Vol 5, No 3 (2024)
- Year: 2024
- Published: 04.12.2024
- Articles: 21
- URL: https://jdigitaldiagnostics.com/DD/issue/view/9838
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD.53
Full Issue
Original Study Articles
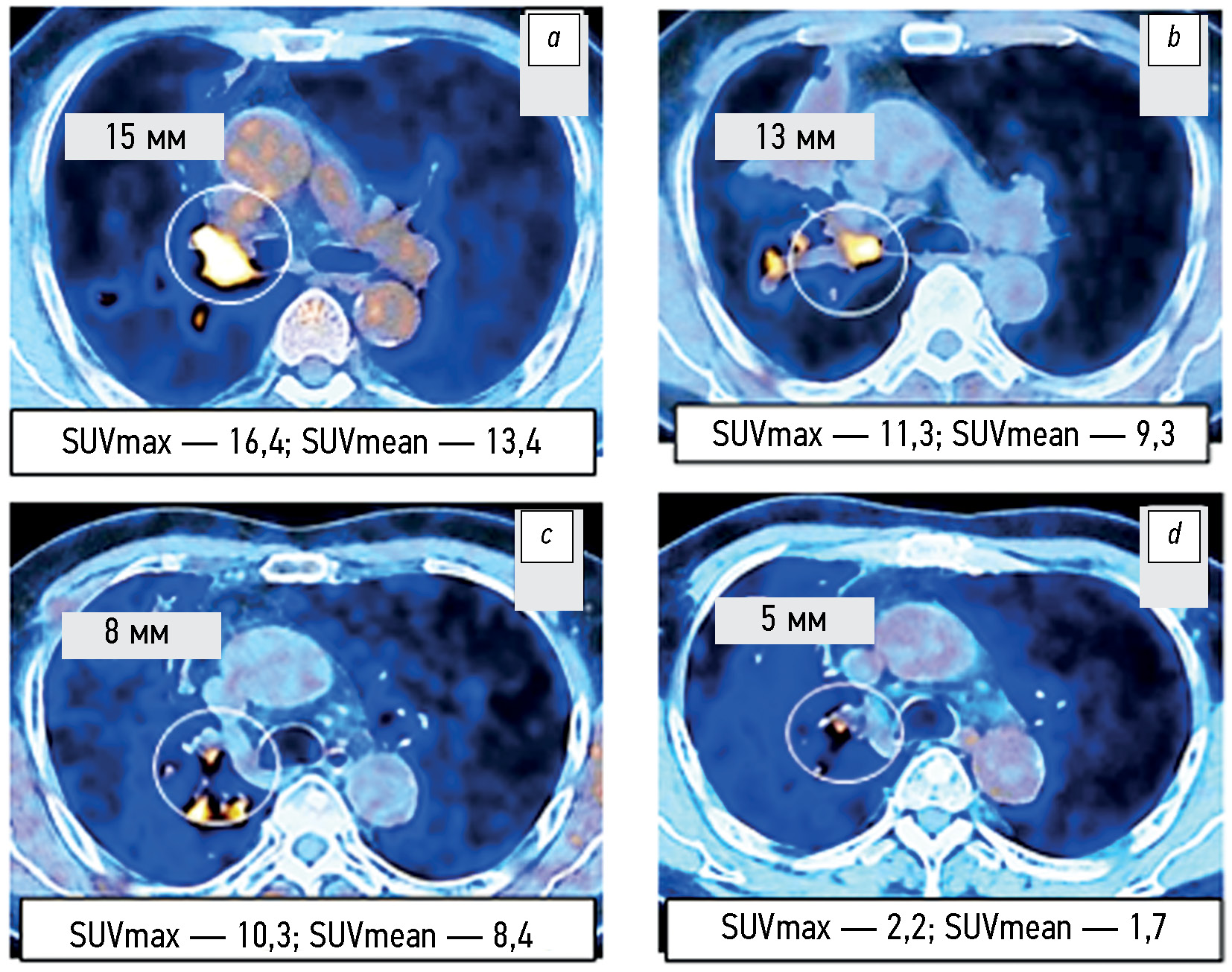
Capabilities of positron emission tomography/computed tomography in a comparative assessment of the effect of various targeted therapy options in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
BACKGROUND: No publications in the Russian medical literature have examined the potential of positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography through a comparative evaluation of the effect of various targeted therapies involving tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and mutations in the EGFR gene.
