Vol 4, No 3 (2023)
- Year: 2023
- Published: 26.09.2023
- Articles: 16
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/5662
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.43
Original Study Articles
Methodology for testing and monitoring artificial intelligence-based software for medical diagnostics
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The global amount of investment in companies developing artificial intelligence (AI)-based software technologies for medical diagnostics reached $80 million in 2016, rose to $152 million in 2017, and is expected to continue growing. While software manufacturing companies should comply with existing clinical, bioethical, legal, and methodological frameworks and standards, there is a lack of uniform national and international standards and protocols for testing and monitoring AI-based software.
AIM: This objective of this study is to develop a universal methodology for testing and monitoring AI-based software for medical diagnostics, with the aim of improving its quality and implementing its integration into practical healthcare.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The research process involved an analytical phase in which a literature review was conducted on the PubMed and eLibrary databases. The practical stage included the approbation of the developed methodology within the framework of an experiment focused on the use of innovative technologies in the field of computer vision to analyze medical images and further application in the health care system of the city of Moscow.
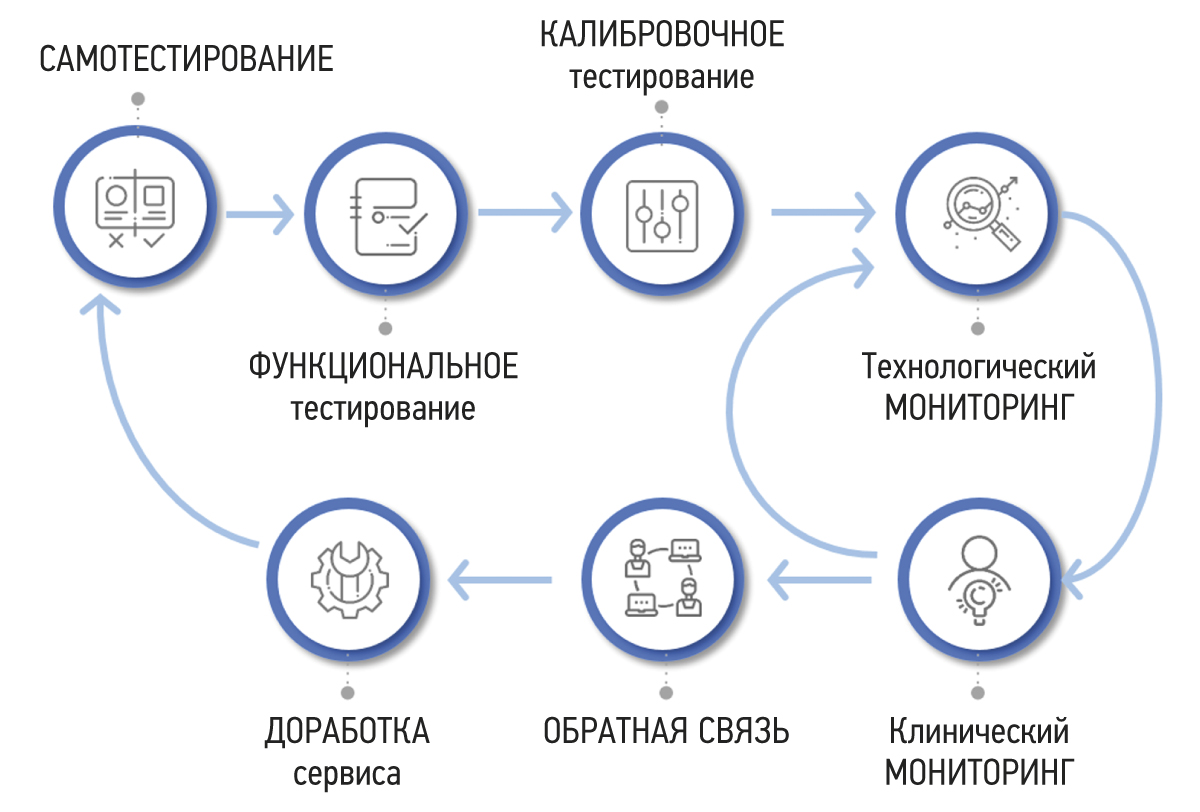
RESULTS: A methodology for testing and monitoring AI-based software for medical diagnostics has been developed, aimed at improving its quality and introducing it into practical healthcare. The methodology consists of seven stages: self-testing, functional testing, calibration testing, technological monitoring, clinical monitoring, feedback, and refinement.
CONCLUSION: Distinctive features of the methodology include its cyclical stages of monitoring and software development, leading to continuous improvement of its quality, the presence of detailed requirements for the results of the software work, and the participation of doctors in software evaluation. The methodology will allow software developers to achieve significant outcomes and demonstrate achievements across various areas. It also empowers users to make informed and confident choices among software options that have passed an independent and comprehensive quality check.
 252-267
252-267


Frequency of various cardiac complications in children with repaired tetralogy of Fallot identified by computer tomography
Abstract
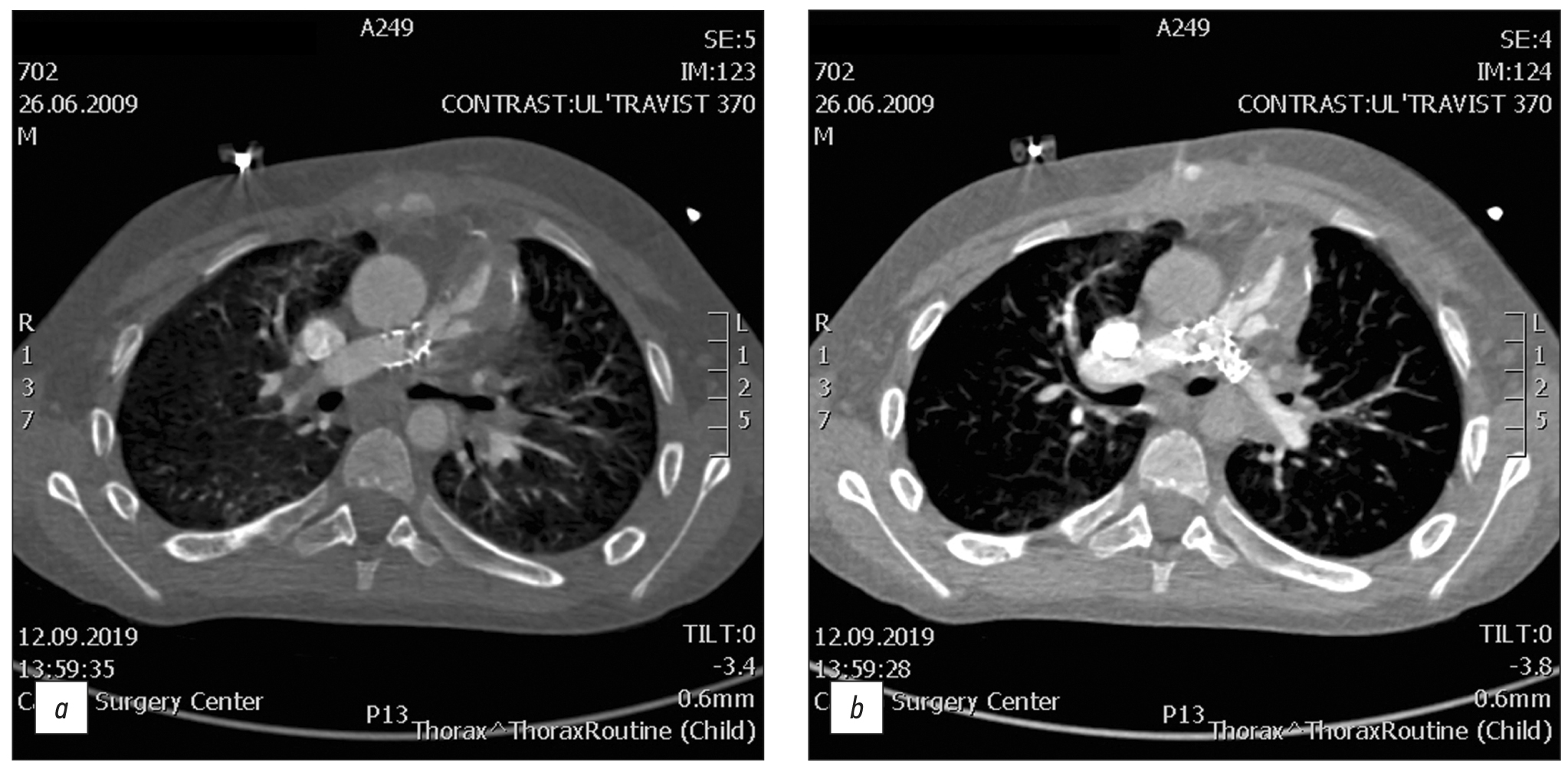
BACKGROUND: Tetralogy of Fallot represents 7–10% of all cases of congenital heart disease, as it occurs in approximately 0.5 per 1,000 live births and is the second most common form of complex congenital heart disease. Advances in diagnosis, surgical techniques, and postoperative treatment have led to an increasing number of patients reaching adulthood, with a dramatic increase in the survival rate to almost 90% at 30 years, thereby creating a need for long-term monitoring of certain anatomic parameters to identify complications in a timely manner. This study aimed to investigate the frequency of computed tomography detected complications after radical correction of Tetralogy of Fallot in pediatric patients.
AIM: to identify markers between the most frequency computed tomography detected complications after repair of Tetralogy of Fallot in pediatric patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 613 patients with Tetralogy of Fallot from October 2011 to June 2020. The study included a total of 116 patients (69 men and 47 women) who experienced complications after a repair of Tetralogy of Fallot, as identified by computed tomography. At the time of repair of Tetralogy of Fallot, the patient’s average age ranged from 10 to 36 months (mean: 12 months), average body weight was 21 kg, average height was 105.4 cm, and average body surface area was 0.74 m2. The patients’ median age at the time of the computed tomography examination was 17.5 years (age range: 7–36 years).
RESULTS: Among the 116 patients who exhibited complications after an repair of Tetralogy of Fallot, 49 had a pulmonary artery stenosis, 92 had a pulmonary artery branch stenosis (56 of them of the left main pulmonary artery branch, and 36 of them of the right main pulmonary artery branch), 8 had a right ventricular outflow tract stenosis, 32 had a ventricular septal defect, 1 had a shunt thrombosis, 12 had a postoperative deformation of the pulmonary artery, 10 exhibited a marked right ventricular dilatation, 2 had an right ventricular outflow tract aneurysm, and 6 suffered from conduit calcification and stenosis. Moreover, patients with left main pulmonary artery branch stenosis had a 6.5 times greater chance of developing an right main pulmonary artery branch stenosis in (p <0.001).
CONCLUSION: The most frequently computed tomography detected complications after a repair of Tetralogy of Fallot were pulmonary artery stenosis and pulmonary artery branch stenosis. Patients with pulmonary artery stenosis and pulmonary artery branch stenosis exhibit no significant differences in terms of age, anthropometric parameters (height, weight, and body surface area), and gender distribution in the presence or absence of different stenosis types (pulmonary artery, right main pulmonary artery branch, or left main pulmonary artery branch). However, an right main pulmonary artery branch stenosis increases the chances of developing an left main pulmonary artery branch stenosis.
 268-279
268-279


