Vol 6, No 1 (2025)
- Year: 2025
- Published: 25.03.2025
- Articles: 13
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/9911
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.61
Full Issue
Original Study Articles
Autonomous artificial intelligence for sorting results of preventive radiological examinations of chest organs: medical and economic efficiency
Abstract
BACKGROUND: This article proposes a model for organizing preventive radiological examinations of chest organs through autonomous sorting of examination results using medical devices based on artificial intelligence technologies, optimized for maximum sensitivity — 1.0 (95% CI: 1.0; 1.0). Sorting involves classifying the results of mass preventive screenings (fluoroscopy and chest X-rays) into two: “not normal” and “normal.” The “not normal” category includes all cases of abnormalities (e.g., pathological conditions, post-disease or post-surgery consequences, and age-related and congenital features), which are sent for interpretation by a radiologist. The “normal” category consists of cases without signs of pathological deviations, which potentially do not require a radiologist’s description.
AIM: To evaluate the feasibility, effectiveness, and efficiency of autonomous sorting of results from preventive radiological examinations of chest organs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A prospective multicenter diagnostic study was conducted on the safety and quality of autonomous sorting of results from preventive radiological examinations of chest organs. Analytical and statistical methods of scientific inquiry were used.
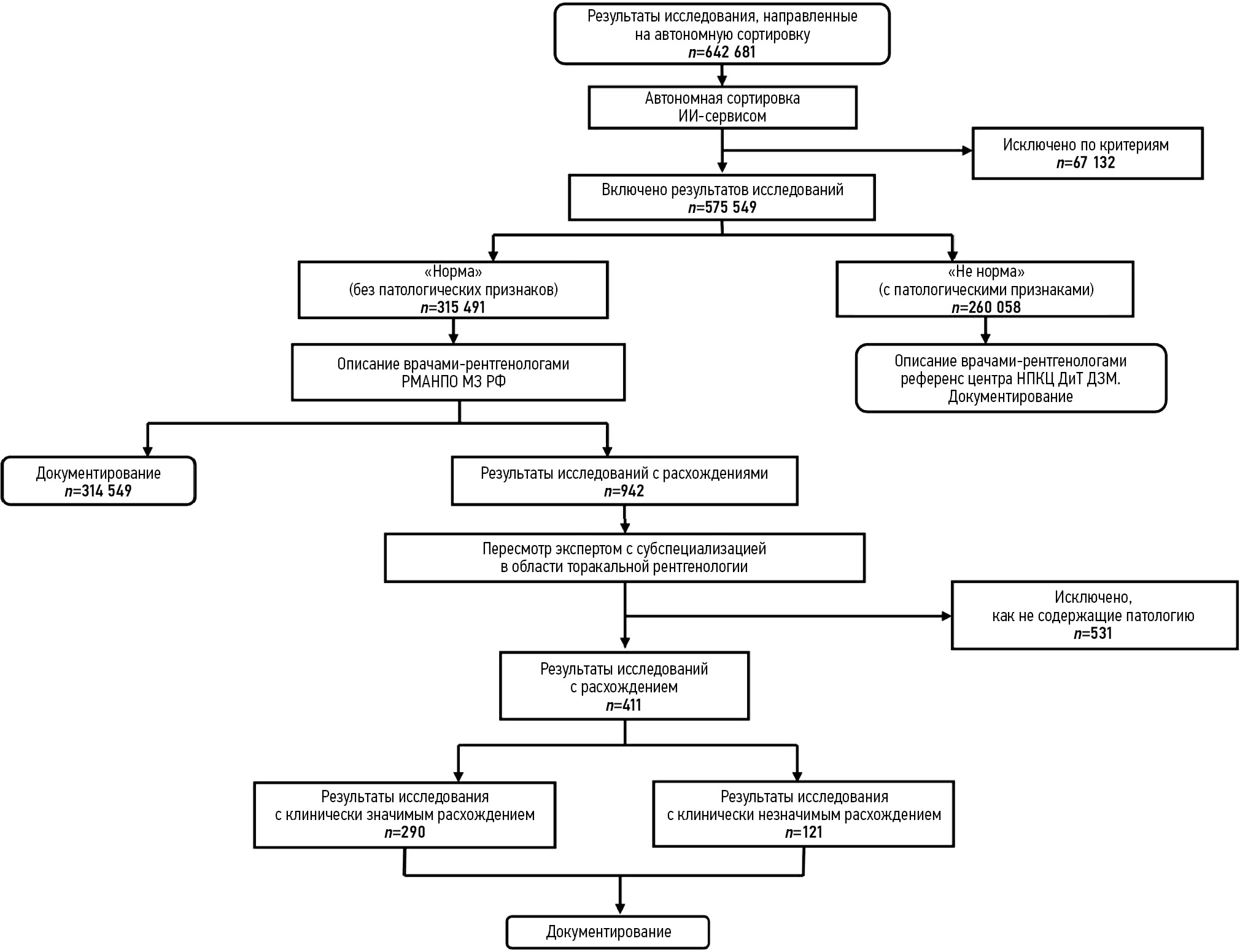
RESULTS: The study included results from 575,549 preventive radiological examinations obtained through fluoroscopy and chest X-rays and processed using three medical devices based on artificial intelligence technologies. In autonomous sorting, 54.8% of the preventive radiological examinations of chest organs were classified as “normal,” resulting in a proportional reduction in the radiologist’s workload for interpreting and describing the examination results. Fully correct autonomous sorting was achieved in 99.95% of cases. Clinically significant discrepancies were determined in 0.05% of cases (95% CI: 0.04; 0.06%).
CONCLUSIONS: This study confirmed the medical and economic effectiveness of the model for autonomous sorting of results from preventive radiological examinations of chest organs using medical devices based on artificial intelligence technologies. The next phase should involve updating the regulatory framework and ensuring the legitimacy of the autonomous application of certain medical devices based on artificial intelligence technologies in established conditions and preventive tasks.
 5-22
5-22


Datasets
CT angiography dataset with abdominal aorta segmentation
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Artificial intelligence algorithms are used to analyze images obtained through radiological diagnostic methods. The effectiveness of such algorithms depends on the availability of relevant and representative training datasets. The volume of such data in the public domain should be increased, particularly datasets containing abdominal aorta computed tomography angiography images, with pathology classification and vessel segmentation. The limitations of existing solutions include small sample sizes, restricted dataset specialization, and inconsistent dataset preparation methodologies.
Aim: To create an open dataset containing computed tomography angiography images of abdominal aorta segmentation for normal aorta, aneurysm, thrombosis, and calcification.
