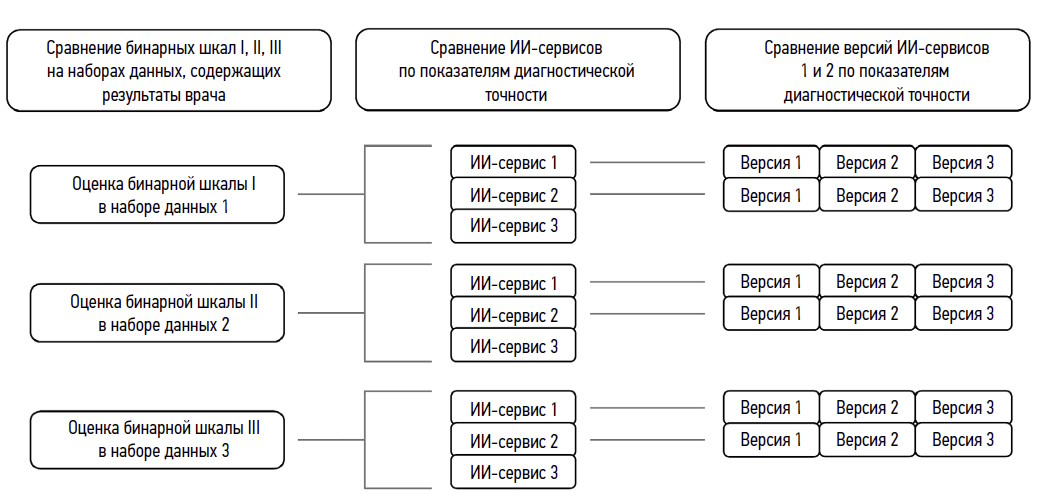
AIM: The aim of the study was to compare mammography assessments using three types of AI services in multiple versions with radiologists’ conclusions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Binary mammography scoring scales were compared with several types and versions of AI services regarding diagnostic accuracy, Matthews correlation coefficient, and maximum Youden’s index.
RESULTS: A comparative analysis showed that the use of a binary scale for evaluating digital mammography affects the number of detected abnormalities and accuracy of AI results. In addition, diagnostic accuracy was found to be threshold dependent. AI Service 1 in version 3 had the best performance, as confirmed by most diagnostic accuracy parameters.
CONCLUSIONS: Our results can be used to select AI services for interpreting mammography screening data. Using Youden’s index maximization to set up an AI service provides a balance of sensitivity and specificity that is not always clinically relevant.
 695-711
695-711


Neuroendocrine tumors of stomach and pancreas: diagnostic potential of radiomics, issues, and solutions
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Radiomics is currently a promising and prospective tool for diagnosing and treating neuroendocrine neoplasms at various sites. This method is often used for differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors with other neoplasms at this site.
AIM: The aim of the study was to evaluate the potential of radiomics for differential diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors of stomach and pancreas.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included data of 12 patients with morphologically proven neoplasms of the stomach (6 with neuroendocrine tumors and 6 with adenocarcinomas) and data of 22 patients with morphologically proven neoplasms of the pancreas (11 with neuroendocrine tumors and 11 with adenocarcinomas). All patients underwent abdominal computed tomography (CT) with intravenous contrast enhancement prior to treatment at the Russian Scientific Center of Roentgenology and Radiology. Radiomics parameters were calculated for the area of gastric and pancreatic tumor manually segmented in the native phase of the CT scan. The results were processed and statistically analyzed using Microsoft Office Excel and R-Studio, a free, open-source software development environment for the R programming language.
RESULTS: CT scan examples demonstrate typical and atypical visual signs of neuroendocrine tumors of stomach and pancreas, contrast enhancement characteristics, location and structure of neoplasms. Fifteen radiomics parameters were identified that were statistically significantly different between gastric neuroendocrine tumor and gastric adenocarcinoma. In pancreas, neuroendocrine tumors differed significantly from adenocarcinomas in 14 radiomics parameters.
CONCLUSIONS: Neuroendocrine tumors of stomach and pancreas are rare neoplasms that are mostly asymptomatic and difficult to visualize due to their small size and contrast enhancement characteristics. Texture analysis may be a promising approach to differentiate gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors from other neoplasms at these sites, especially in the view of the difficulty in obtaining a biopsy.
 712-724
712-724