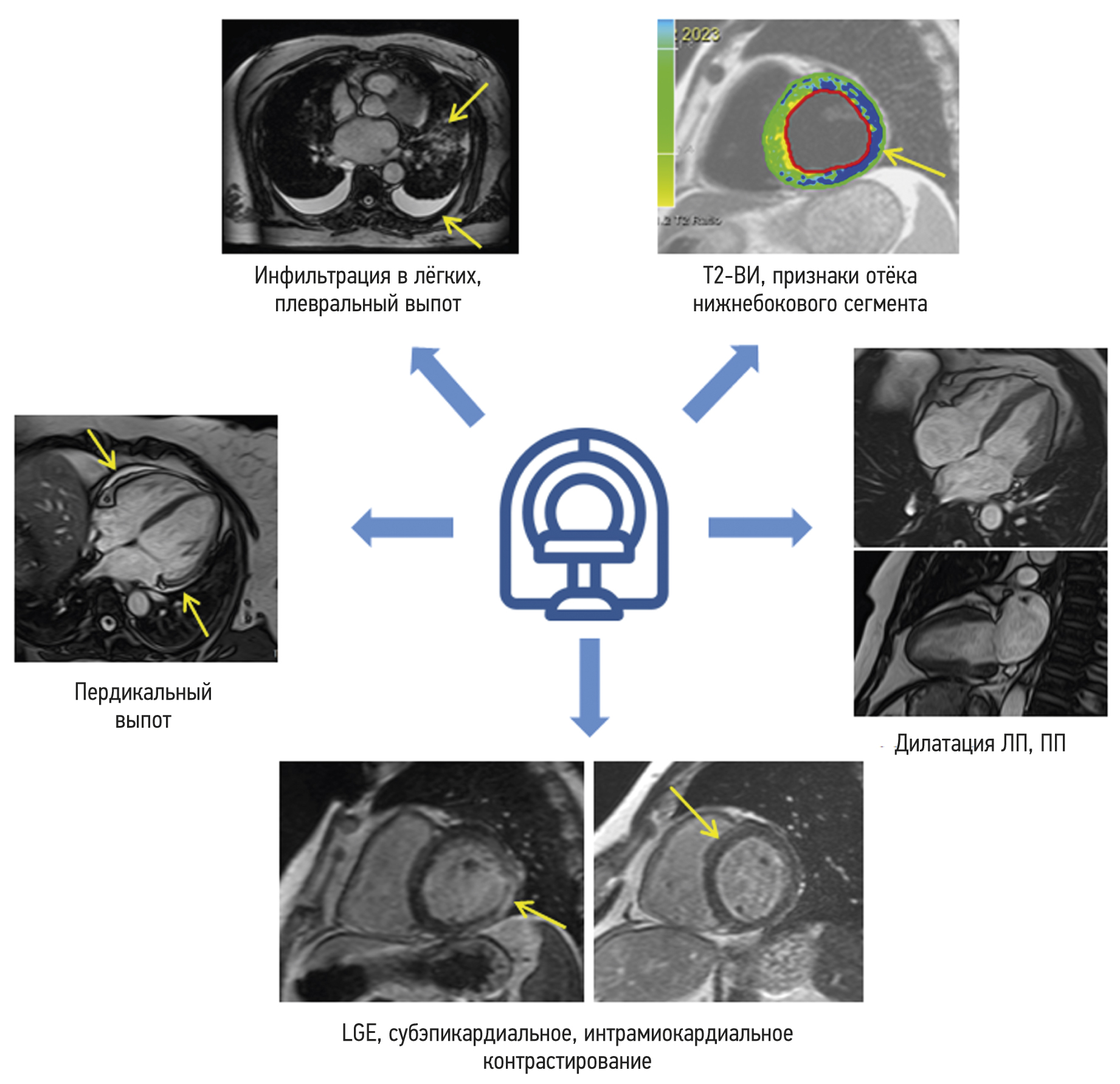
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with history of COVID-19
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Myocarditis is among the most common complications arising from coronavirus infection (COVID-19).
AIM: This study aims to find the differences in the patterns of myocardial injury between patients who had COVID-19 and those from the pre-pandemic period, as determined by contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study encompassed a retrospective analysis of 47 patients who underwent contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to rule out acute myocarditis. Group 1 comprised 34 patients with a confirmed history of COVID-19 through PCR testing (nasal and/or throat swabs), while Group 2 comprised 13 individuals who underwent contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in 2017 prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. All patients enrolled in the study had clinical manifestation of cardiac injury without signs of coronary artery disease as an underlying cause of condition.
RESULTS: The mean time from the onset of heart symptoms to the administration of contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging was 166 days. In group 1, a decrease in exercise tolerance was observed in 77% of patients, and 14 (42%), 30 (88%), and 28 (85%) of patients complained of chest pain, shortness of breath, and heart palpitations, respectively. In group 2, four patients (30%) had dyspnea, nine patients (69%) complained of chest pain, and six patients (46%) had heart palpitations and/or feeling of arrhythmia. Myocardial injury in group 1 was more generalized. The third of them had displayed preserved increased pulmonary vascularity and pleural effusion. Within group 1, men had significantly lower left ventricular ejection fraction, lower values of global longitudinal deformation, and higher values of left atrial function compared with the corresponding parameters in women. Differences in women were found only in the number of the affected segments in the left ventricular myocardium.
CONCLUSION: SARS-CoV-2 virus caused extended myocardial injury, affecting a significant number of myocardial segments. Men had more frequent postinflammatory complications, characterized by abnormal function of the left ventricle and left atrium. Obtained results require continuous efforts for further assessment of long-term consequences of previous COVID-19 to the cardiovascular system. In this regard, contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging may represent a sensitive imaging tool for the assessment of cardiac injury severity.
 280-291
280-291