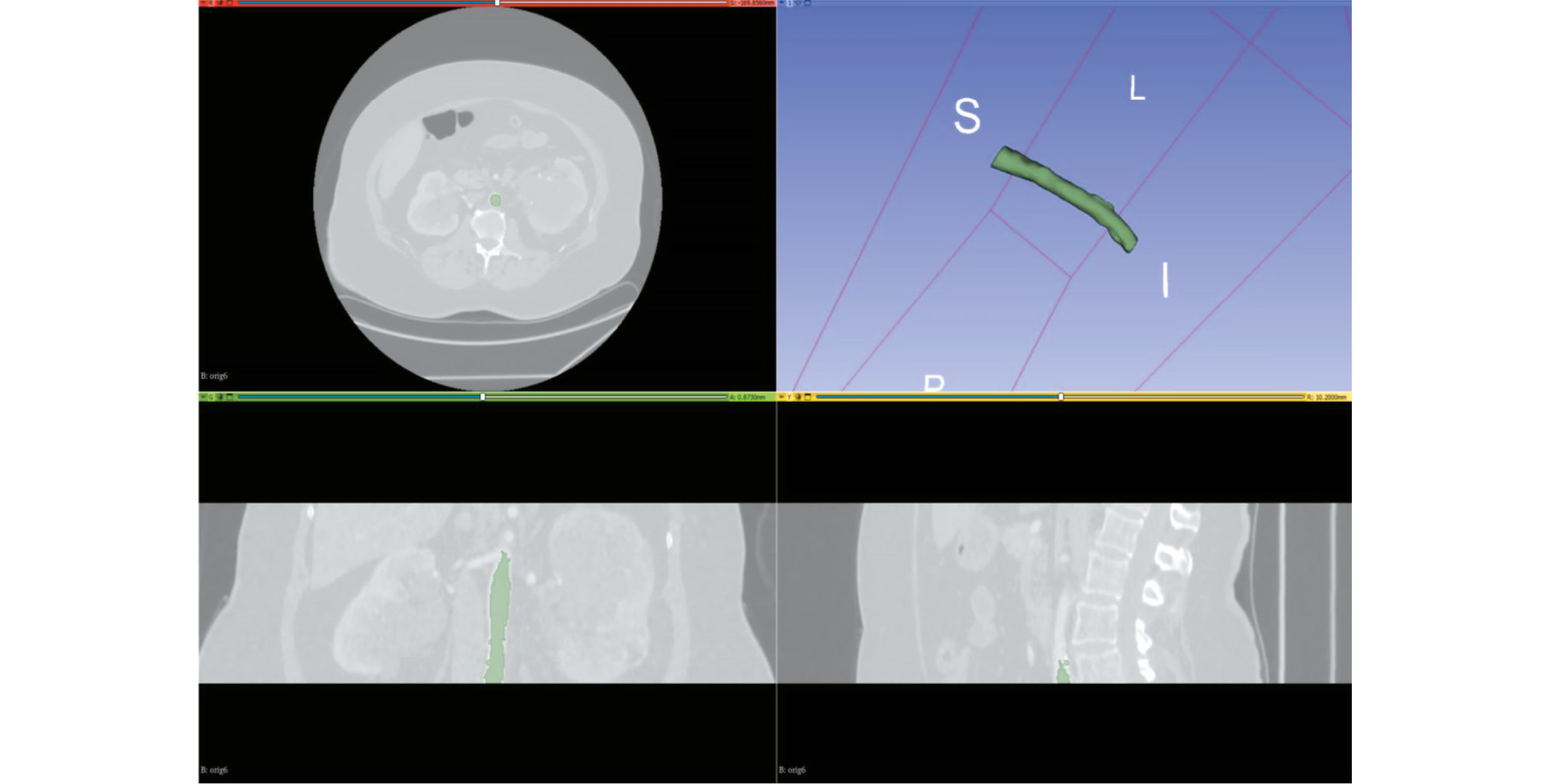
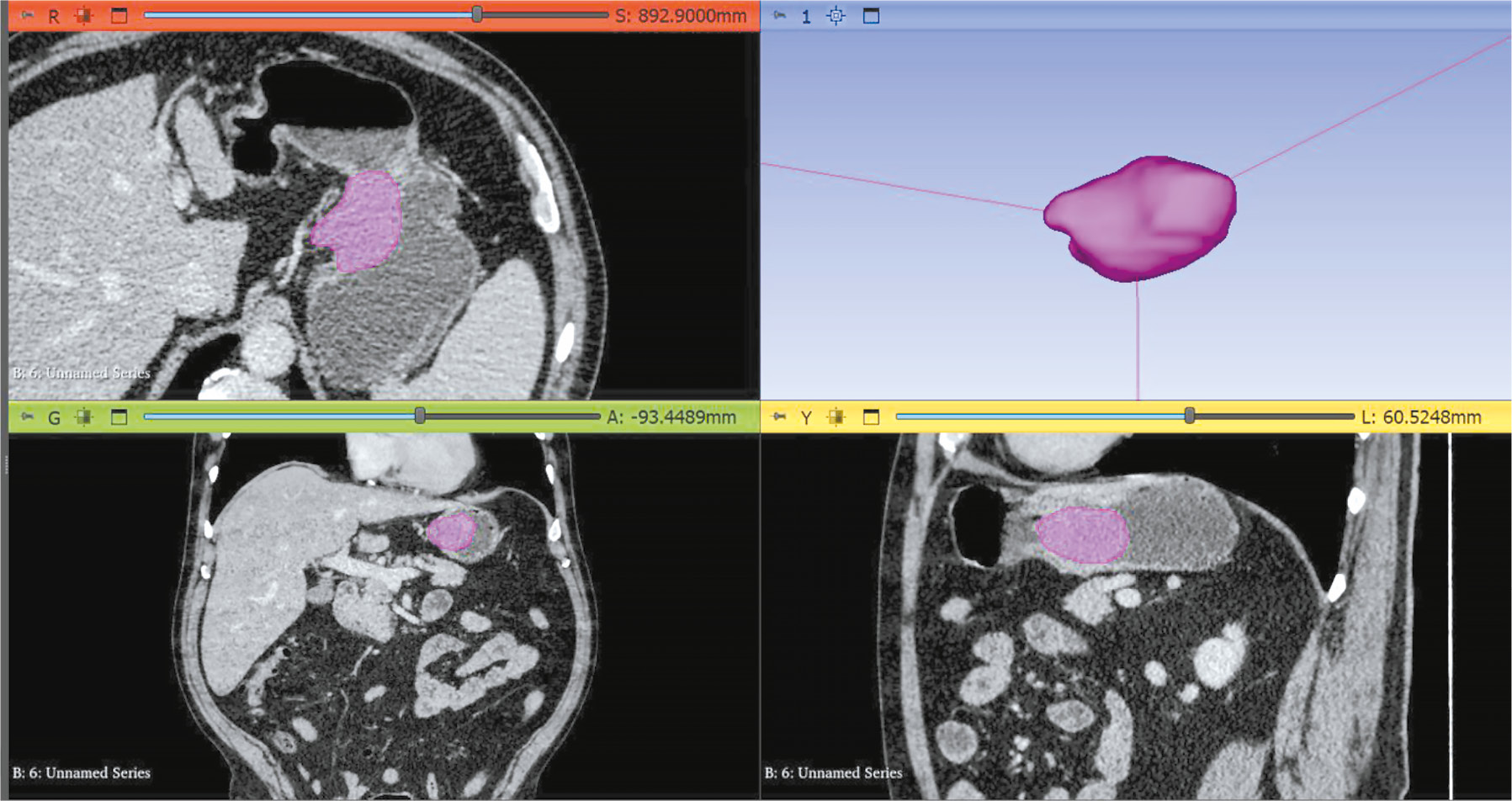
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A technical specification for dataset preparation was developed according to the methodology for testing artificial intelligence algorithms, the required sample size was calculated, and approval was obtained from an independent ethics committee. Regarding dataset creation, a previously developed original semiautomatic segmentation algorithm using Slicer 3D software was employed. The inclusion criteria were computed tomography angiography or abdominal computed tomography scans with contrast, arterial phase, and slice thickness ≤3 mm. Conversely, the exclusion criteria were presence of foreign bodies in the aorta lumen and aortic dissection. The algorithm was tested on patient data obtained from the Unified Radiological Information System. An expert evaluation was conducted to assess the compliance of obtained results with the established requirements and evaluate the time efficiency of using the developed segmentation algorithm.
RESULTS: The calculated sample size was 100 angiographic studies, including arterial phase scans with a slice thickness of ≤1.2 mm. Population data: number of unique patients, 100; percentage of female patients, 51%; and median age, 62 years (age range: 18–84 years). Pathology (including combined pathology) was detected in 61% of cases: 60 studies showed signs of calcification, 18 revealed aortic dilation, and 18 determined signs of thrombosed lumen. The average time to process one study (100 slices) using the developed segmentation algorithm was 0.8 hours.
CONCLUSIONS: A dataset containing 100 computed tomography angiography results with abdominal aorta segmentation for normal cases, aneurysm, thrombosis, and calcification was created. The dataset is publicly available and can be used for developing and testing artificial intelligence algorithms and for anthropomorphic modeling of the abdominal aorta.