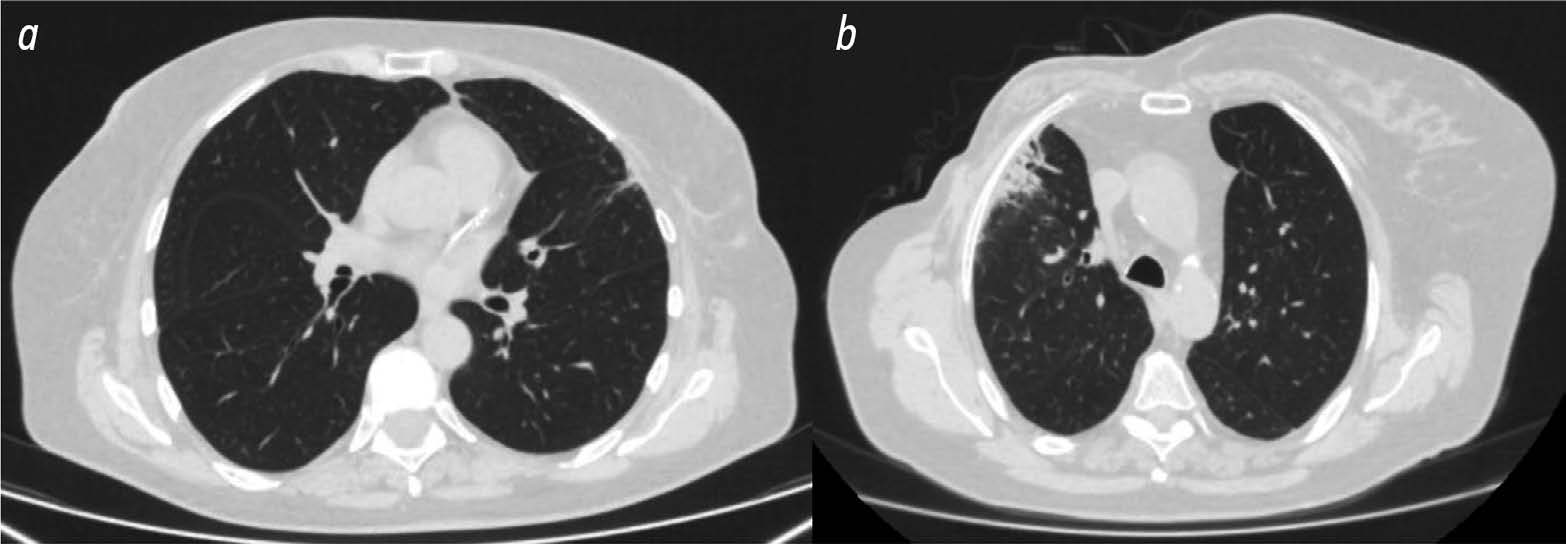
Detecting new lung cancer cases using artificial intelligence: clinical and economic evaluation of a retrospective analysis of computed tomography scans 2 years after the COVID-19 pandemic
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Chest computed tomography (CT) is the main modality used to diagnose lung lesions caused by COVID-19 infection. Since 2020, the use of this modality in the Krasnoyarsk krai has increased. However, the incidence of lung cancer decreased by 5.2%. The current situation has raised concerns about missing radiographic signs typical of lung cancer and has stimulated the search for new diagnostic modalities using artificial intelligence (AI) for data analysis.
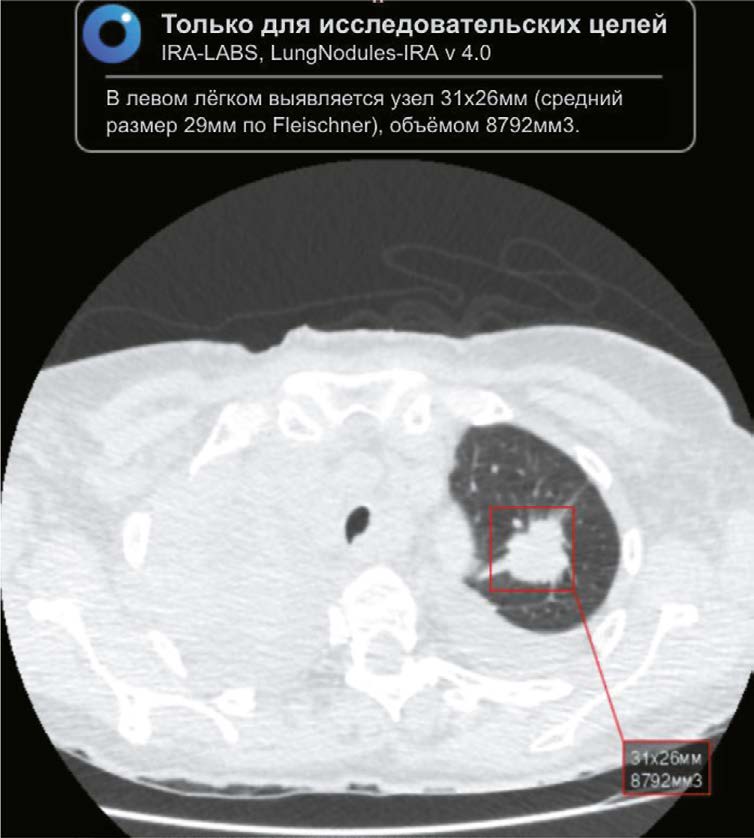
AIM: The aim of the study was to evaluate the feasibility of using an AI algorithm to search for lung nodules based on chest CT data obtained during the COVID-19 pandemic to identify lung cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The retrospective study included chest CT scans of patients from Krasnoyarsk krai diagnosed with COVID-19 reported in the PACS base between 1 November 2020 and 28 February 2021. The interval between chest CT and AI analysis ranged from two years and one month to two years and five months. Chest-IRA algorithm was used. AI detected lung nodules with a volume greater than 100 mm3. The radiologists divided the results into three groups based on the potential for lung cancer. The assessment of the economic benefits of using the AI algorithm considered the cost of wages and savings in the treatment of early stage lung cancer, which affects gross regional product.
RESULTS: The AI algorithm identified nodules in 484 out of 10,500 CT scans. A total of 192 patients with a high potential for lung cancer, 103 with no signs and 60 with inconclusive signs were identified, and 112 patients with a high and moderate potential for lung cancer did not seek medical care. AI confirmed 100 (28.2%) histologically proven cases of lung cancer, with stages I–II detected in 35%.
Using AI instead of radiologists would save 25 months and 4 days of work, which is equal to 2 million 430 thousand rubles. Expected budget savings due to early detection of lung cancer vary from 10 million 600 thousand to 12 million 500 thousand rubles for each 10,500 CTs. The total economic effect for a five year period would be from 259 million 400 thousand rubles to 305 million 100 thousand rubles.
CONCLUSIONS: The use of AI to evaluate chest CT scans demonstrates high performance in identifying lung nodules, including those in patients with COVID-19, confirming its potential use for early detection of incidental lung nodules that might otherwise be missed.
 725-739
725-739


Remote monitoring of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using a personal messenger
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Remote medical technologies are a promising way to monitor patients during disease diagnosis, treatment, and subsequent rehabilitation. This paper reviews the clinical implementation and effectiveness of digital tools for remote monitoring and treatment control in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
AIM: The aim of the study was to evaluate safety, efficacy and technological features of monitoring patients with rheumatoid arthritis using a remote monitoring platform.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The prospective, non randomized, controlled study included patients over 18 years of age with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who were discharged from the hospital for outpatient monitoring. Patients were divided into two groups for remote and in person monitoring. Data for remote patient monitoring was collected through questionnaires using a Telemedbot Personal Messenger. The authors also used the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) to assess daily life functioning in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; the European Quality of Life Questionnaire EQ-5D questions to assess patient adherence, duration of morning stiffness, number of painful and swollen joints; and a visual analog scale to assess the overall condition. After 6 months, efficacy of rheumatoid arthritis treatment was assessed in both groups using the DAS28 index.
RESULTS: The remote monitoring program involved 30 patients for 6 months. The in person monitoring group also included 30 people. After 6 months, patients using the Telemedbot Personal Messenger achieved low rheumatoid arthritis activity and remission more often than the second group (p=0.049). In the remote monitoring group, 9 (30.0%) and 11 (36.7%) patients achieved remission and low disease activity, compared to 3 (10.0%) and 8 (26.7%) patients in the in person monitoring group. Therefore, 20 (66.7%) people in the remote monitoring group were able to control the disease, while only 11 (36.7%) patients in the in person monitoring group were able to do so.
CONCLUSIONS: Remote monitoring using the Telemedbot Personal Messenger can be considered a potential way to increase the availability of medical care and efficacy of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
 740-751
740-751