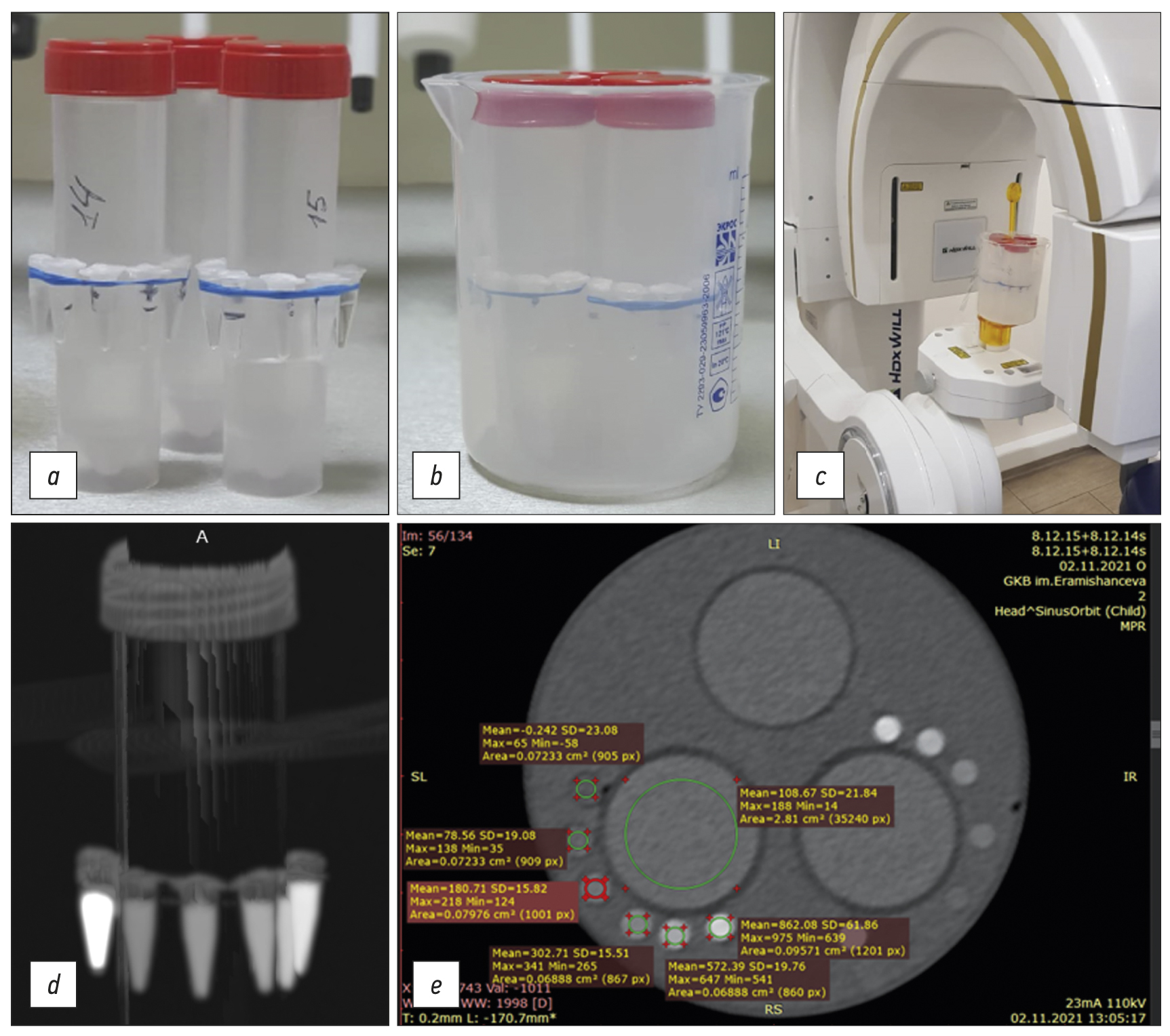
Bone mineral density radiopaque templates for cone beam computed tomography and multidetector computed tomography
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Cone beam computed tomography is widely applied for diagnostics and planning various manipulations in the maxillofacial region, for example, dental implantation. Its advantages include high spatial resolution, low radiation exposure, and cost-effectiveness. However, it has a significant drawback: the inability to determine the density of the jaw bone in Hounsfield Units (HU).
AIMS: This study aimed to develop radiopaque templates with sets of X-ray density based on potassium hydrophosphate and beta-tricalcium phosphate, to study templates on various cone beam computed tomography and multidetector computed tomography devices, and to determine a cross-calibration algorithm for assessing the bone mineral density of the jaw in HU.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The bone mineral density template comprised microtubes (0.25 ml) with potassium hydrophosphate concentrations of 49.96, 99.98, 174.99, 349.99, and 549.98 mg/ml, and a suspension of beta-tricalcium phosphate with an equivalent concentration of potassium hydrophosphate 1,506 mg/ml, designed to simulate the types of bone density according to C. Mish. The study was carried out on two multidetector computed tomography and four cone beam computed tomography machines. Cross-calibration was referred on the “standard” multidetector computed tomography 1 mode 120 kV, 200 mA.
RESULTS: There was a significant scatter of the X-ray values (HU for multidetector computed tomography and GV for cone beam computed tomography) vs. bone mineral density, with varying slopes, bias, and curve shapes. After cross-calibration, good comparability corresponding to the multidetector computed tomography 1 mode was shown. The median of the differences before cross-calibration was 160 relative units (HU, GV), after decreased by 10 times and amounted to 16 rel. units (p=0.000). The mean difference for cone beam computed tomography was significantly higher (30 rel. units) than for multidetector computed tomography (8 rel. units) (p=0.024, Mann–Whitney U test).
CONCLUSION: The developed radiopaque template enables the standardization of densitometric indicators for cone beam computed tomography and various multidetector computed tomography modes. On average, the spread after cross-calibration is reduced by 10 times, which makes it possible to classify bone tissue in HU according to C. Mish.
 292-305
292-305


Clinical Practice Guidelines
Тerminology of rectal cancer: consensus agreement of the expert working group
Abstract
Unified terminology is a necessary condition for successful interdisciplinary communication within the field of oncology. The variety of anatomical, pathomorphological, and clinical terms used in rectal cancer is often accompanied by their ambiguous interpretation both in domestic and foreign scientific literature. This not only complicates the interaction between specialists, but also complicates the comparison of the results of rectal cancer treatment obtained in different medical institutions.
Based on the analysis of recent domestic and international scientific and methodological literature on rectal cancer, the key terms used in the diagnosis and treatment planning of rectal cancer were selected, followed by a two-time online discussion of their interpretations by experts from the Russian Society of Radiologists and Therapeutic Radiation Oncologists, the Association of Oncologists of Russia, and the Russian Association of Therapeutic Radiation Oncologists until reaching consensus (≥80%) of experts on all items. Terms that fail to attain consensus were excluded in the final list.
A list of anatomical, pathomorphological, and clinical terms used in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning of rectal cancer has been compiled and, based on expert consensus, their interpretation has been determined.
A lexicon recommended in the description and formulation of the conclusion of diagnostic studies in patients with rectal cancer is proposed.
 306-321
306-321