 23-32
23-32


Systematic reviews
Category PI-RADS 3: the role of texture analysis in prostate cancer risk stratification (a systematic review)
Abstract
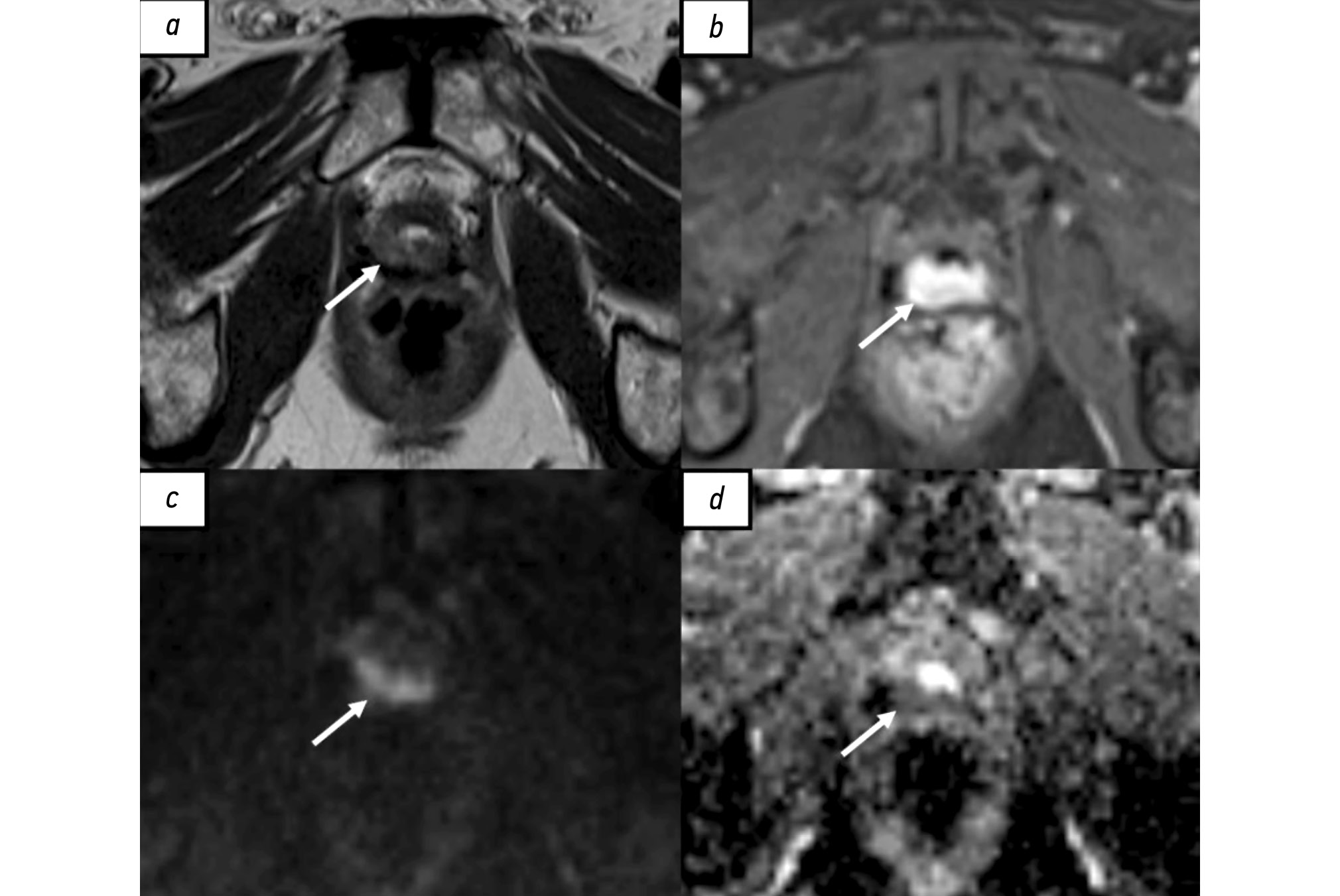
BACKGROUND: Prostate changes classified as PI-RADS 3 are a clinical situation requiring diagnostic accuracy and minimization of invasive procedures. Exploring the potential value of texture analysis in magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer risk stratification is critical in modern medical diagnostics.
AIM: To systematize and analyze current data on the application of texture analysis for prostate cancer risk stratification in patients with PI-RADS 3 and evaluate its diagnostic significance in differentiating clinically significant from clinically insignificant prostate cancer.
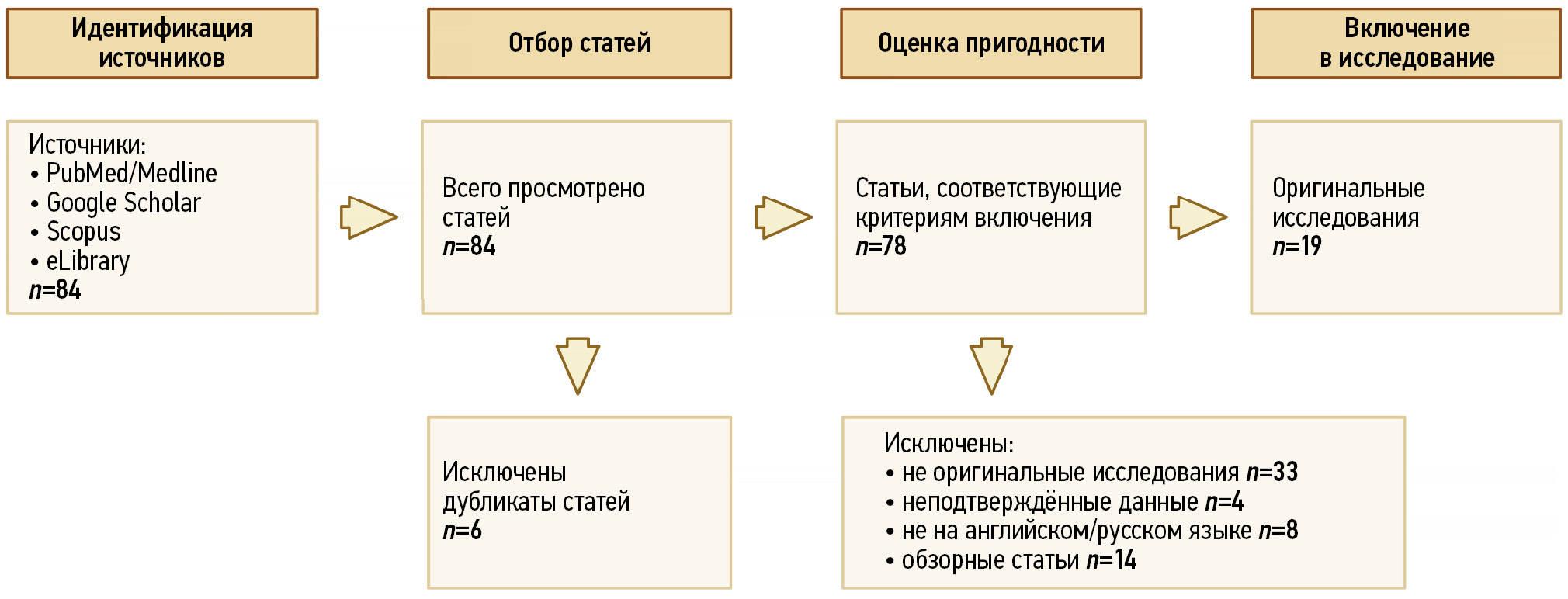
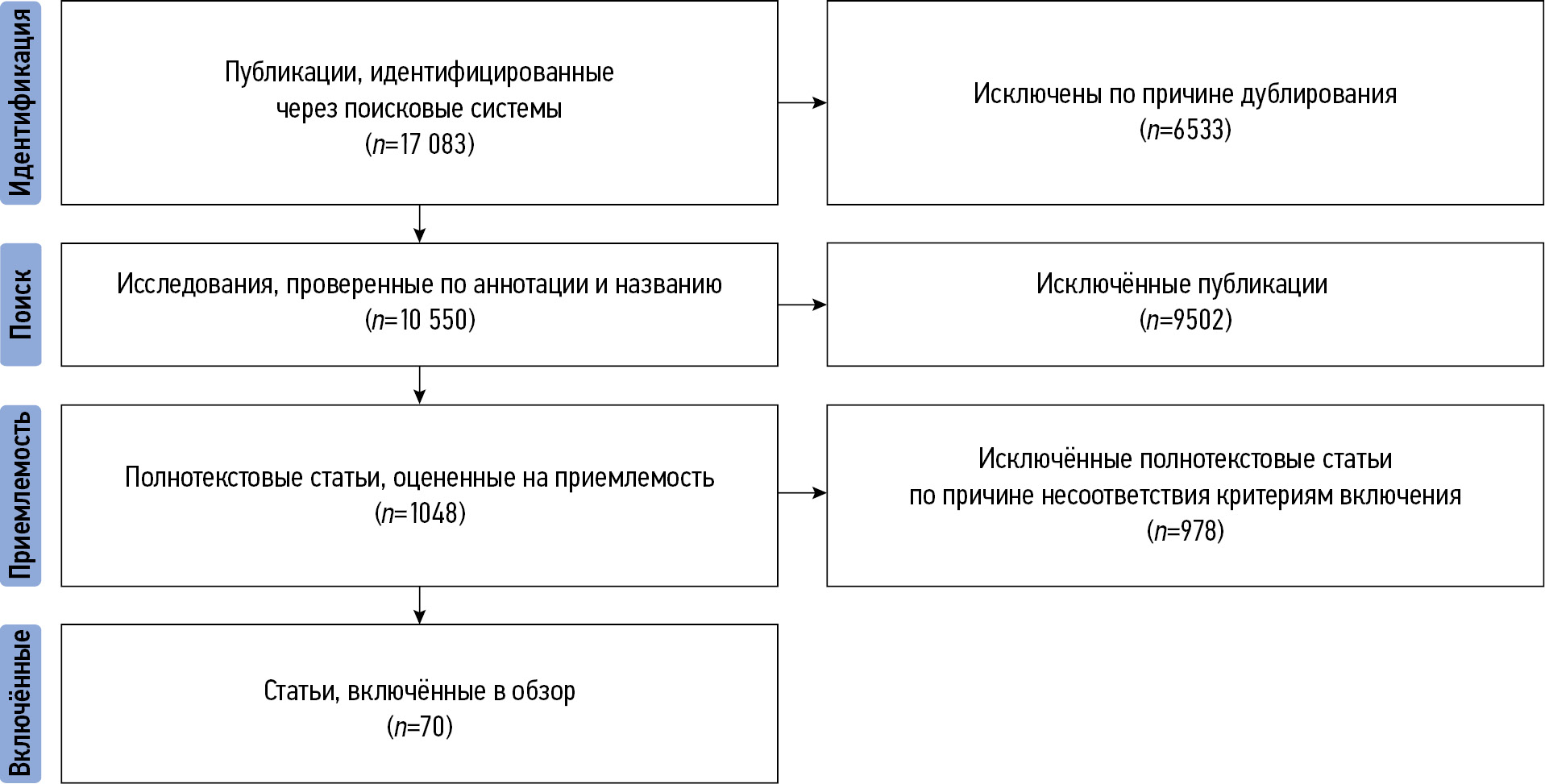
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Articles published in the last 7 years were selected and analyzed from research reference and analytical databases (Medline and Scopus) using search engines (PubMed, Google Scholar, and eLibrary). Keywords related to texture analysis and radiomics regarding prostate cancer diagnosis and risk stratification were used.
RESULTS: Analysis of the selected publications showed that machine learning and texture analysis significantly enhance the diagnostic accuracy of prostate cancer. These methods allow for more accurate risk stratification and determination of the actual need for biopsy, potentially leading to a reduction in unnecessary invasive procedures.