Use of radiomics and dosiomics to identify predictors of radiation induced lung injury
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Radiomics is a machine learning based technology that extracts, analyzes, and interprets quantitative features from digital medical images. In recent years, dosiomics has become an increasingly common term in the literature to describe a new radiomics method. Dosiomics is a texture analysis method for evaluating radiotherapy dose distribution patterns. Most of the published research in dosiomics evaluates its use in predicting radiation induced lung injury.
AIM: The aim of the study was to identify predictors (biomarkers) of radiation induced lung injury using texture analysis of computed tomography (CT) images of lungs and chest soft tissues using radiomics and dosiomics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study used data from 36 women with breast cancer who received postoperative conformal radiation therapy. Retrospectively, the patients were divided into two groups according to the severity of post radiation lung lesions. 3D Slicer was used to evaluate CT results of all patients obtained during radiation treatment planning and radiation dose distribution patterns. The software was able to unload radiomic and dosiomic features from regions of interest. The regions of interest included chest soft tissue and lung areas on the irradiated side where the dose burden exceeded 3 and 10 Gy.
RESULTS: The first group included 13 patients with minimal radiation induced lung lesions, and the second group included 23 patients with post radiation pneumofibrosis. In the lung area on the side irradiated with more than 3 Gy, statistically significant differences between the patient groups were obtained for three radiomic features and one dosiomic feature. In the lung area on the side irradiated with more than 10 Gy, statistically significant differences were obtained for 12 radiomic features and 1 dosiomic feature. In the area of chest soft tissues on the irradiated side, significant differences were obtained for 18 radiomic features and 4 dosiomic features.
CONCLUSIONS: As a result, a number of radiomic and dosiomic features were identified which were statistically different in patients with minimal lesions and pulmonary pneumofibrosis following radiation therapy for breast cancer. Based on texture analysis, predictors (biomarkers) were identified to predict post radiation lung injury and identify higher risk patients.
 752-764
752-764


Technical Reports
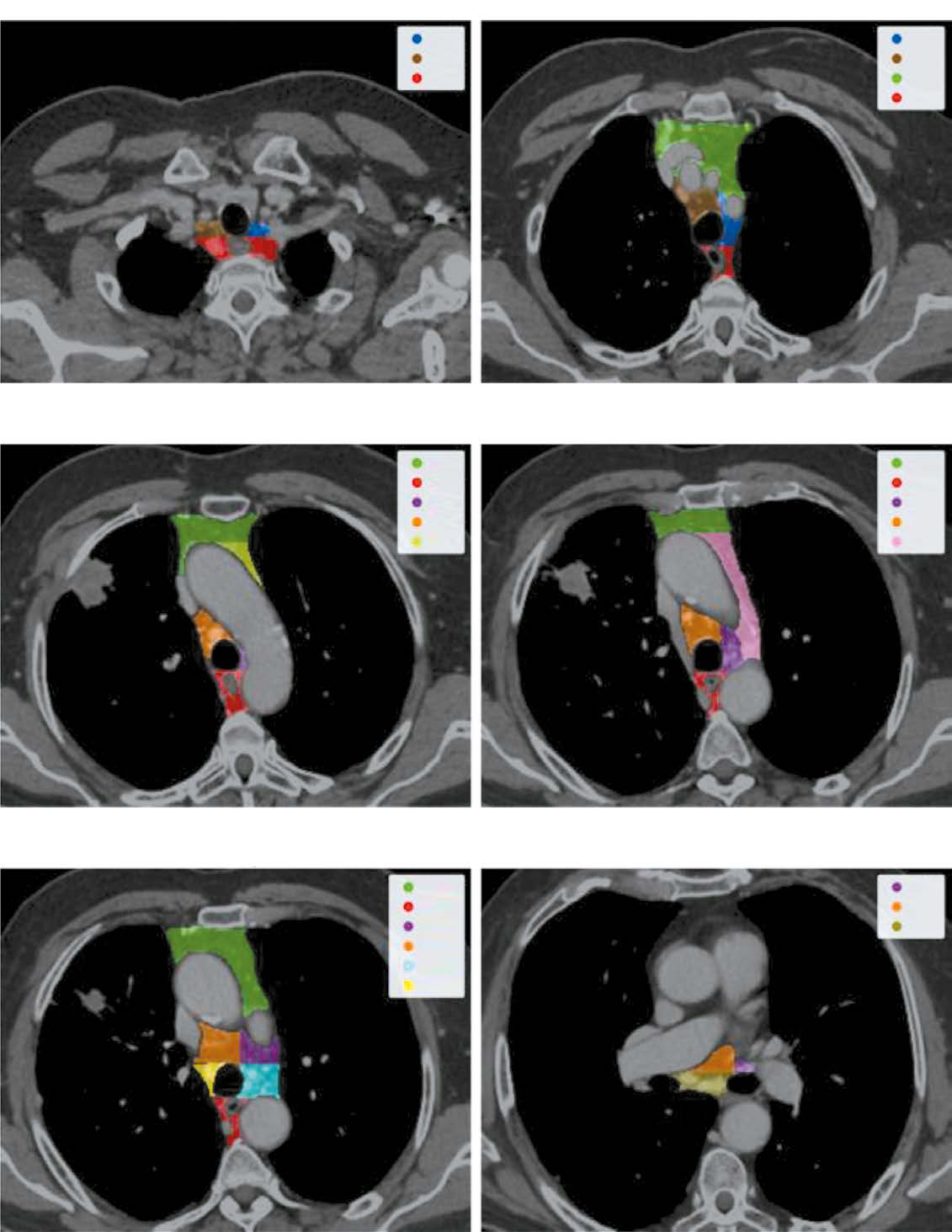
Assessing the probability of metastatic mediastinal lymph node involvement in patients with non small cell lung cancer using convolutional neural networks on chest computed tomography
Resumo
BACKGROUND: Lung cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide, accounting for approximately 20% of all cancer related deaths and having a <10% 5 year survival rate for very late stage cases. For the prevalent non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), recent guidelines advise staging based on the 8th edition of the TNM classification, highlighting the importance of mediastinal lymph node involvement. While noninvasive methods are generally accurate, they often lack sensitivity, and invasive methods may not be suitable for all patients. Advances in deep learning present potential in solving such problems. However, most research focuses on algorithm development more than clinical relevance. Moreover, none of them addressed individual lymph node malignancies, limiting comprehensive analysis and interpretability and leaving clinicians without sufficient means to validate the results effectively.
AIM: To develop a local data trained and validated algorithm for segmenting each mediastinal lymph node in chest computed tomography (CT) and assessing the probability of its involvement in metastasis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Initially, IASLC lymph node stations are segmented, providing a bounding box of the mediastinum for further processing. Next, the image is cropped to this box and passed through a second network to identify and mask all visible lymph nodes. Finally, each detected lymph node is extracted, stacked with its mask, and evaluated by a feed-forward network to determine malignancy probabilities.
RESULTS: The pipeline achieved an average recall and object Dice Score of 0.74±0.01 and 0.53±0.26 for the clinically relevant lymph node segmentation task. Further, it recorded a 0.73 ROC AUC for predicting a patient’s N-stage, outperforming traditional size based criteria.
CONCLUSIONS: The proposed algorithm enables new research algorithms to optimize the management of patients with nonenlarged intrathoracic lymph nodes, thus improving the quality of medical care for patients with cancer.
 765-783
765-783