Update of the federal governmental statistical surveillance form № 3-DOZ: “Data on patient doses from medical X-ray examinations”— Part 2 (FORM completion Recommendations)
Abstract
The form of federal governmental statistical surveillance № 3-DOZ, titled “Data on patient doses from medical X-ray examinations,” has changed significantly by the order of Rosstat N 880. In particular, the structure of the form’s has been revised: studies involving high doses were dedicated from the rest; the section on radionuclide diagnostics has been redesigned; the information on the levels of patient exposure when using individual radionuclides and in hybrid studies have been displayed; information on the number of radiological studies and collective doses for pediatric patients have been introduced; and the number of studies for which typical (average) effective doses of patients are presented has been reduced. The structure of the updated form № 3-DOZ is presented within the framework of this work.
In this article, recommendations for filling out № 3-DOZ have been developed in order to increase the reliability of the data provided and reduce the number of procedural errors.
This work is a continuation of the article Vodovatov A.V., Chipiga L.A., Bratilova A.A., Druzhinina P.S., Shatskiy I.G., Petryakova A.V., Sarycheva S.S., Biblin A.M., Akhmatdinov R.R., Kapyrina Yu.N., Soldatov I.V., Puzyrev V.G., and Ryzhov S.A. “Update of the federal governmental statistical surveillance form № 3-DOZ “Data on patient doses from medical X-ray examinations”. Perquisites for the update, published in the journal Radiatsionnaya Gygiena (2023. Vol. 16, N 2. P. 126–136. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21514/1998-426X-2023-16-2-126-136).
 322-339
322-339


Systematic reviews
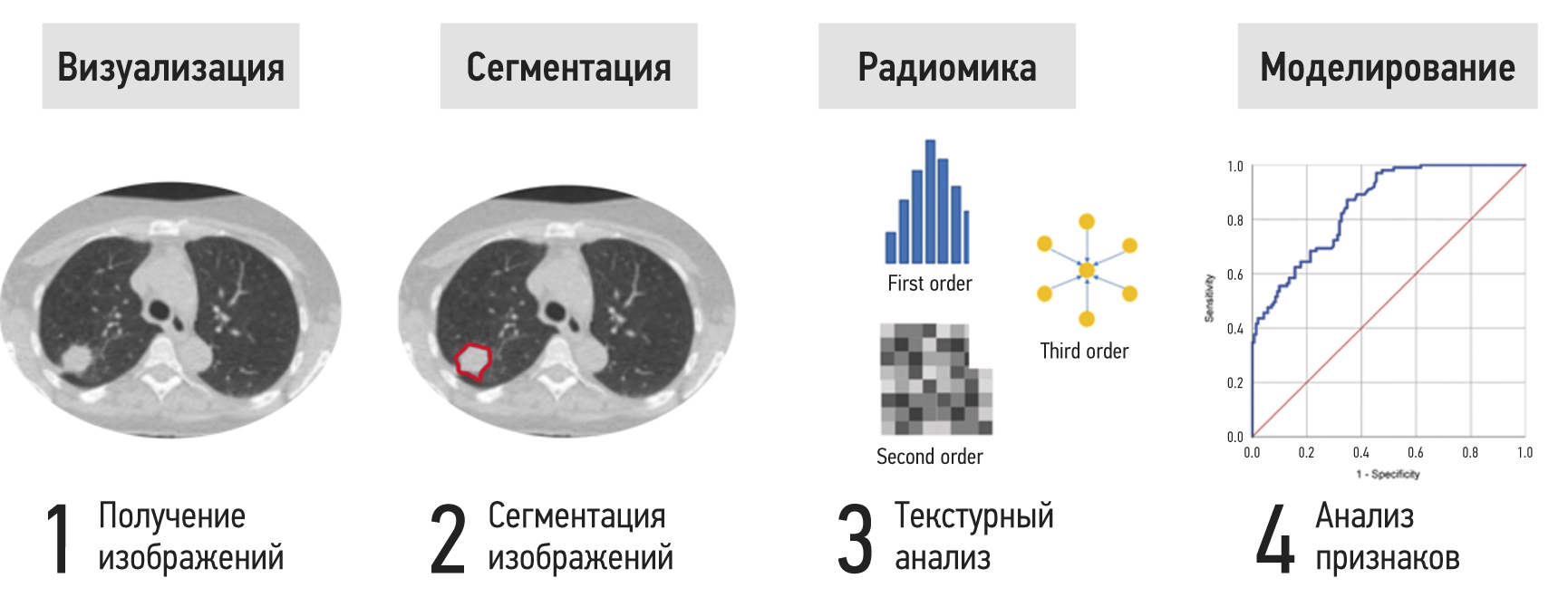
Dosiomics in the analysis of medical images and prospects for its use in clinical practice
Abstract
BACKGROUND: In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the number of articles using the term “dosiomics”. However, there are no literature reviews on this topic in the Russian language.
AIM: This study aims to describe the basic principles of dosiomics as a derivative of radiomics and to analyze studies devoted to assessing the possibilities of its application in clinical practice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A systematic literature search was performed in the PubMed database using the search query “dosiomics OR dosiomic”, and in the eLibrary database using the search query “dosiomics”. By April 2023, 43 foreign articles and 1 Russian article had been published.
RESULTS: The analysis encompassed 43 foreign studies investigating the use of dosiomics in clinical practice, alongside one Russian article that provided a definition of the term “dosiomics”. The analyzed papers were divided into three groups according to their subject matter, and two tables describing the results of 27 studies on the prediction of clinical outcomes were created.
CONCLUSION: Currently, dosiomics is a new and promising derivative of radiomics used in the textural analysis of medical images associated with radiation treatment of cancer patients. Dosiomics can contribute to the development of a more personalized approach to the planning of radiotherapy, the prediction of radiation damage of normal tissues, and the diagnosis of recurrence.
 340-355
340-355


Reviews
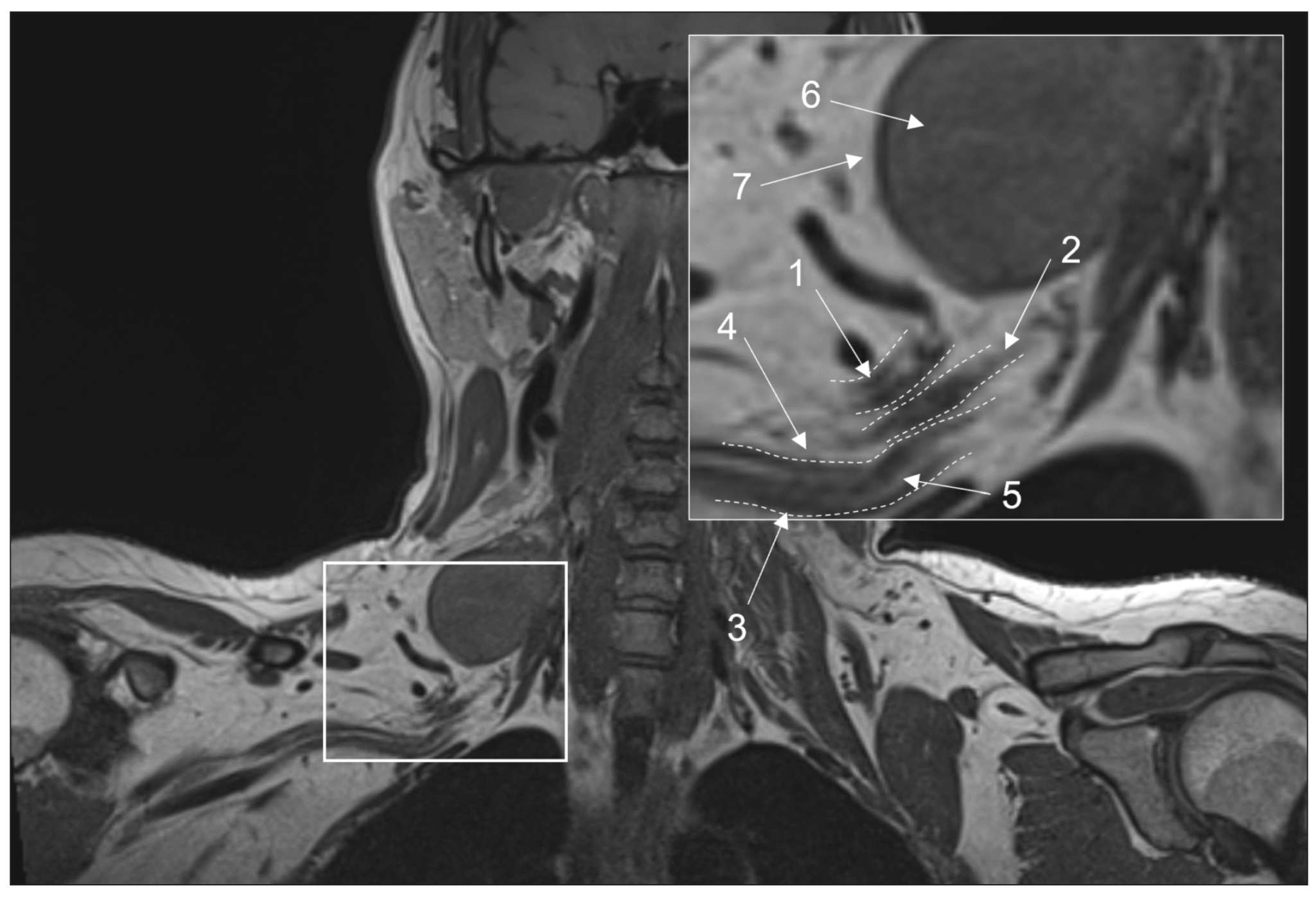
Conventional magnetic resonance imaging of peripheral nerves: MR-neurography
Abstract
Peripheral neuropathy is known to be one of the most common neurological disorders. Despite the great diagnostic value of electroneuromyography and ultrasound, addressing the diagnostics and differential diagnostics of peripheral nerve diseases of different origin could be challenging. In recent years, magnetic resonance tomography has been increasingly used for evaluating cases of suspected or established peripheral neuropathy with excellent results.
This manuscript mainly deals with the advantages and limitations of the aforementioned diagnostic instruments, technical considerations according to different anatomy of peripheral nerves, along with state-of-the-art technical decisions, frequently used magnetic resonance imaging sequences and their diagnostic value based on own observation, and recommendations for contrast enhancement use and different methods of fat suppression.
Currently, there is practically no standardized description of normal magnetic resonance imaging features of peripheral nerves, as well as their changes in different diseases. The evaluation of images is mainly based on the radiologist experience, which obviously decreases method’s diagnostic value. Studies of large numbers involving healthy volunteers and patients with peripheral neuropathies of different origin are required to address this issue.
 356-368
356-368