CONCLUSION: Texture analysis potentially enhances diagnostic accuracy in cases of prostate gland changes classified as PI-RADS 3. However, further research focused on standardizing techniques and conducting multicenter clinical trials is required for its widespread clinical application.
 33-45
33-45


Reviews
Comparative role of radiological imaging methods in biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer
Abstract
Biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer following radical treatment, including radical prostatectomy and radiotherapy, occurs in approximately 25%–50% of patients. However, the clinical course and prognosis of the disease vary among patients and depend on several factors. Consequently, the optimal diagnostic and treatment methods for patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer remains debatable. Biochemical recurrence may be caused by local recurrence, metastatic dissemination, or a combination of these processes. Recently, approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer have undergone significant changes with the introduction of more accurate diagnostic methods. This article provides a review of the current capabilities of radiological imaging and radionuclide diagnostic methods in visualizing local recurrence and metastases in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer.
 46-62
46-62


Application of radiomics in osteoporosis detection — current capabilities and future prospects (a review)
Abstract
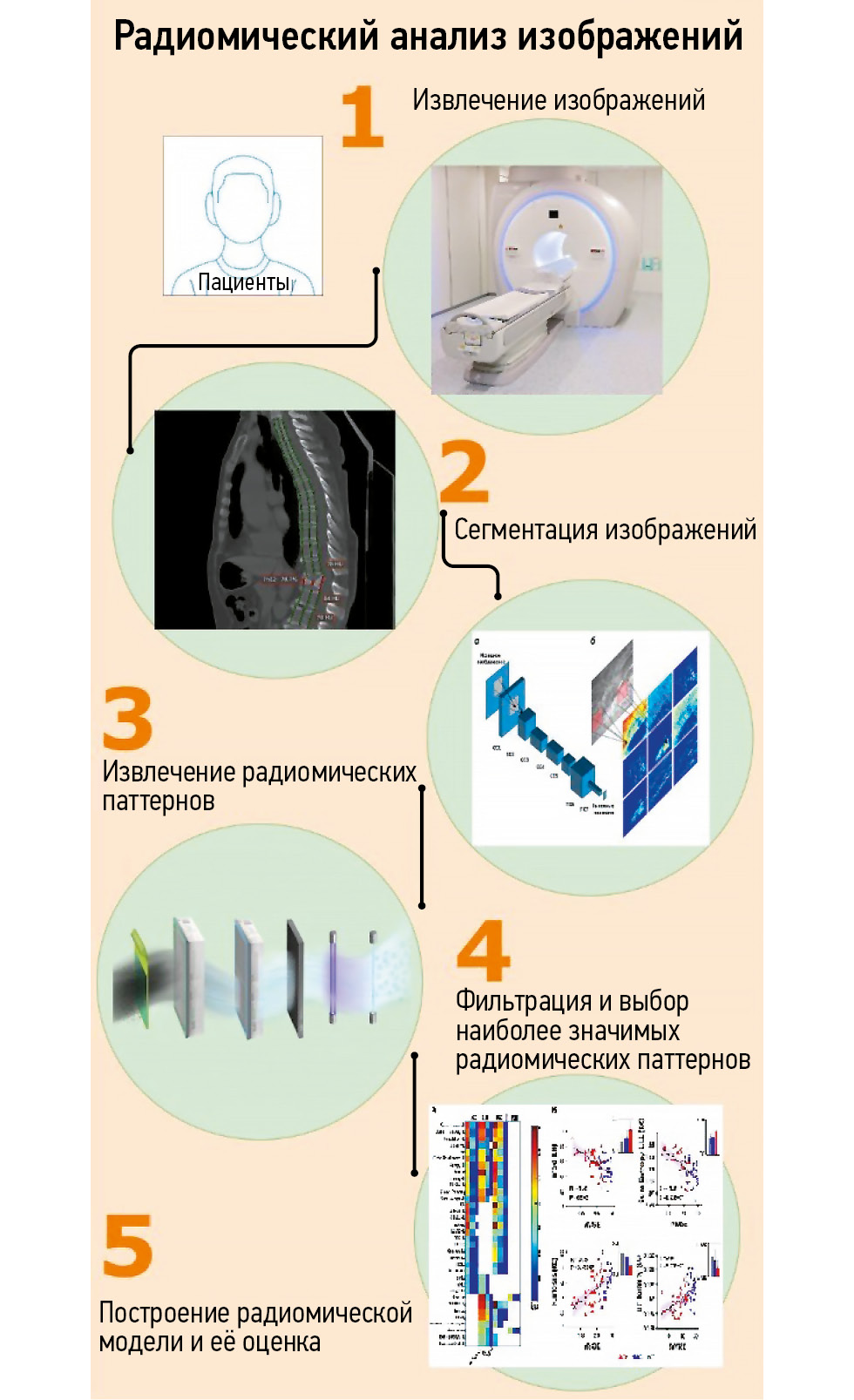
The prevalence of osteoporotic fractures continues to increase as the population ages due to demographic transition. This is particularly relevant for developed countries, including Russia. Radiomics may emerge as a valuable tool for osteoporosis detection.