Reviews
Challenges and benefits of using texture analysis of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans in diagnosis of bladder cancer
Resumo
Radiomics and texture analysis is a new step in the evaluation of digital medical images using specialized software and quantitative assessment of signs invisible to the eye. The textural parameters obtained through mathematical transformations correlate with morphological, molecular, and genotypic characteristics of the examined area.
This article reviews scientific studies on challenges and benefits of using texture analysis in diagnosis of bladder cancer. The authors describe the practical value of this approach, and consider the challenges and potential of using it. Forty publications published between 2016 and 2024 were selected using keywords from PubMed and Google Scholar.
Multiple studies demonstrate high accuracy of radiomics in local staging of bladder cancer, morphologic assessment of the tumor, and prediction of long term clinical outcomes.
Therefore, texture analysis of medical images can provide additional information to diagnose bladder cancer in uncertain cases. Standardization of the method is currently one of the key issues to accelerate implementation of radiomics analysis in clinical practice.
 784-793
784-793


Remote monitoring of patients with chronic heart failure: a non invasive approach
Resumo
Remote monitoring of patients, including those with chronic heart failure, has been actively used in recent years. Unlike invasive methods, non invasive methods are not associated with surgical risks and offer a wide range of patient management options such as telemonitoring, virtual visits, emergency department pre triage, in hospital telemedicine, telemedicine rehabilitation, psychological support, etc. Previously, remote monitoring required a multidisciplinary medical team to ensure high efficiency, and attempts to use advanced technology to reduce human involvement were often unsuccessful. However, all electronic and telemedicine technologies in healthcare have been dramatically transformed by the COVID-19 pandemic. There is currently a wide variety of remote monitoring methods and technologies. But it is still impossible to clearly assess their effectiveness due to a lack of common standards, inadequate legislation, and regional, social, and economic differences in the availability of these technologies. However, in 2021, remote monitoring was included in the European Society of Cardiology clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute and chronic heart failure (IIb). This review describes the history of modern remote monitoring methods and the problems they are designed to solve in order to improve outpatient health monitoring for patients with chronic heart failure.
 794-807
794-807


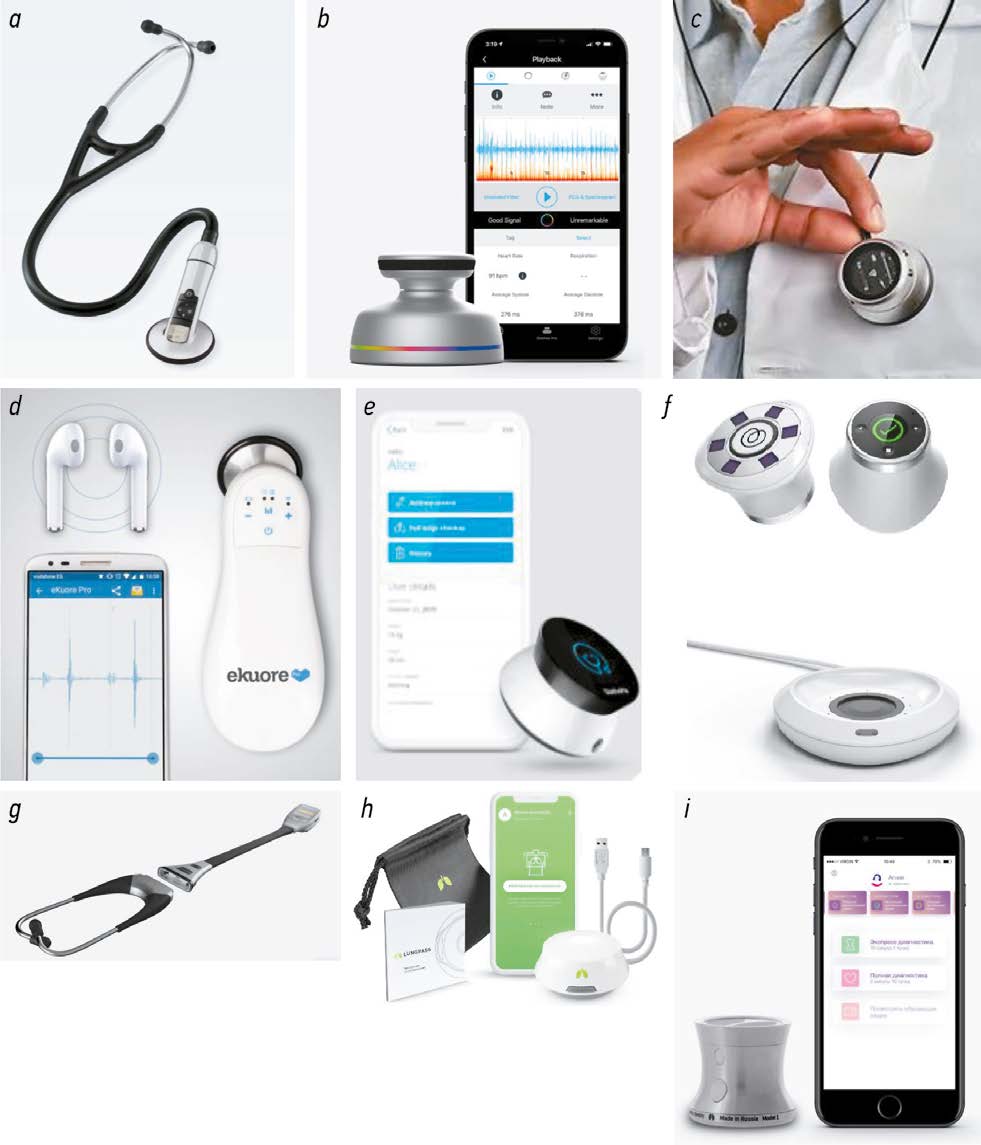
Digital stethoscope: a new era of auscultation
Resumo
The article reviews modern electronic and digital stethoscopes. The publications of the last 10 years were analyzed using eLIBRARY.ru, PubMed, Google Scholar with “аускультация” (“auscultation”), “электронный стетоскоп” (“electronic stethoscope”), “цифровой стетоскоп” (“digital stethoscope”), and “телемедицина” (“telemedicine”) keywords. New ways to auscultate using digital stethoscopes were considered. Products from the most popular manufacturers were briefly characterized. Improved functionality and versatility of a digital stethoscope (ability to evaluate heart, lung, bowel, and other organ sounds), noise reduction and sound filtering make digital stethoscopes an even more attractive tool. If these challenges are met, a digital stethoscope will undoubtedly become an indispensable tool in the diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of diseases and in patient self monitoring. Telemonitoring of patients with cardiovascular and respiratory diseases is a promising area of application for modern models of digital stethoscopes. Auscultation is especially important to evaluate changes during long term follow up, for early detection of complications and decompensated chronic non infectious diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, myocardial infarction, etc.
 808-818
808-818