Postmortem radiology studies in global and national healthcare: literature analysis and perspectives of Russian specialists
Abstract
Despite the significant importance of autopsies for determining the cause of death and the evaluating the effectiveness of treatments, there is a progressive decrease in their number across all countries. At the same time, there is an active introduction of postmortem radiological studies to analyze the bodies of deceased patients.
The article presents literature analysis summarizing the results of surveys from foreign specialists, as well as the opinions of Russian specialists, regarding the possibilities and features of postmortem radiological studies, mainly focusing on deceased newborns and infants. It is noted that postmortem radiological studies are carried out as part of both pathoanatomical autopsy and forensic medical examination. Postmortem computed tomography in cases of violent death and postmortem magnetic resonance imaging in cases of death from diseases were performed more often. General clinical equipment located in clinical radiology departments was more frequently used than those located in the mortuary, pathology department, or forensic facility. The analysis of the results of postmortem radiological examinations was predominantly carried out by radiologists, with a joint analysis involving a radiologist and a pathologist being less common. It is emphasized that in the Russian Federation, postmortem radiological studies are mostly of a single nature. According to Russian researchers, in the current era of advancing personalized medicine, radiation techniques, and information technologies, there arises a need to use postmortem radiological studies to objectify and improve the accuracy of traditional autopsies. Postmortem radiological studies, which are objective operator-independent methods of examining the bodies of dead people, should be considered as a highly effective stage of pathology and, especially, forensic autopsy.
 369-383
369-383


Case reports
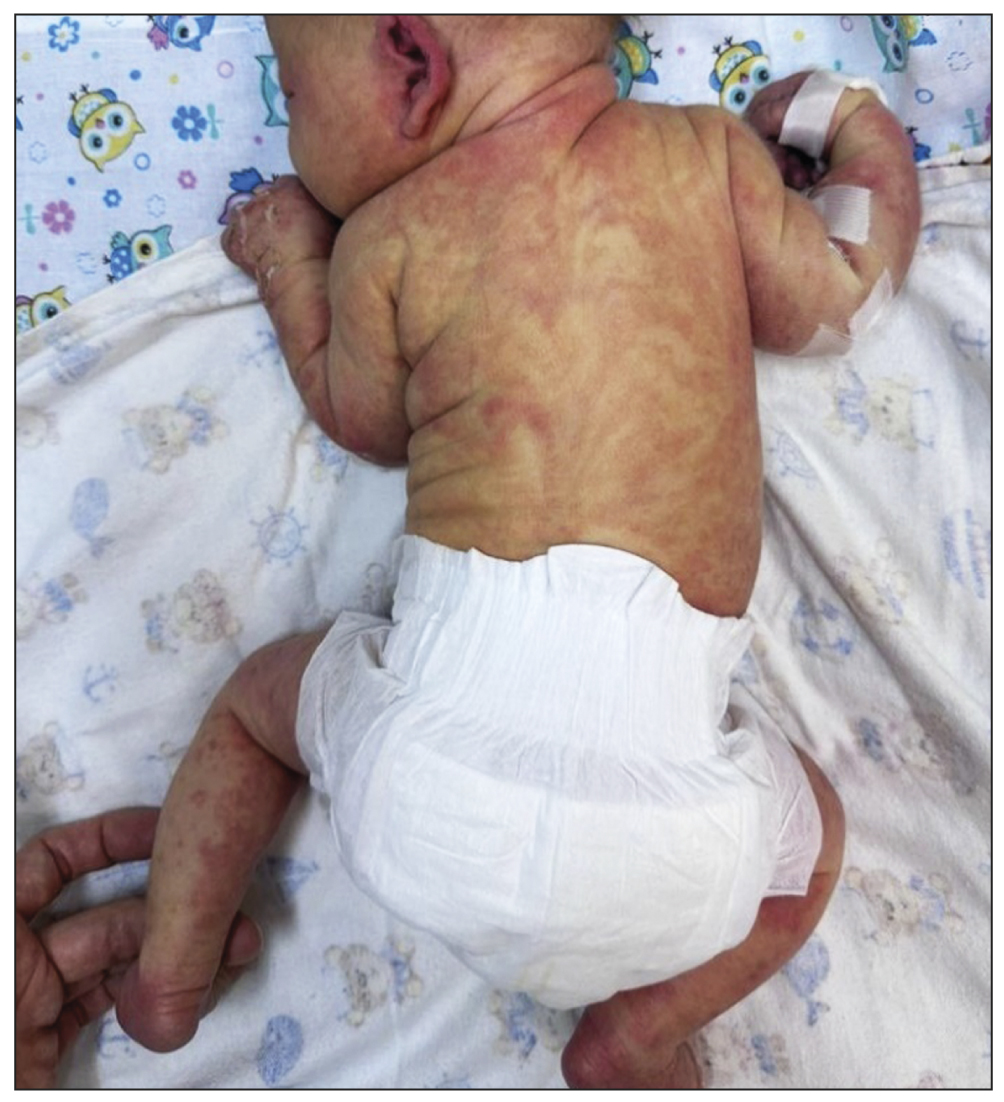
Magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing a rare disease: incontinentia pigmenti (Bloch–Sulzberger syndrome) on the example of a clinical case
Abstract
Incontinentia pigmenti, also known as Bloch–Sulzberger syndrome, is a rare hereditary disease characterized by typical skin rashes and involvement of other organs and systems. Magnetic resonance imaging stands as the primary method for visualizing the structural pathology of the brain and predicting neurological manifestations in an affected child.
Diagnosing incontinentia pigmenti predominantly falls within the domain of dermatologists; verification is performed by molecular genetic analysis of the IKBKG gene. This study involved magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in a patient with skin rashes, characteristic of Bloch–Sulzberger syndrome, and deletion in the IKBKG gene, where numerous foci of ischemia, hemorrhages, and lesions of the tracts were detected.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in patients with Bloch–Sulzberger syndrome is used to evaluate the severity of damage to the brain substance, which makes it possible to explain the cause of neurological symptoms and correct habilitation, as well as predict the development of the child.
 384-392
384-392