This review demonstrates the development and application of radiomics in diagnosing oncological and non-oncological diseases including osteoporosis.
A literature search was conducted using the databases PubMed, Google Scholar, and eLibrary over the past 5 years. Data on the prevalence and epidemiology of osteoporosis were obtained from publications in the last 15 years. The search was performed using the following keywords: "radiomic", "osteoporosis", "texture", "magnetic resonance imaging", "computed tomography", "non-oncological radiomics", «магнитно-резонансная томография» ("magnetic resonance imaging"), «компьютерная томография» ("computed tomography"), «радиомика» ("radiomics"), «остеопороз» ("osteoporosis"), «текстурный анализ» ("texture analysis"), «радиомический анализ» ("radiomic analysis"). Data from original clinical studies were included. In total, 247 articles were found and analyzed. Finally, 59 studies were selected for the review.
The number of studies examining the potential of radiomics in detecting osteoporosis was limited. Further research is required to explore the potential of radiomic analysis using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for detecting osteoporosis compared to established methods such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and the FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment Tool) algorithm.
 63-77
63-77


Radiomics in application to diseases of the musculoskeletal system: a review
Abstract
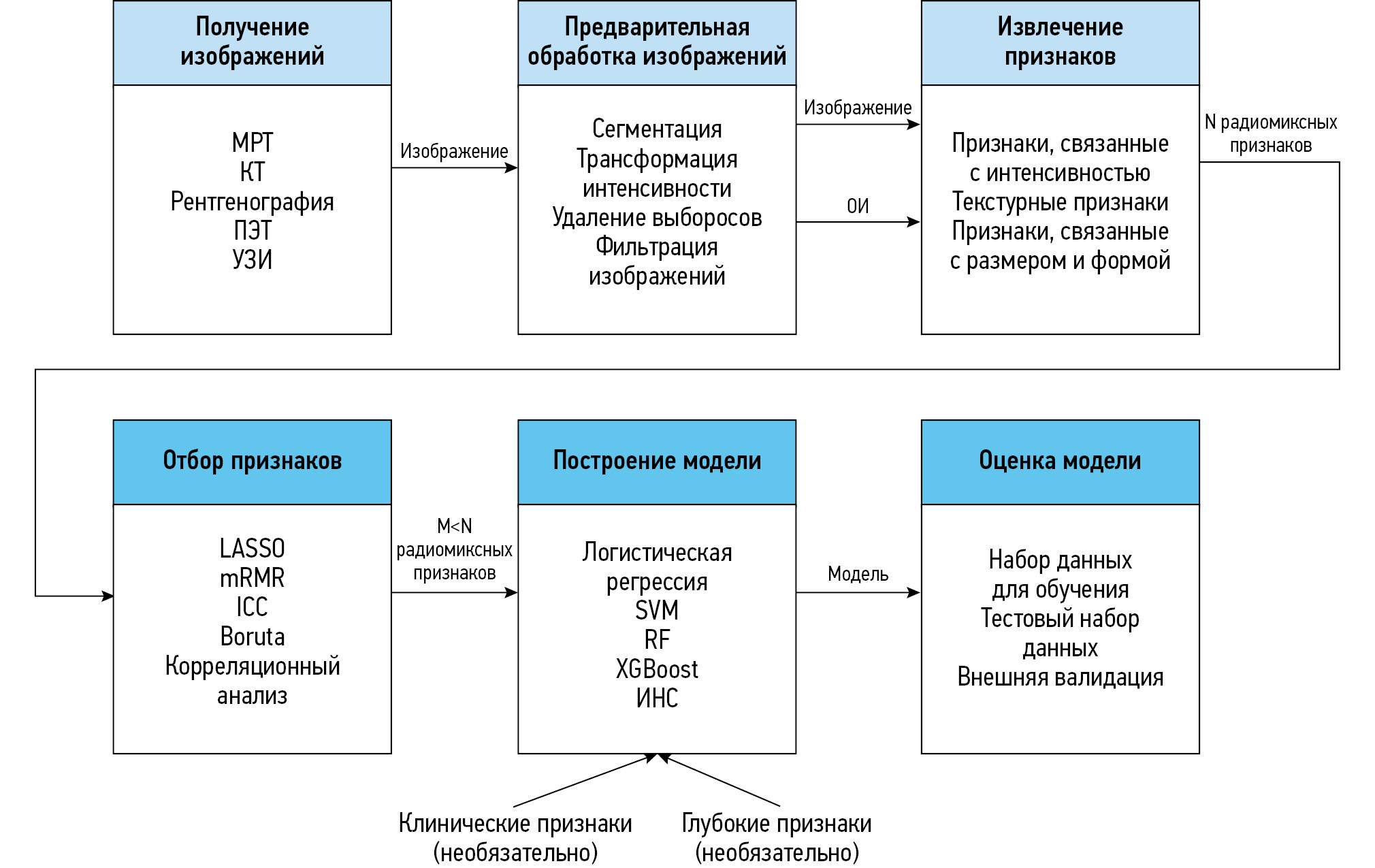
Radiomics is a technique used to extract numerous quantitative features from digital medical images. A decade ago, this method was applied in oncology, but now it has expanded to non-oncological diseases, particularly those affecting the musculoskeletal system and connective tissues. This article provides an overview of the current advances in radiomics for diagnosing diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
In this review, we assessed 37 original research papers published in English between 2020 and 2023. The most commonly used imaging modalities were magnetic resonance imaging (54%) and computed tomography (32%), while dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (14%), ultrasound (5%), and radiographs (5%) were less frequently used. The majority of the studies apply manual segmentation to identify the regions of interest. Various classification models have been developed that incorporate clinical, radiomics, and deep features, with combined clinical-radiomics models being the most prevalent one. The most commonly affected areas in diseases of the musculoskeletal system were the spine and large joints.
The prevalence of the multi-source input models (primarily clinical-radiomics) compared to that of single-source input models (clinical only, radiomics only) for diagnosing diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be explained by the higher classification performance, likely due to the inclusion of a larger number of independent information sources. Although the development of models or deep-learning features for automatic segmentation and classification holds promise, it requires significant efforts in creating image databases for deep model training. Thus, radiomics may be particularly beneficial for the early detection of diseases of the musculoskeletal system that cause pathological changes in the soft tissues, which may not be visible to the naked eye.