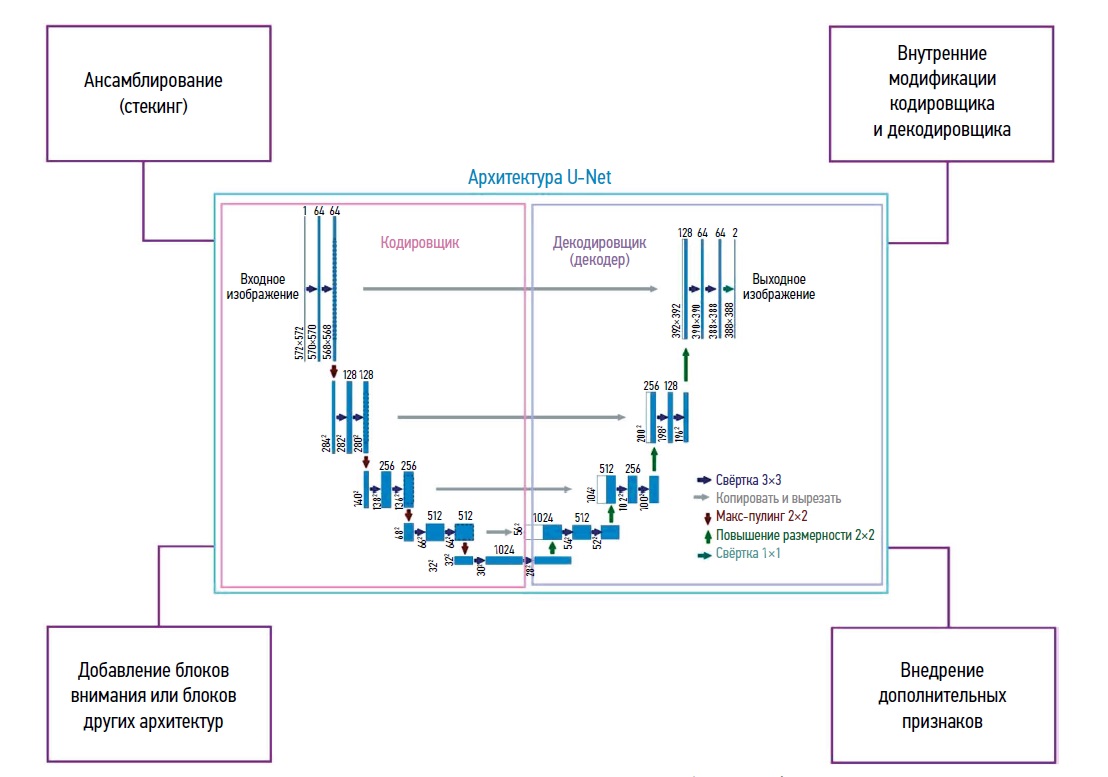
Comparative analysis of modifications of U-Net neuronal network architectures in medical image segmentation
Resumo
Data processing methods based on neural networks are becoming increasingly popular in medical diagnostics. They are most commonly used to evaluate medical images of human organs using computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and other non invasive diagnostic methods. Disease diagnosis involves solving the problem of medical image segmentation, i.e. finding groups (regions) of pixels that characterize specific objects in the image. The U-Net neural network architecture developed in 2015 is one of the most successful tools to solve this issue. This review evaluated various modifications of the classic U-net architecture. The papers considered were divided into several key categories, such as modifications of the encoder and decoder; use of attention blocks; combination with elements of other architectures; methods for introducing additional attributes; transfer learning; and approaches for processing small sets of real world data. Different training sets with the best parameters found in the literature were evaluated (Dice similarity score; Intersection over Union; overall accuracy, etc.). A summary table was developed showing types of images evaluated and abnormalities detected. Promising directions for further modifications to improve the quality of the segmentation are identified. The results can be used to detect diseases, especially cancer. Intelligent medical assistants can implement the presented algorithms.
 833-853
833-853


Potential use of virtual and augmented reality technologies in modern cardiology and cardiac surgery
Resumo
Innovative technologies have dramatically changed medical practice, particularly in cardiac surgery, which requires precision and caution due to the challenging nature of procedures. The use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in this area has great potential to improve surgical planning, medical education and patient outcomes.
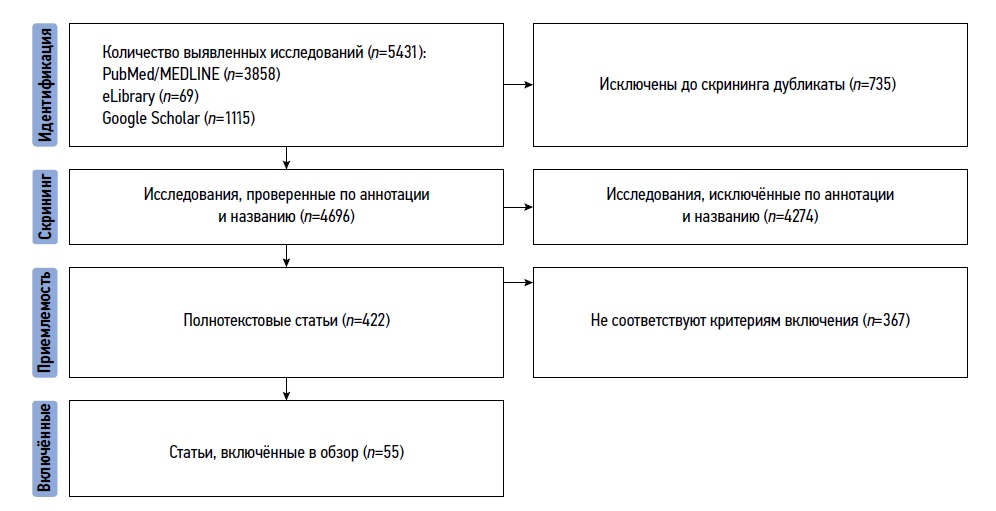
This review analyzes the literature on the role of VR and AR in modern cardiology and discusses possible directions for their development.
The search retrieved 3,858 publications from PubMed/MEDLINE, 69 publications from eLibrary, and 1,115 publications from Google Scholar. Searches included the following keywords and combinations thereof: virtual reality; augmented reality; cardiology; cardiac surgery. Publications were searched from the time the relevant databases were created to May 2024.
Cardiac care today involves increasingly sophisticated procedures that require a high level of expertise. VR becomes a powerful tool for both surgical planning and education. It opens new opportunities for educating and training cardiologists. It can be used to create realistic simulations of situations healthcare professionals may encounter in their practice. Students are able to gain hands on experience with no risk to real patients. Integrating virtual reality into cardiology practice has great potential, but several issues need to be addressed. Standards for safety and efficacy of the medical use of virtual reality should be developed. Further research is also needed to assess the long term health effects of VR use on patients.
 819-832
819-832