AIM: To explore the capabilities of positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography based on the RECIST 1.1 criteria and changes in SUVmax and SUVmean metabolic parameters for the comparative assessment of the tumor response to targeted monotherapy and combination therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The 2019–2022 examination records of positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) in 105 patients with non-small cell lung cancer were analyzed, including 75 patients with EGFR-activating mutation. The radiation exposure was adjusted individually and ranged from 45 to 90 mSv. The volume activity of the 18F-FDG radiopharmaceutical was 260–500 MBq. The change in the total largest diameters of the target lesions and SUVmax and SUVmean metabolic parameters were assessed before treatment initiation and 1.5–2.0 months after it. The follow-up duration for the changes in positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography findings in 17 patients with non-small cell lung cancer was at least 12 months.
RESULTS: According to positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography images and SUVmax and SUVmean changes, disease progression was significantly less common (p = 0.043 and p =0.029) in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer from Groups 2 and 3 who received combination therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and bevacizumab or chemotherapy than in Group 1 and control group (4.2% vs. 20.0%–21.8%). An insignificant trend (p =0.092) to a higher partial response to therapy (58.3% vs. 40.0%) was noted. Similar changes in the total largest diameters of the target lesions at the early stage of therapy appeared to be not significant (p =0.187). Within the long-term follow-up of some patients with non-small cell lung cancer, in at least 50% of cases, changes in the total largest lesion diameters are consistent with the relevant SUVmax and SUVmean alterations found in the first control study.
CONCLUSIONS: Based on the positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography data and alterations in SUVmax and SUVmean metabolic parameters, the early tumor response to combined therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and bevacizumab or chemotherapy compared with targeted monotherapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors or chemotherapy of the control group was characterized by a significantly lower rate of metabolic disease progression, although a similar tendency of the change in the total largest diameters of target lesions according to RECIST 1.1. was not significant. Changes in SUVmax and SUVmean metabolic parameters at the early stage of therapy are at least 50% faster than similar changes in the total largest diameters of the target lesions, which can be used for the timely identification of patients with a high risk of further progression as determined by RECIST 1.1.