 78-96
78-96


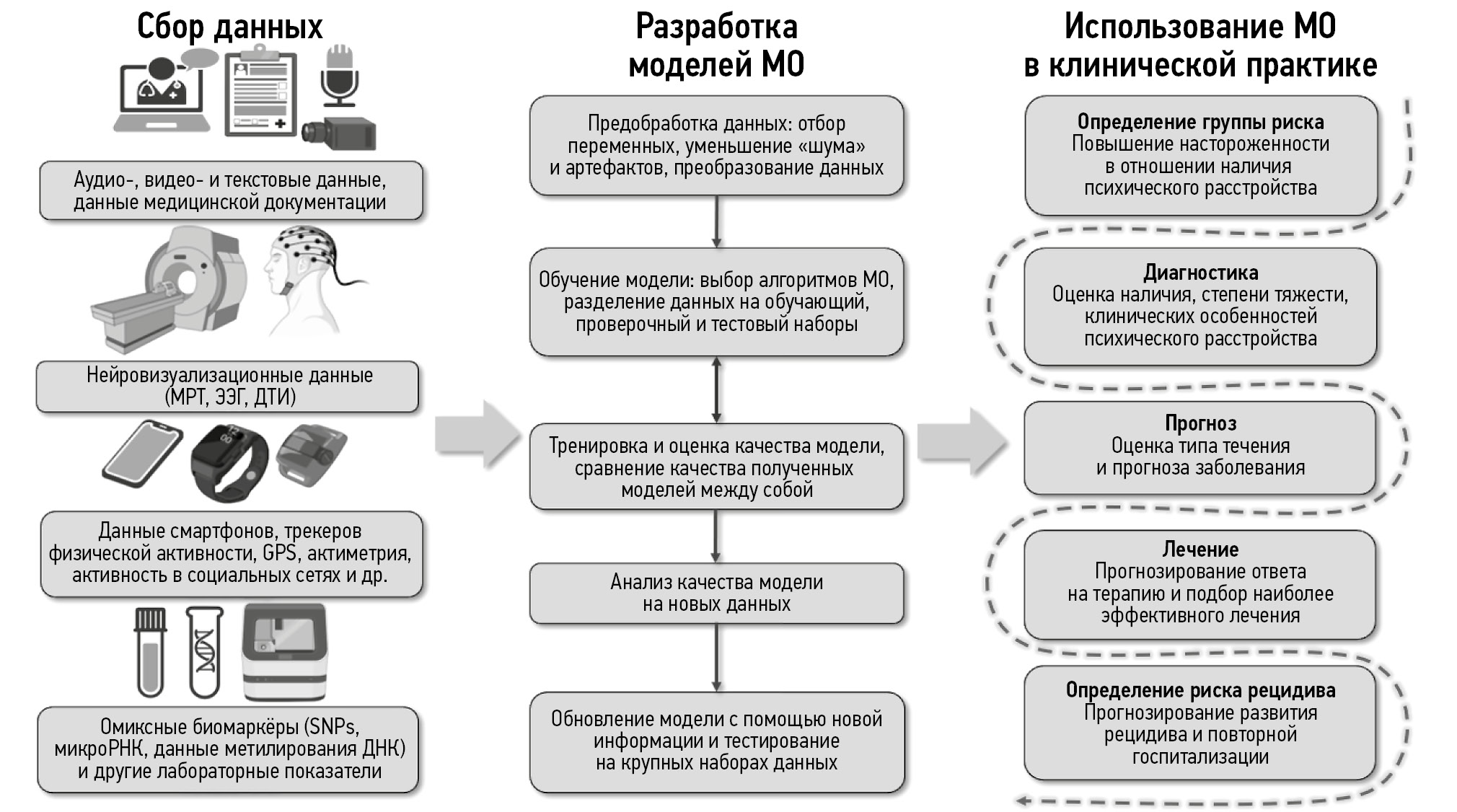
Prospects of machine learning applications in affective disorders
Abstract
Mental disorders are a significant medical and social issue globally. Currently, approximately 970 million individuals suffer from mental disorders, with over 300 million diagnosed with depression or bipolar disorder. Recently, there has been significant advancement in digital technologies, particularly in artificial intelligence, encompassing machine learning and deep learning. Given the growing interest in their use in psychiatry and the need to develop new approaches to psychiatric care. This review explores the current and promising directions for the application of artificial intelligence technologies in clinical practice, focusing on patients with depression and bipolar disorder.
A literature search was conducted from January to February 2024 in the databases PubMed, Google Scholar, and eLibrary using the following keywords: «психиатрия» ("psychiatry"), «психическое здоровье» ("mental health"), «психическое расстройство» ("psychiatric disorder"), «депрессия» ("depression"), «депрессивный эпизод» ("depressive episode"), «рекуррентное депрессивное расстройство» ("recurrent brief depression"), «биполярное расстройство» ("bipolar disorder"), «машинное обучение» ("machine learning"), «глубокое обучение» ("deep learning"), «искусственный интеллект» ("artificial intelligence"); "psychiatry", "mental health", "psychiatric disorder", "depression", "depressive episode", "major depressive disorder", "bipolar disorder", "machine learning", "deep learning", "artificial intelligence". Studies on the use of artificial intelligence technologies in patients with depression and bipolar disorders and review articles discussing the difficulties of their application in psychiatry were excluded. Publications in Russian and English in the past 10 years were selected.
The most commonly used machine learning models for diagnosing patients with affective disorders utilize neuroimaging data (primarily magnetic resonance imaging and electroencephalography), text, audio, and video data and data from electronic devices, molecular-genetic markers, and clinical indicators. The models were trained using mono- or multimodal datasets. Notably, many of the reviewed studies have significant limitations, making the implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in clinical practice challenging. These include small sample sizes, low representativeness and standardization, inclusion of “noise” and correlated variables, and absence of validation using independent datasets.
Studies on machine learning methods have demonstrated promising results in the early diagnosis of affective episodes and in predicting treatment responses. However, their clinical application is limited, owing to insufficient validation. Well-designed prospective cohort studies and the creation of extensive, high-quality datasets and models capable of uncovering new relationships between variables are required to address this limitation.
 97-115
97-115


Modern capabilities of artificial intelligence technologies in cardiovascular imaging
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide. The emergence of new technologies and integration of artificial intelligence with machine learning have broadened opportunities for doctors to improve the effectiveness of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. The development of artificial intelligence technologies, particularly in the fields of machine and deep learning, is rapidly attracting the interest of clinicians in creating novel, integrated, reliable, and efficient diagnostic methods to provide medical care. Cardiologists use various imaging-based diagnostic techniques, which provide more extensive quantitative data about patients.
This review summarizes current literature on the application of artificial intelligence technologies in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases and identifies knowledge gaps that require further research. Machine and deep learning methods are widely used and have shown promising results in cardiology. Convolutional neural networks have been used to measure cardiac function parameters from echocardiography results. Deep learning algorithms provide more accurate identification of stenosis and calcification in coronary arteries and characterization of plaques in cardiac CT scans. Convolutional neural networks have been employed for tasks such as automatic segmentation of heart chambers and structures, tissue property determination, and perfusion analysis using magnetic resonance imaging results. As artificial intelligence technologies, particularly machine learning, continue to develop, their integration opens up new possibilities.
Thus, artificial intelligence technologies are of great interest in healthcare, as they enable the rapid analysis of large amounts of data, demonstrating high effectiveness. artificial intelligence can provide additional assistance to specialists, contributing to enhanced workflow efficiency and improved medical care.