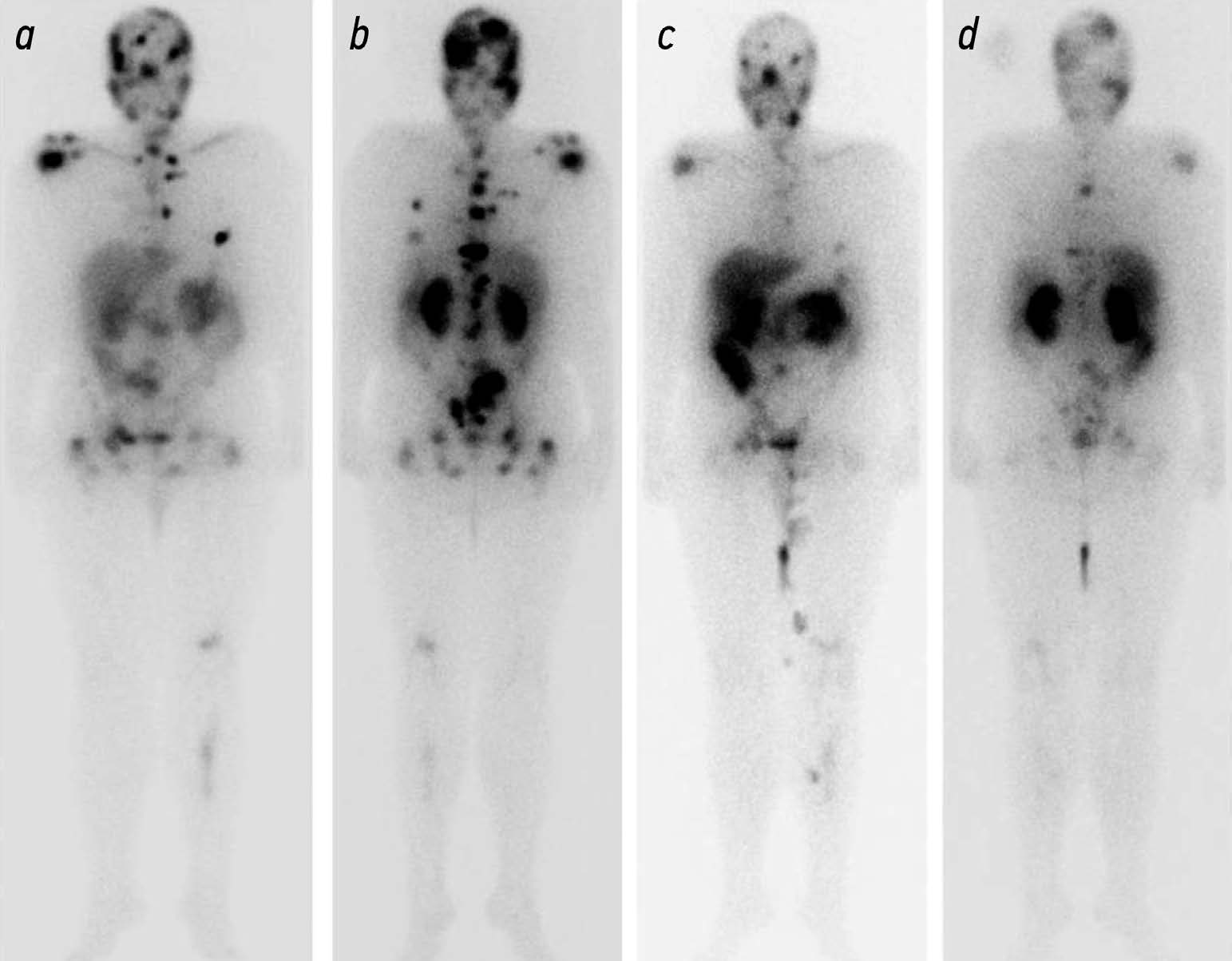
Potential use of radiation methods for diagnosing bone metastases of castration-resistant prostate cancer: a literature review
Resumo
Metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is the tumor progression with the development of resistance to androgen deprivation therapy. The incidence of bone metastases in these patients reaches 90%. Radiology is widely used to diagnose mCRPC. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are beneficial in anatomic imaging, but have some limitations in evaluating effectiveness of disease treatment. Scintigraphy is used to screen for bone metastases, but is poorly suited for assessing disease progression. Positron emission tomography (PET) combined with CT and single photon emission CT are used for early detection of local or systemic spread of prostate cancer. PET of prostate specific membrane antigen is used to predict the effectiveness of anti tumor therapy based on the absorbed dose of a radiopharmaceutical (RP). The introduction of RPs (177Lu-PSMA) opens up new perspectives for radionuclide therapy with simultaneous evaluation of its efficacy using hybrid visualization. The potential use of radiology in the diagnosis of bone metastases is of particular interest for the analysis and systematization of the data obtained and for the development of indications for radioligand therapy and the evaluation of its efficacy.
Published data indicate that radiologic modalities for the diagnosis of mCRPC vary in sensitivity and specificity and have their own advantages and limitations, so these modalities should be combined.
The development and improvement of methods to quantitatively assess treatment efficacy and identify prognostic markers will enable more informed selection of treatment strategies and radiopharmaceuticals, leading to improved overall survival.
 854-869
854-869