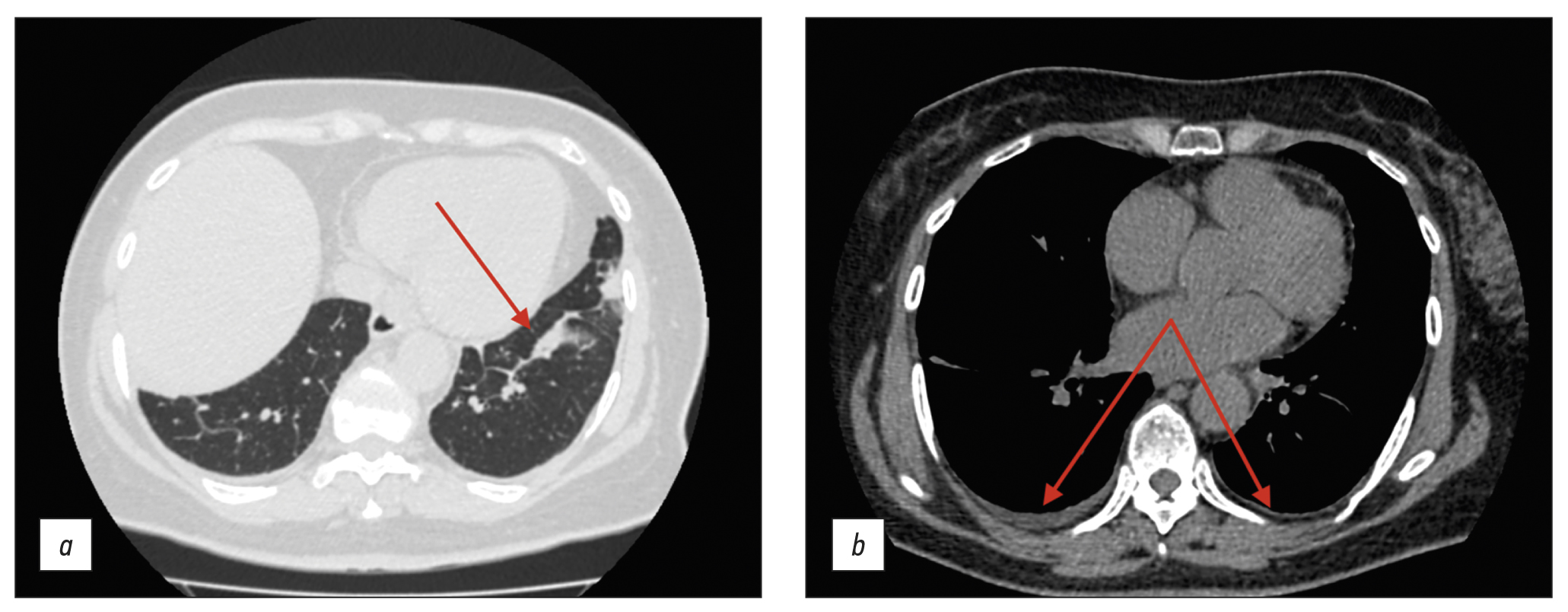
Computed tomography in the diagnosis of fever of unknown origin: A case report
Abstract
Fever of unknown origin can be a symptom of at least 200 diseases. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography, although highly informative, may not be readily available as an imaging tool. We present a clinical case of giant cell arteritis where computed tomography played a key role in arriving at a diagnosis.
A 61-year-old woman presented to the hospital with a nocturnal fever up to 39.5°С, accompanied by chest and scapular pain, and substantial weight loss (10 kg over 3 months). Lymphoproliferative and infectious diseases were excluded. Baseline colonoscopy had revealed erosions in the colonic mucosa, leading to a preliminary diagnosis of ulcerative colitis, and subsequently, the patient was admitted to the gastroenterology department. Follow-up colonoscopy had excluded this diagnosis. Additional imaging via chest and abdominal computed tomography scan revealed wall thickening of aorta and its branches with subtle contrast enhancement.
Conditions, such as tuberculous aortoarteritis and syphilitic aortitis, were excluded. The patient was diagnosed with giant cell arteritis involving brachiocephalic trunk, subclavian arteries, and celiac trunk. Prednisolone was administered with subsequent reduction in symptoms.
Although computed tomography may not be regarded as the gold standard for the differential diagnosis of fever of unknown origin, this case underscores its valuable contribution in establishing a definitive diagnosis.
 393-402
393-402


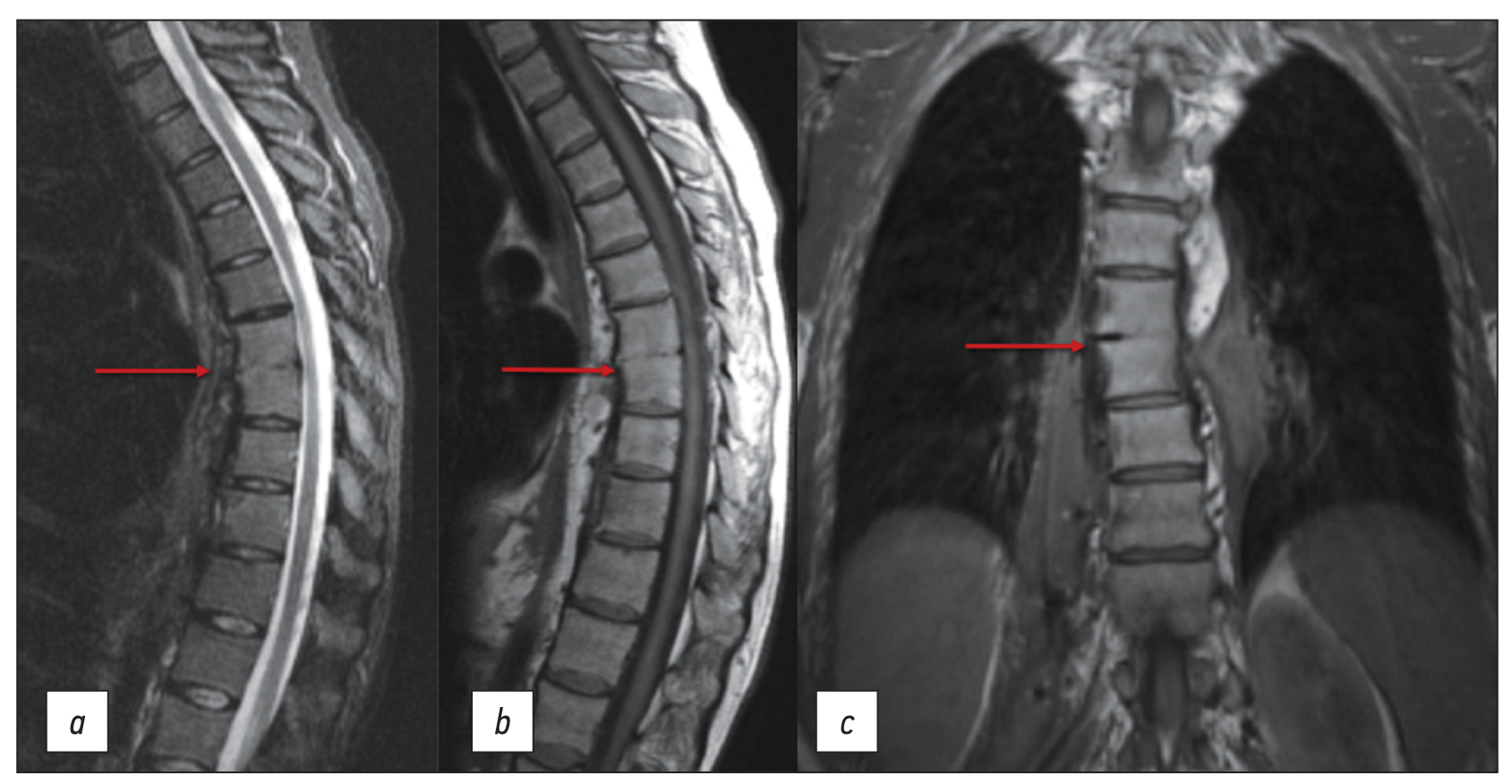
Chronic esophageal fistula as a rare cause of secondary osteomyelitis of the thoracic spine
Abstract
Infectious diseases affecting the spine are inflammatory destructive diseases that involved the organ and its structural elements as a result of infection by hematogenic, lymphogenic, or contact pathways, including may be a complication of surgical intervention. In arriving at an accurate diagnosis, it is extremely important to evaluate the anamnesis, the clinical picture, as well as the data of laboratory studies and radiation diagnostics in the aggregate.
This article presents a clinical case with the development of secondary ThVII–ThVIII vertebral spondylitis due to esophageal fistula. At the initial diagnosis, spondylitis was associated with spinal anesthesia performed six months prior to onset of the disease, as there was a fistulous defect on the skin in the lumbar region. Consequently, surgical interventions were performed three times in a surgical hospital at the place of residence. The data from the endoscopic examination, as well as the patient’s complaints regarding the relationship between meals, the appearance of pain, and the nature of the discharge from the fistula were not taken into account by doctors initially. With the help of an additional examination, including computed tomography of the esophagus with oral contrast and computed tomography fistulography, the main diagnosis was esophageal fistula. Thoracic spondylitis was only a secondary complication.
Thus, the final diagnosis of back pain and fistula in the lumbar region should be formulated after differential diagnosis with alternative diseases of the spine.
 403-410
403-410