 394-406
394-406


Limitations of using artificial intelligence services to analyze chest x-ray imaging
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Chest X-ray examination is one of the first radiology areas that started applying artificial intelligence, and it is still used to the present. However, when interpreting X-ray scans using artificial intelligence, radiologists still experience several routine restrictions that should be considered in issuing a medical report and require the attention of artificial intelligence developers to further improve the algorithms and increase their efficiency.
AIM: To identify restrictions of artificial intelligence services for analyzing chest X-ray images and assesses the clinical significance of these restrictions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective analysis was performed for 155 cases of discrepancies between the conclusions of artificial intelligence services and medical reports when analyzing chest X-ray images. All cases included in the study were obtained from the Unified Radiological Information Service of the Unified Medical Information and Analytical System of Moscow.
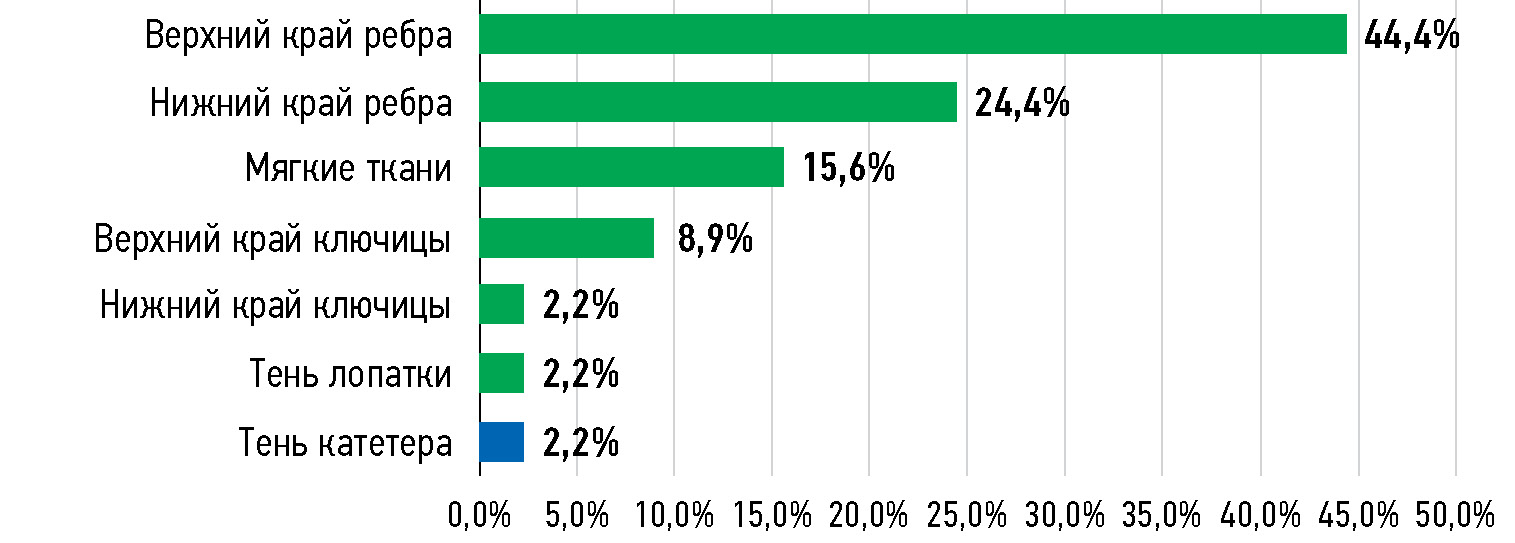
RESULTS: Of the 155 analyzed difference cases, 48 (31.0%) were false-positive and 78 (50.3%) were false-negative cases. The remaining 29 (18.7%) cases were removed from further studies because they were true positive (27) or true negative (2) in the expert review. Most (93.8%) of the 48 false-positive cases were due to the artificial intelligence service mistaking normal chest anatomy (97.8% of cases) or catheter shadow (2.2% of cases) for pneumothorax signs. Overlooked clinically significant pathologies accounted for 22.0% of false-negative scans. Nearly half of these cases (44.4%) were overlooked lung nodules. Lung calcifications (60.9%) were the most common clinically insignificant pathology.
CONCLUSIONS: Artificial intelligence services demonstrate a tendency toward over diagnosis. All false-positive cases were associated with erroneous detection of clinically significant pathology: pneumothorax, lung nodules, and pulmonary consolidation. Among false-negative cases, the rate of overlooked clinically significant pathology was low, which accounted for less than one-fourth.
 407-420
407-420


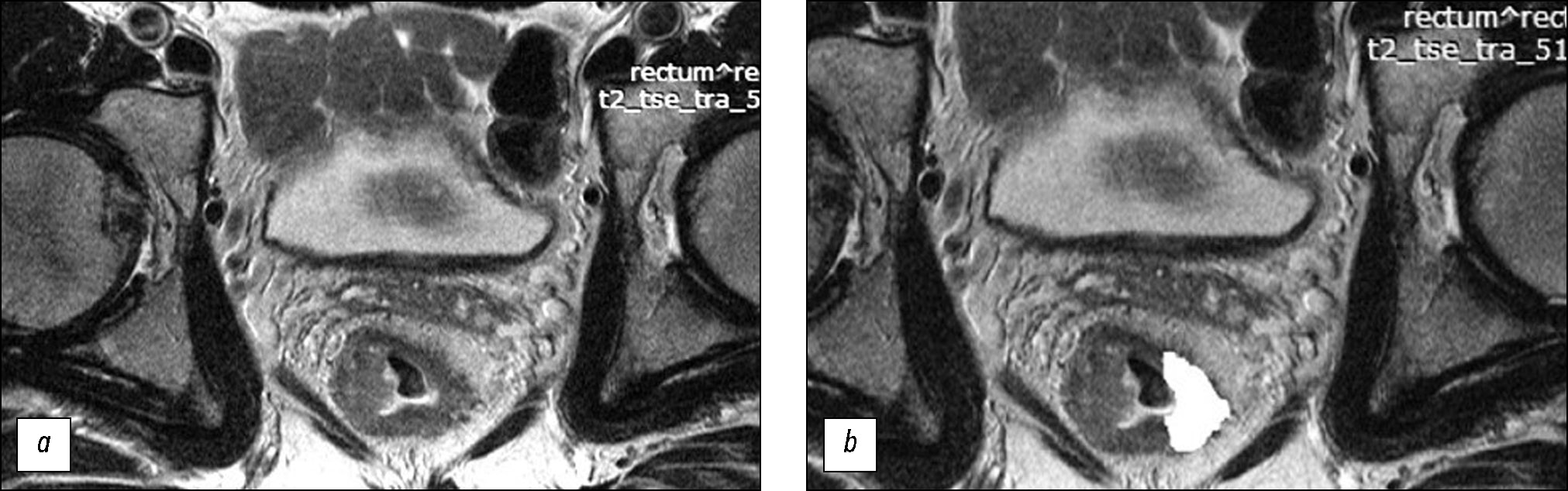
Prediction of the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer based on a texture analysis of T2-weighted magnetic resonance tumor image obtained at primary staging
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Recently, significant efforts have been undertaken to find potential noninvasive biomarkers for predicting the response of locally advanced rectal cancer to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.