Ultrasound in in vitro fertilization programs
Resumo
Currently, increasing attention is being paid to the value of ultrasound as an integral part of in vitro fertilization programs, which determines the relevance of the topic of this review. This review analyzes the main studies published in recent years and attempts to identify the leading method for assessing ovarian reserve and predicting in vitro fertilization outcome, which remains controversial. The paper evaluates advantages and limitations of two dimensional and three dimensional transvaginal ultrasound methods for counting ovarian follicles. Ultrasound characteristics of the endometrium and blood flow parameters in the uterine arteries are presented as possible predictors of the outcome of in vitro fertilization programs. The current options for transabdominal oocyte aspiration for in vitro fertilization programs are presented. The analysis of literature data concluded the high informational value of ultrasound for in vitro fertilization programs.
 870-881
870-881


Case reports
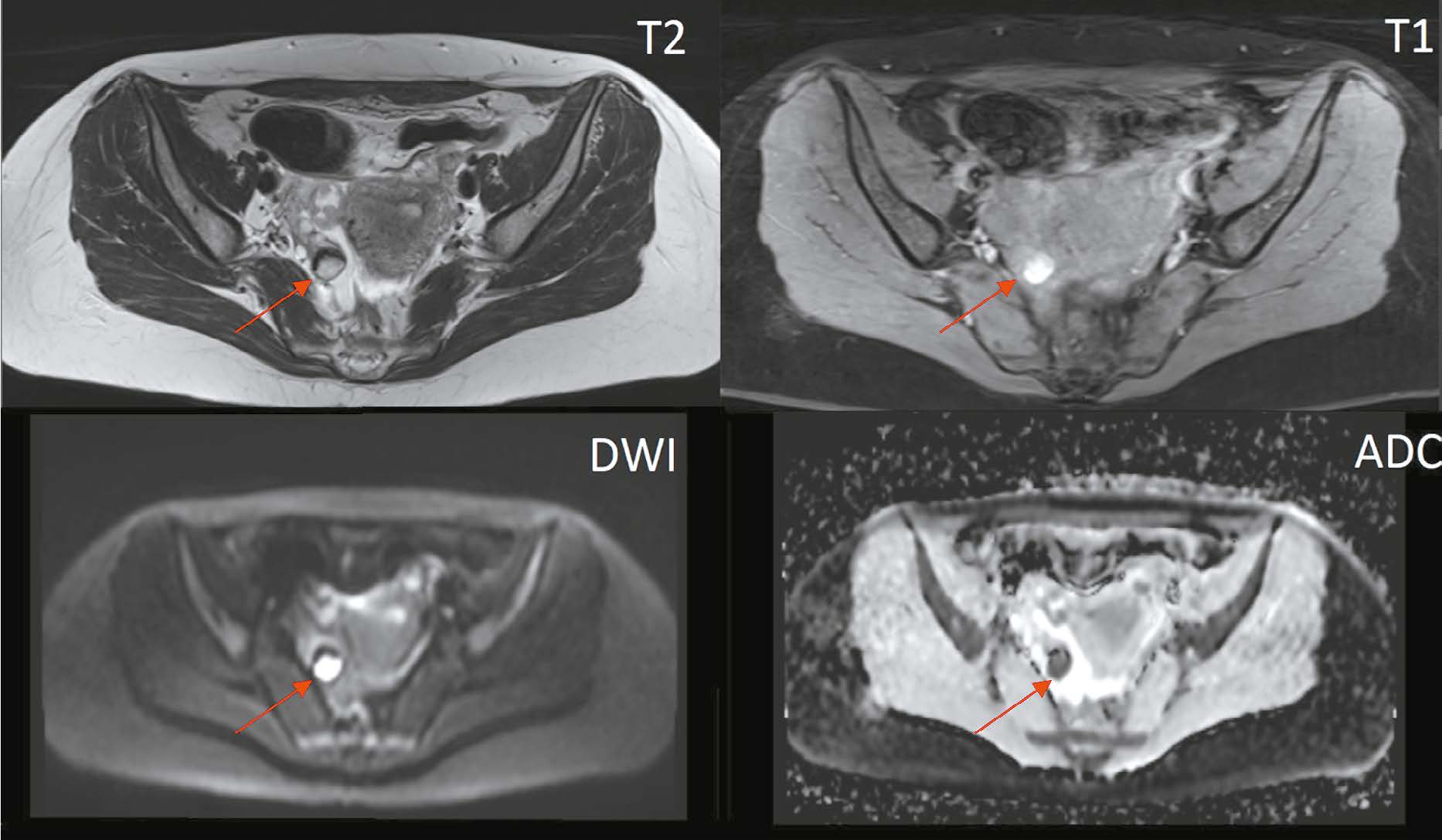
Magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of serous adenocarcinoma of fallopian tubes: a case report
Resumo
Serous adenocarcinoma of fallopian tubes is an extremely rare and difficult to diagnose type of cancer of the female reproductive system. This condition is often asymptomatic or has a non specific clinical presentation including serosanguineous vaginal discharge and colic like pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis. These symptoms are reported in the literature as the Latzko’s triad and are considered pathognomonic for tubal cancer, but their combination is observed in less than 15% of patients. The low incidence and lack of the pathognomonic clinical presentation lead to many diagnostic errors or detection of advanced disease, which significantly worsens the patient’s prognosis. An accurate surgical diagnosis is made in only 4% of cases. This case report describes serous adenocarcinoma of fallopian tubes with all signs of the Latzko’s triad and MRI suggestive of serous adenocarcinoma of fallopian tubes at a preoperative stage.
 882-892
882-892