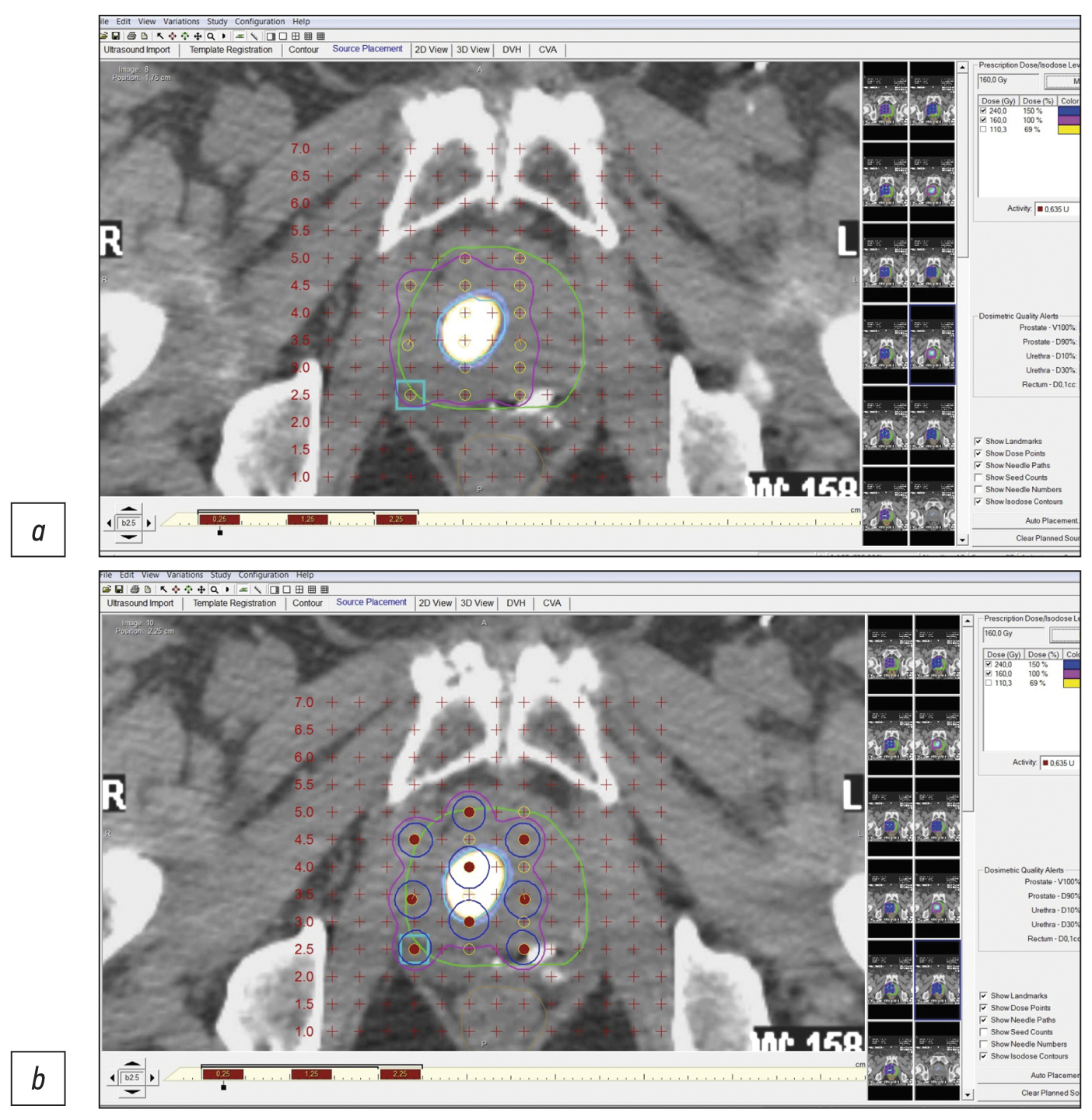
Precision low-dose brachytherapy of prostate cancer under PSMA-receptor molecular visualization
Abstract
Brachytherapy with implantation of micro sources based on isotope 125I is a preferred treatment for localized prostate cancer without signs of germination of the gland capsule and in the absence of signs of metastases (stage cT1-T23aN0M0). Structural imaging methods (ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging) do not have high specificity in the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer. Hybrid technologies of radiation imaging (single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography, positron emission tomography/computed tomography, and positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging) combine the advantages of high sensitivity of cross-sectional structural imaging methods (computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) and high specificity of molecular imaging methods (single-photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography) with tumorotropic radiopharmaceuticals. In this original clinical study, based on seven observations of localized prostate cancer (Gleason 6–7), it was shown that the precision of low-dose brachytherapy using 125I micro sources of localized prostate carcinomas, along with targeted biopsy, can be increased using hybrid methods of PSMA-receptor molecular imaging (single-photon emission computed tomography/ computed tomography, positron emission tomography/ computed tomography). The single-photon emission computed tomography/ computed tomography method is more accessible than positron emission tomography/ computed tomography. Moreover, when coupled with cold kits (HYNIC-PSMA), it allows research within any radioisotope diagnostics laboratory equipped with single-photon emission computed tomography/ computed tomography. The innovative technology of PSMA-navigation biopsy and brachytherapy, under the control of hybrid molecular imaging, can be used in primary and recurrent cases of localized prostate cancer, increases the accuracy and reduces the traumatic nature of procedures, and increases the medical and economic efficiency of low-dose brachytherapy with 125I micro sources. Further research is needed to improve the technology and evaluate its long-term results.
 411-426
411-426