 116-129
116-129


Imaging techniques in diagnosing acute pulmonary thromboembolism
Abstract
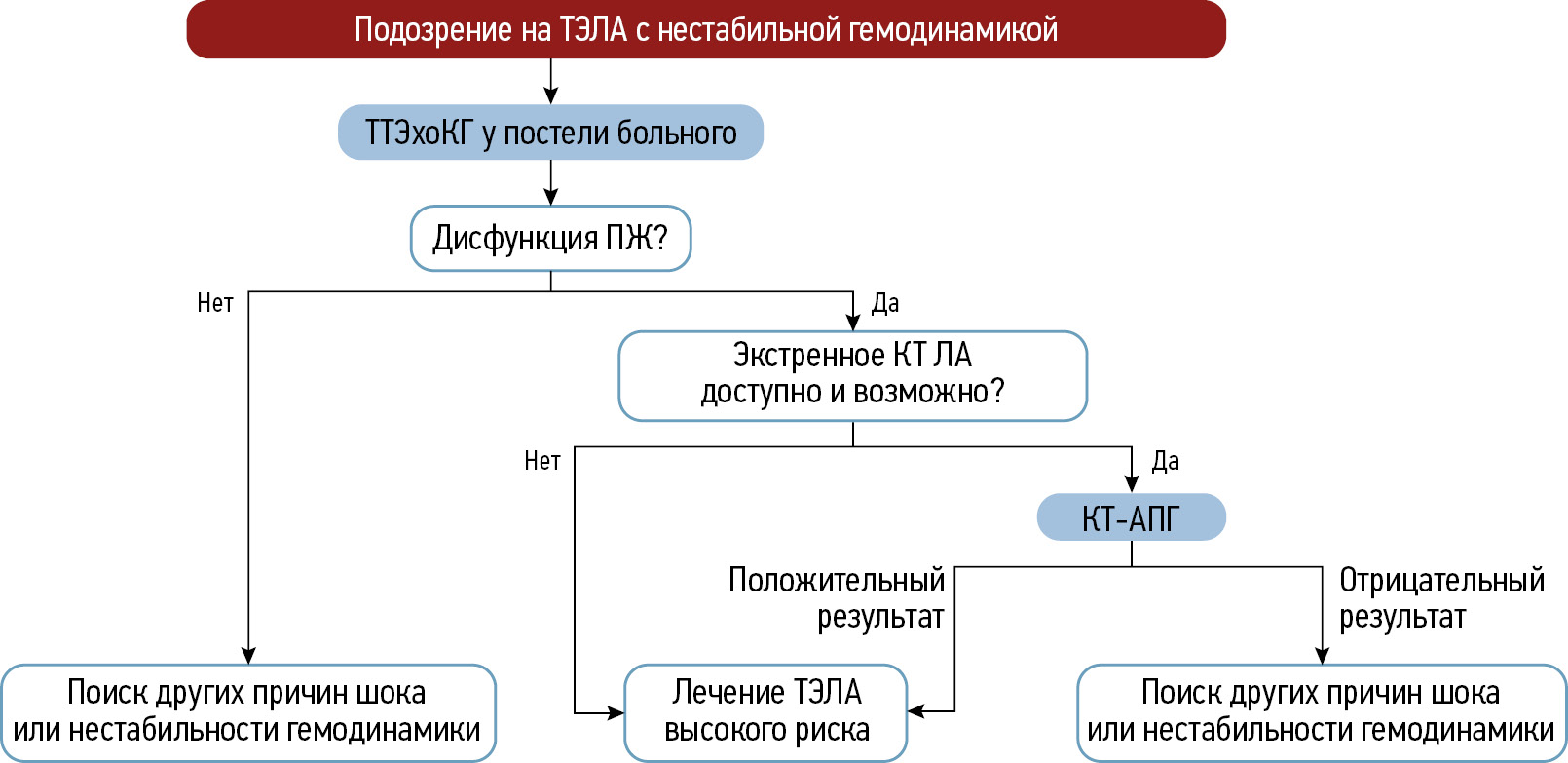
Pulmonary thromboembolism is the occlusion of the pulmonary arteries by thrombi of any origin, which commonly originates in the large veins of the legs and pelvis. This article provides an overview of existing imaging techniques used in diagnosing this pathology. A review of scientific studies by Russian and international authors is provided. Moreover, the article discusses diagnostic algorithms and the characteristics and challenges of risk stratification in patients with suspected acute pulmonary thromboembolism. The key imaging aspects for this pathology and criteria for assessing its severity are highlighted. The contribution of relatively new perfusion tomography methods, such as dual-energy and subtraction computed tomography pulmonary angiography, and magnetic resonance pulmonary angiography is demonstrated. Despite the presence of established methods for diagnosing acute pulmonary embolism, there is growing interest in additional and alternative imaging techniques, which have been more integrated into routine clinical practice. Special attention is given to subtraction computed tomography pulmonary angiography, which has the ability to generate iodine maps for indirect perfusion assessment, and its application in clinical practice. The feasibility of using various imaging techniques in diagnosing acute pulmonary thromboembolism is discussed, highlighting their advantages and prospects in emergency medical care.
 130-142
130-142


The role of radiomics in diagnosing gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a review
Abstract
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are the most common mesenchymal neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract originating from the interstitial cells of Cajal, accounting for approximately 80% of all primary gastric tumors. Despite their widespread use, traditional diagnostic methods for gastrointestinal stromal tumors, such as computed tomography, endoscopic examination, endoscopic ultrasound, and fine-needle aspiration biopsy, have several limitations, including diagnostic uncertainty and limited capabilities of biopsy.
Radiomics, which involves analyzing texture features in medical images, is considered an innovative approach, with the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy in gastrointestinal stromal tumors detection. This method allows for the interpretation of tissue changes through the mathematical processing of images, revealing information beyond the human eye’s ability to detect, which can be beneficial for the early detection of tumors.
This article assesses the advantages and disadvantages of current methods for diagnosing gastrointestinal stromal tumors and the potential of radiomics to improve diagnostic outcomes. The review allows to determine the best applications and promising directions for future research in this crucial field.
 143-155
143-155


Case reports
Magnetic resonance imaging in prenatal diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex: a case report
Abstract
Early detection of orphan diseases, including tuberous sclerosis complex, requires a multidisciplinary approach and the integration of new prenatal diagnostic methods, utilizing ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Accumulated knowledge of the clinical manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex and advancements in diagnostic techniques enable the identification of this condition. Magnetic resonance imaging allows for high-quality anatomical and functional imaging of the brain in various planes, improving the sensitivity and diagnostic value of the method for early (prenatal) detection of cerebral manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex. Additionally, magnetic resonance imaging detects mediastinal masses. This highlights the need for a comprehensive approach in diagnosing tuberous sclerosis complex, with magnetic resonance imaging as the primary method for assessing the fetus’s cardiovascular and central nervous systems.
This article presents a clinical case of tuberous sclerosis complex determined by intrauterine diagnosis followed by postnatal examination of the newborn and genetic confirmation of the diagnosis. This case report demonstrates the diagnostic value of magnetic resonance imaging in the prenatal diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex.
 156-165
156-165


Combination of familial transthyretin amyloidosis and hyperlipoproteinemia(a) in a patient with spinal canal stenosis: a case report
Abstract
Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis is a rare, progressive, systemic autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the extracellular deposition of insoluble amyloid fibrils in the peripheral nervous system, heart, and other organs. Among the specific signs of this condition, symptomatic spinal canal stenosis is prominent. Lipoprotein(a) is an atherogenic lipoprotein, and increased plasma concentrations are a significant risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Data regarding the relationship between transthyretin amyloidosis and lipoprotein(a) levels are limited.
This article presents a clinical case of a patient with arterial hypertension, with blood pressure elevated to 150/90 mmHg for 5 years. Following a COVID-19 infection between June 2, 2021, and June 25, 2021, the patient experienced a marked increase in blood pressure to 290/150 mmHg; sharp left-sided chest pain lasting 20–30 minutes unrelated to physical activity, which was relieved with medication; and pain in the cervical and thoracic spine. Despite antihypertensive therapy, the patient’s blood pressure stabilized at 110/70 mmHg. Further evaluation revealed dyslipidemia, with increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels at 4.53 mmol/L and lipoprotein(a) at 1.46 g/L. Doppler ultrasound revealed atherosclerosis in the extracranial parts of the brachiocephalic arteries, with up to 20% stenosis of the right internal carotid artery. Echocardiography showed thickening of the left ventricular wall, interatrial septum, and mitral valve leaflets, although the ejection fraction remained preserved. Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine revealed cervical spinal canal stenosis (C5–C6). Genetic testing identified a nucleotide sequence variant in the transthyretin gene (Chr18: 29171879 G>A, p. Arg5His) in the heterozygous state in the patient and her blood relatives. Specific anti-amyloid therapy with tafamidis was considered, and hypolipidemic therapy was initiated.
In patients with symptomatic spinal canal stenosis and left ventricular wall thickening, even in the presence of hypertension, comprehensive evaluation is crucial for the timely diagnosis and adequate management of amyloid cardiomyopathy. Thus, we describe the first reported clinical case of the combination of familial transthyretin amyloidosis and hyperlipoproteinemia(a).