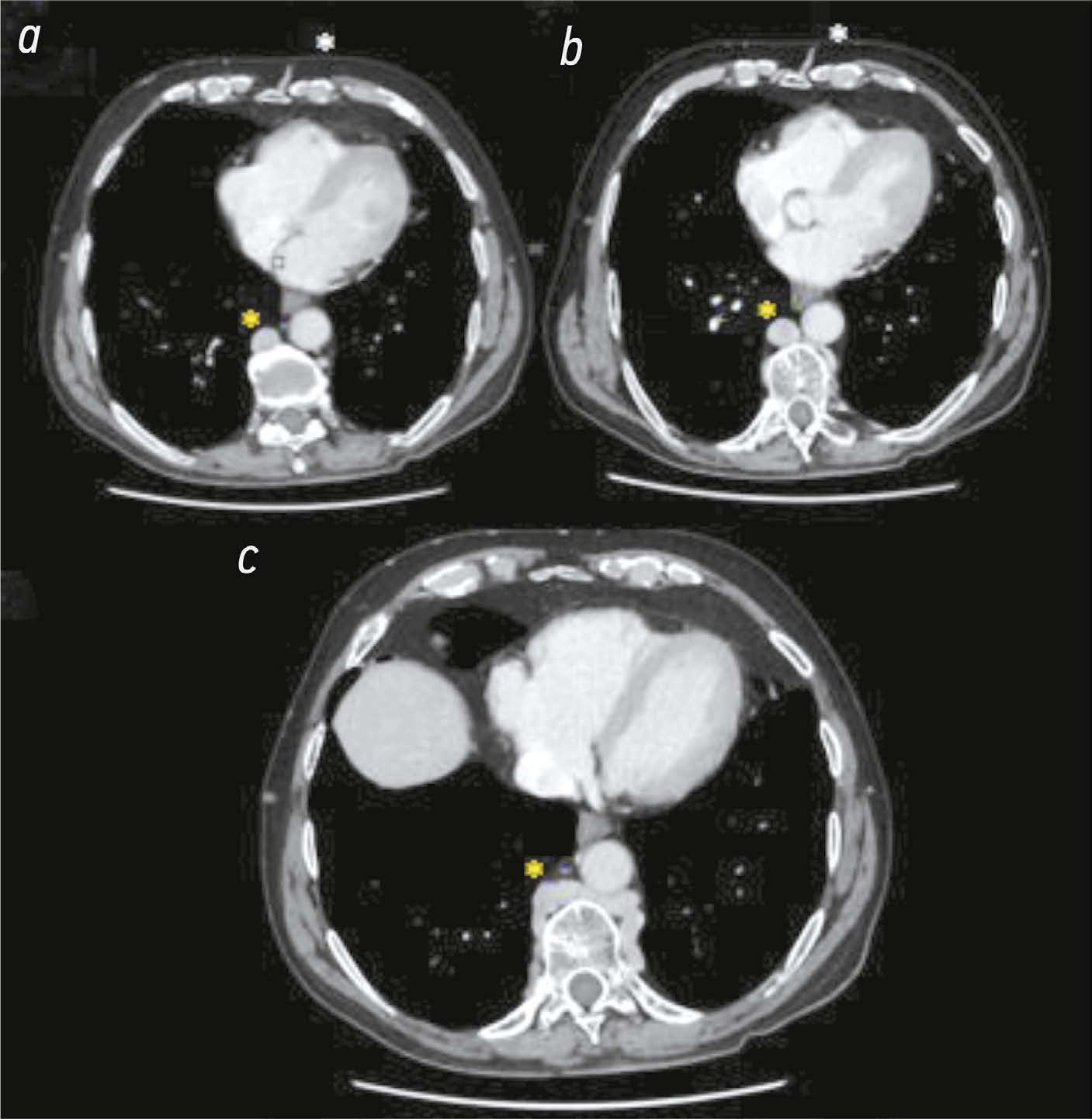
The role of computed tomography in the differential diagnosis of an intracardiac mass of the mitral valve: a case series
Resumo
The differential diagnosis of an echocardiographically detected intracardiac mass in the mitral annulus can be challenging and usually requires a multimodal approach. This type of lesion is very often associated with subvalvular calcification of the mitral valve. The rare, caseous, variant is the most difficult to diagnose. This case series highlights the clinical significance of computed tomography in detecting and characterizing subvalvular mitral annular calcification when other modalities, particularly echocardiography, are inconclusive. The aim of this article was to raise awareness among specialists of the classic signs of caseous subvalvular calcification of the mitral annulus when visualized with different modalities. Special attention is also given to providing a differential diagnostic series that identifies features that differentiate subvalvular calcification of the mitral annulus from other conditions at this site. Healthcare professionals need to be aware of these mitral valve lesions in order to predict possible associated complications and plan a treatment strategy that may help avoid unnecessary surgical procedures in some cases.
 893-901
893-901


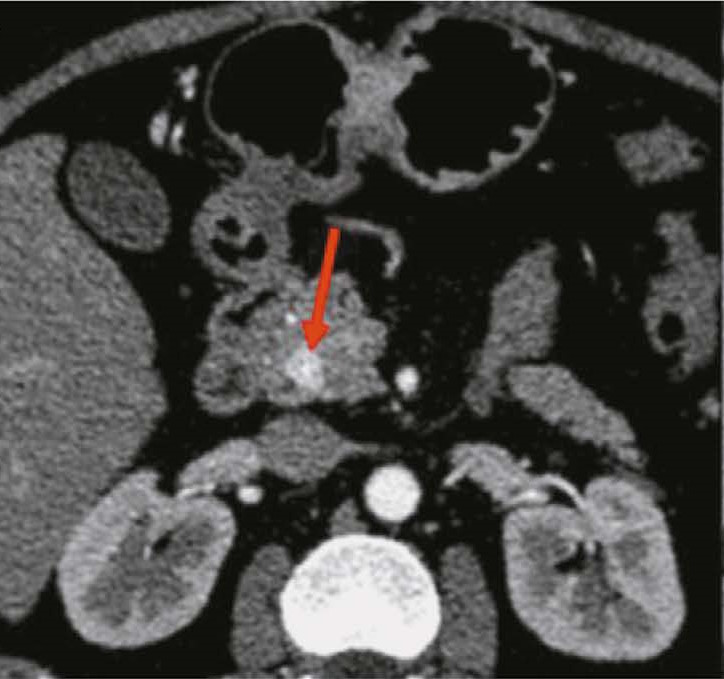
Hypoplasia of the inferior vena cava with hypertrophic azygos/hemiazygos and collateral venous circles of the abdomen: a case report
Resumo
Hypoplasia of the inferior vena cava is a rare congenital vascular defect with various forms; thus, identifying a specific anatomical variant in the literature is challenging. In some cases, the inferior vena cava may also be interrupted. Herein, we present a unique case of of an unknown subrenal hypoplasia of the inferior vena cava with azygos and hemiazygos hypertrophy and the creation of several collateral circles, particularly in the anterior wall of the abdomen, in an asymptomatic 75 year old man. This report not only describes this unusual instance but also quickly demonstrates the variations of the venous system in the abdomen, particularly on the right side, and the inferior vena cava and the azygos system, and explains the significance of imaging in recognizing vascular anomalies. The case was explored using a multiphase computed tomography technique, which correctly identified this complex vascular anomaly. The patient had never experienced symptoms associated with the same vascular defect previously. Moreover, his symptoms did not appear to be related; therefore, a periodic follow up was recommended.
 902-910
902-910