AIM: To assess the texture characteristics of locally advanced rectal cancer in primary T2-weighted imaging (T2-WI) as a potential predictor for the efficacy of standard neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and develop a prediction system for the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy based on them.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The retrospective study enrolled 82 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer who received combination treatment with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Patient data were divided into the training (n=58) and control (n=24) sets. For texture analysis, primary high-resolution T2-WI at the level of the tumor center, oriented perpendicular to the intestinal wall, was used. The texture analysis was performed by second-order statistics based on the gray-level co-occurrence matrices using MAZDA ver. 4.6 featuring the calculation of 11 texture parameters. In the training set, based on the morphological assessment of surgical specimens, significantly different texture analysis parameters were found for two groups of patients: neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy responders (good prognosis group) and nonresponders (poor prognosis group). Accordingly, a scoring system was created for assessing the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. The system was tested on the control set, and diagnostic efficacy parameters were determined.
RESULTS: In the training set, the good and poor prognosis groups differed significantly in five texture parameters: AngScMom (p=0.021), SumofSqs (p=0.003), SumEntrp (p=0.003), Entropy (p=0.038), and SumVarnc (p=0.015), for which the cutoff points were found. These parameters were applied to create the scoring system (excluding the Entropy parameter, which had a strong direct correlation with SumEntrp and the lowest area under the curve, and SumofSqs, which had low reproducibility). The diagnostic efficiency of the scoring system for predicting the response had sensitivity, specificity, positive-predictive value, and negative- predictive value of 72%, 69%, 70%, and 71% for the training set and 80%, 64%, 62%, and 82% for the control set, respectively. The areas under the ROC curve were 0.77 and 0.72 for the training and control sets, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS: Texture analysis of the primary T2-WI of tumors in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer allows for predicting the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with moderate diagnostic efficiency. The results suggest good prospects for further research in this area.
 421-435
421-435


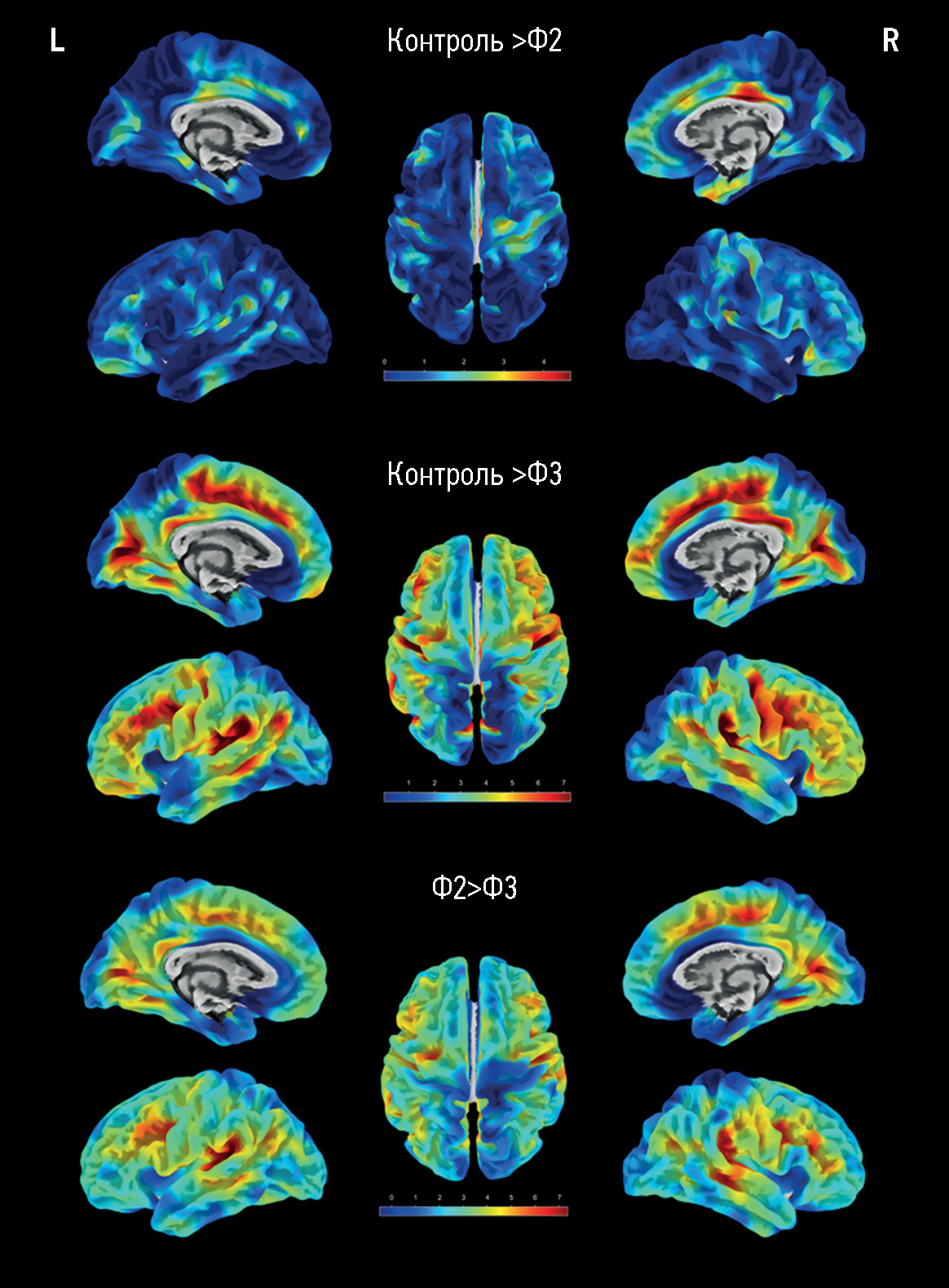