 166-177
166-177


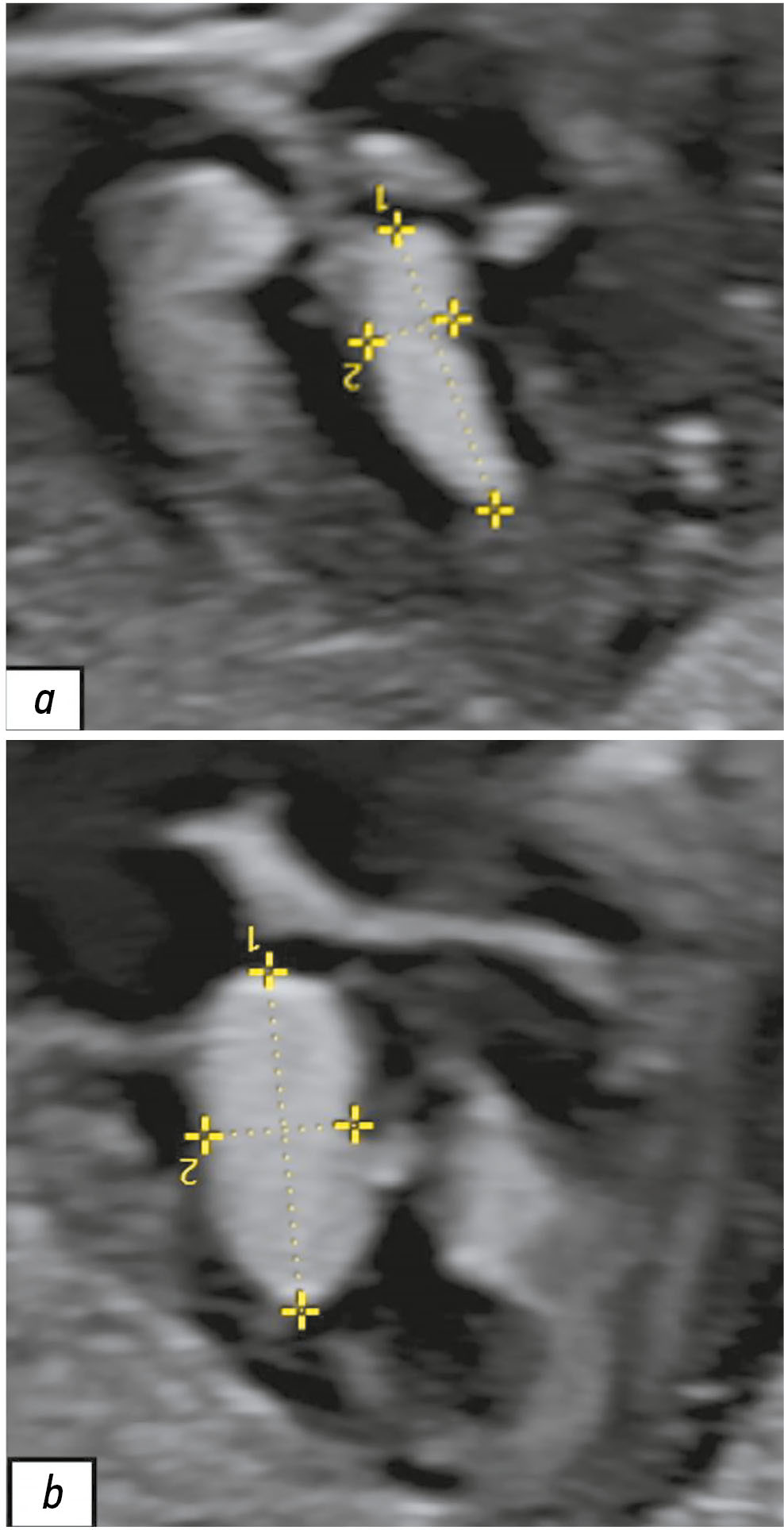
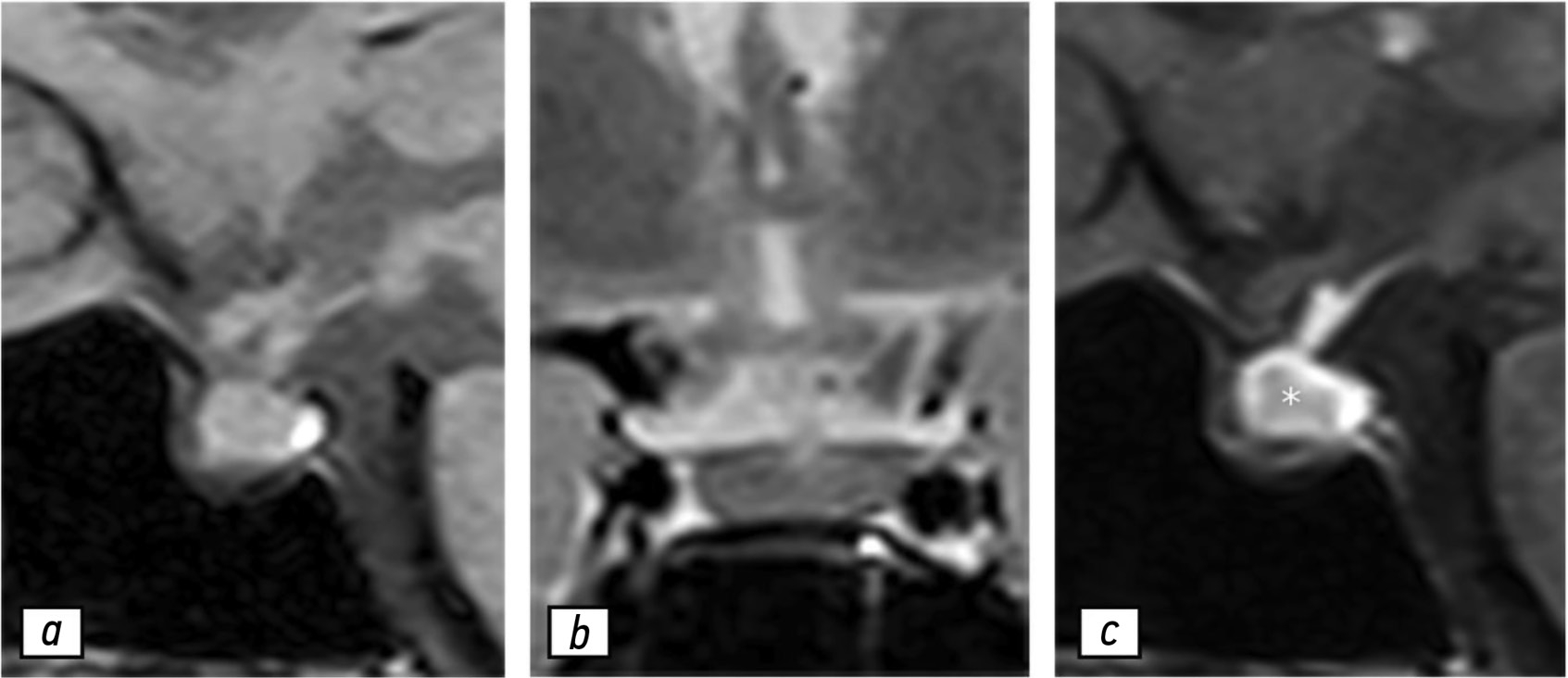
Autoimmune hypophysitis: a case of follow-up during the COVID-19 pandemic period
Abstract
Hypophysitis is a rare inflammatory disorder that affects the pituitary gland and infundibulum, stems from autoimmune, infiltrative, infectious, or unknown causes. Its clinical diagnosis can be challenging because several pituitary lesions, including adenomas and metastases, may clinically present with similar characteristics. Magnetic resonance imaging is crucial for diagnosing suspected cases of hypophysitis and categorizing them as adenohypophysitis (anterior pituitary gland involvement) or infundibulo-neurohypophysitis (pituitary stalk and posterior pituitary involvement). Hypophysitis can be categorized as primary (autoimmune) or secondary due to local lesions (e.g., granulomas, cysts, adenomas) or systemic diseases (e.g., sarcoidosis, Wegener’s granulomatosis). Different factors may have impact on clinical course of hypophysitis. Among them background treatment. These cases have not been sufficiently studied and are practically not presented in publications.
A 37-year-old female with a history of hyperprolactinemia was being treated symptomatically with cabergoline. At first magnetic resonance imaging heterogeneity of the hypophysis was revealed. In September 2021 the follow-up magnetic resonance imaging revealed an increase in the size and heterogeneity of the pituitary gland. In December 2021, the patient developed severe COVID-19-associated pneumonia and was treated with corticosteroids and oxygen support. In May 2022 magnetic resonance imaging revealed a marked increase in the size and heterogeneity of the pituitary gland. Significant clinical and radiological improvement were stated after adding prednisone (10 mg in the morning and 5 mg in the evening) to her treatment.
The patient was followed-up during the COVID-19 pandemic. The management and imaging studies of such patients may be tricky due to the effects related to COVID-19 and its treatment.
During monitoring of hypophysitis, physicians should consider the impact of COVID-19 treatment, particularly corticosteroid therapy, when evaluating the radiological changes.
 178-186
178-186