Correspondence
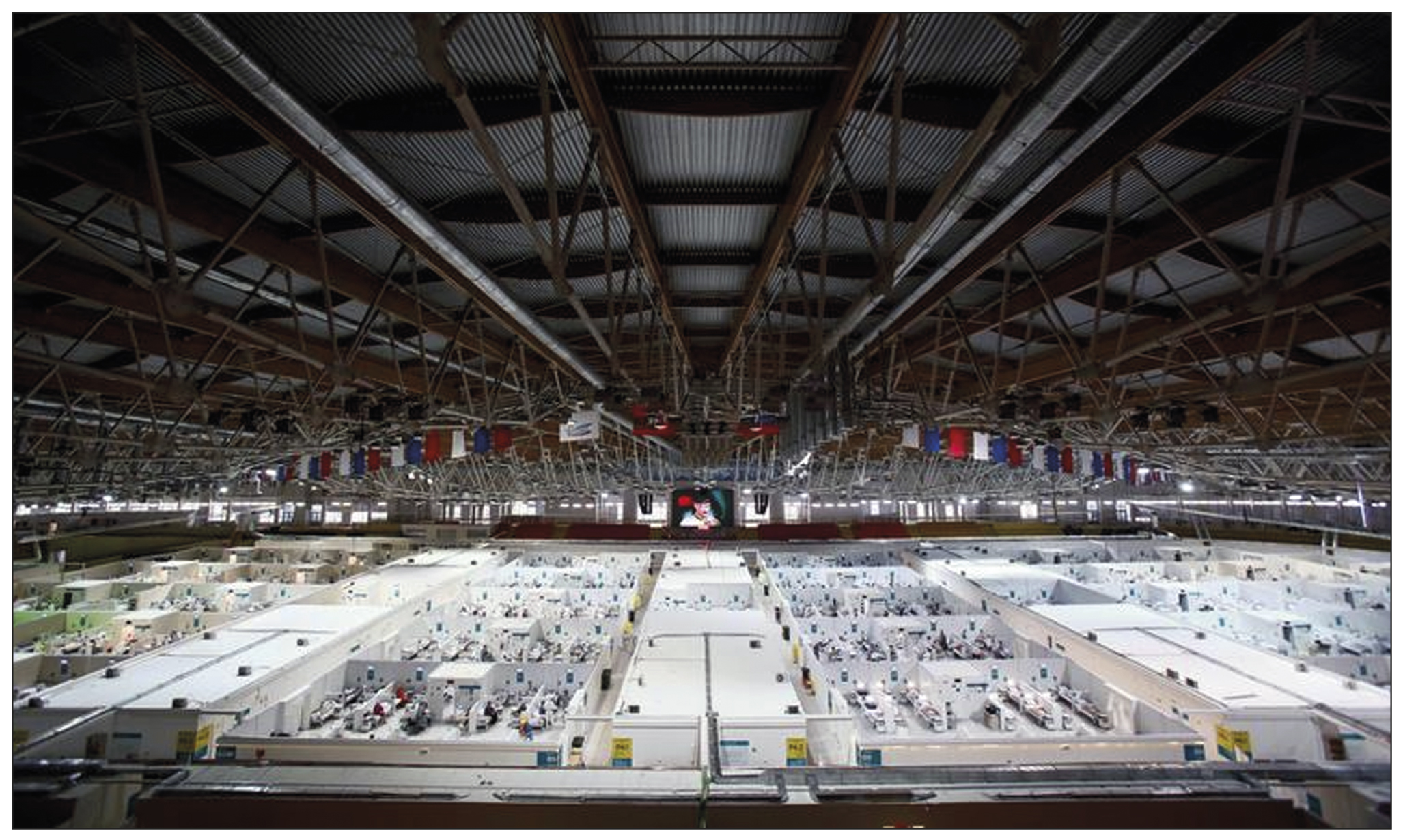
Using a mobile computer tomography scanner in a field hospital setting to manage patients with COVID-19
Abstract
The global outbreak of COVID-19 has posed unprecedented challenges to healthcare systems worldwide. Healthcare administrators had to make quick and effective decisions to ensure high quality of medical care standards in new conditions. The need to form a reserve bed fund during the pandemic was due to the high load on city hospitals in Moscow. Due to this fact, temporary reserved hospitals for COVID-19 patients were organized in non-core facilities, such as ice arenas, shopping malls, and exhibition pavilions. This urgency prompted a search for solutions that could provide the necessary level of diagnosis and treatment appropriate to specialized medical facility. Given the technical and time constraints associated with the installation of a fixed computer tomographic scanner, the deployment of mobile computer tomographic scanners emerged as a viable option.
The study aims to share insights gained from using a mobile computer tomographic scanner within a temporary backup hospital setting to treating patients with COVID-19 coronavirus infection. The paper discusses the features, advantages, and disadvantages of mobile computer tomography. It also presents hardware and control room layouts, along with the placement options for the computer tomography device. The research includes the results of dosimetry studies and provides a clinical assessment of the applicability of this type of diagnostic devices.
 427-438
427-438


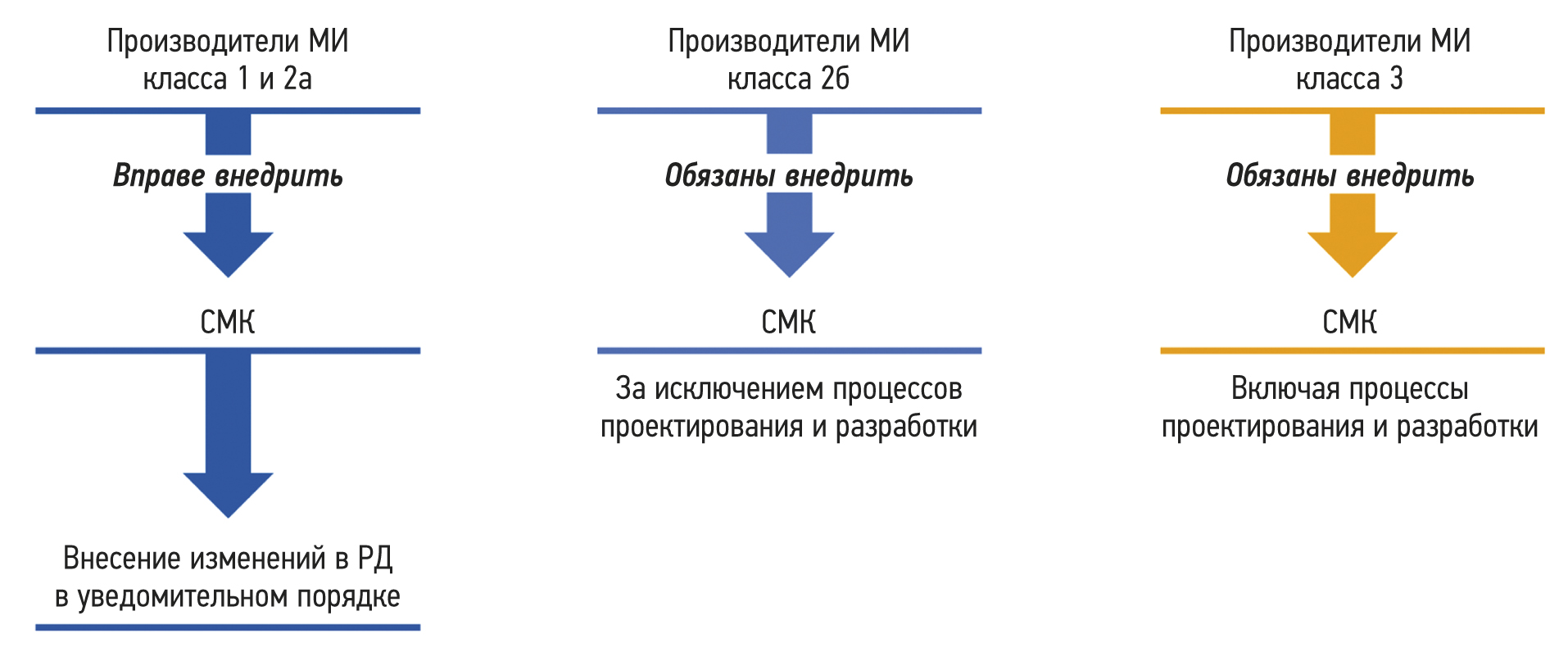
Quality management system: A tool for the development of the organization or an additional burden?
Abstract
A quality management system constitutes one of the organization’s management systems that provides for the selection of a set of processes in the organization’s activities designed to ensure the stable quality of products and services provided.
The growth of global industrial production has underscored the need for the creation of such production and management systems. These systems are designed to ensure that enterprises remains prepared to meet the constantly changing consumer value of manufactured products in accordance with consumer requirements, as well as the satisfaction of consumers themselves. As a result, attention began to focus on the production processes implemented within the organization when creating products. Regarding the production of medical devices, a quality management system can be defined as an organizational structure encompassing its functions, procedures, processes, and resources necessary for the coordinated direction and management of a manufacturing organization with respect to the quality of medical products.
The article reflects the principles of the quality management system and management processes. Noteworthy emphasis is placed on the features of quality management systems for medical devices, including the features of the quality management system for software that is a medical device. Furthermore, the conditions under which the quality management system becomes a tool for ensuring the sustainable development of the organization are noted.
 439-447
439-447


Corrigendum
Erratum in “Volumetry versus linear diameter lung nodule measurement: an ultra-low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening study” (doi: 10.17816/DD117481)
Abstract
In the article "Volumetry versus linear diameter lung nodule measurement: an ultra-low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening study" published in Digital Diagnostics journal Volume 4 Issue 1 in 2023 (doi: 10.17816/DD117481) contained an error in the paragraph with data of funding sources for the study.
At the request of the authors’ team, the error was eliminated, the original version of the published article and the information on the journal’s site was replaced with the corrected one.
Correct text of the changed: This paper was prepared by a group of authors as part of the research work (USIS No. 123031400009-1) in accordance with the Order issued by the Moscow Health Care Department No. 1196 dated December 21, 2022.
The authors and the publisher apologize to readers for the published error and express their confidence that this mistake could not significantly affect the perception and interpretation of the results of the study described in the text of the article.
 448-450
448-450