Surface-based morphometry of the cerebral cortex in cognitive impairments of varying severity in patients with age-related cerebral small vessel disease
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Analysis of structural magnetic resonance images is essential to assessing the main substrate of cognitive impairment in sporadic age-related cerebral small vessel disease, accounting for up to 45% of all dementia cases. Variations in the results of magnetic resonance morphometry applied in cerebral small vessel disease require extensive studies and clinical correlation.
AIM: To assess cerebral atrophy features in cognitive impairment in patients with cerebral small vessel disease by surface-based morphometry.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A prospective study was conducted to assess patients with cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive impairments of varying severity levels (subjective, moderate, and dementia) and sex- and age-matched groups of volunteers. The assessment included the analysis of signs of cerebral small vessel disease based on the results of magnetic resonance imaging with the computation of general cerebral small vessel disease index and processing T1 multiplanar reconstruction images by surface-based morphometry to quantify general and regional brain parameters, including the thickness of the cerebral cortex.
RESULTS: The main group consisted of 173 patients with cerebral small vessel disease, whereas the control group included 47 healthy volunteers. As the severity of brain structural changes and cognitive impairments increased, a significant (p <0.05) decrease in the cortical thickness of certain regions following a similar pattern was reported, particularly in the cingulate gyri, mainly their posterior sections; medial and middle sections of the frontal lobes, various areas of the insular cortex, and temporoparietal areas, particularly the supramarginal gyri. The brain volumes (overall, gray matter, and white matter volumes) in cerebral small vessel disease were significantly different only in controls but not between patients with cognitive impairment of different severity levels. The hyperintense white matter volume was significantly different between patients with dementia and moderate cognitive impairment, dementia, and subjective cognitive impairment (p <0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS: The results confirm secondary/mixed atrophy in cerebral small vessel disease. The clarification of the severity level of cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease based on atrophy data is limited by the wide variety of regions with significant cortical thinning. Thus, the quantification of the cortex can only be a supplementary method in predicting cerebral small vessel disease progression.
 436-449
436-449


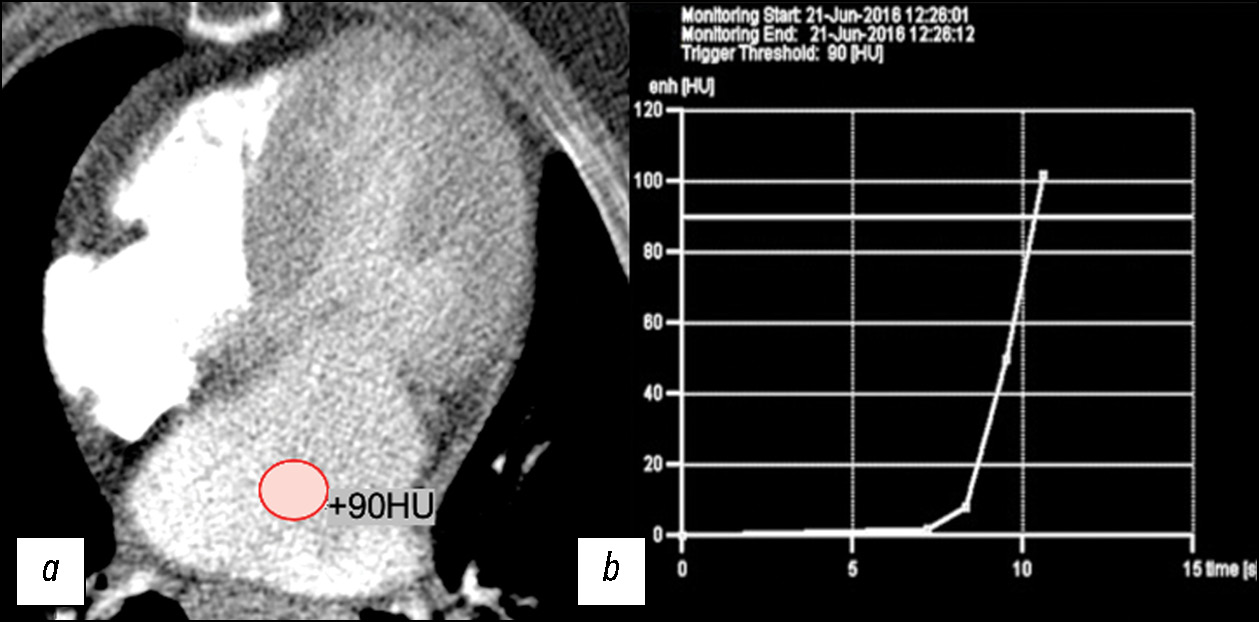
Diagnostic capabilities of cardiac computed tomography in the preoperative diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
BACKGROUND: A comprehensive approach to studying hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with diagnostic equipment and the latest scanning methods will ensure quality control and effective treatment of patients with this condition. The implementation of innovative technologies and computer calculation using next-generation scanners may become relevant and promising in studying various phenotypes of left ventricular remodeling in combination with abnormalities of the chordopapillary apparatus of the mitral valve and myocardial structure.
AIM: To examine the diagnostic capabilities of computed tomography in the preoperative examination of various hypertrophic cardiomyopathy phenotypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The retrospective data analysis included 47 patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (mean age, 52±7 full years) before surgical correction. computed tomography was performed using our protocol with automatic bolus tracking in the left atrium with a 90 HU threshold and biphasic contrast injection to assess the heart chambers and coronary arteries anatomy and mitral valve morphology. Moreover, to assess myocardial structure remodeling, iodine dual-energy computed tomography maps obtained with delayed contrast enhancement were analyzed. All patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy were classified by morphological types. The anatomy of chordopapillary apparatus was evaluated in each case.
RESULTS: This study demonstrated variability in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy phenotypes, which were conventionally divided into five morphological categories, but not restricted by them. Among the patients, 26 (55%) had diffuse septum hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, 5 (11%) had midventricular hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, 2 (4%) had midventricular obstruction and apical aneurysm, 8 (18%) had focal basal septum hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, 4 (8%) had concentric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and the remaining 4 (8%) had apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Most patients were diagnosed with chordopapillary abnormalities of the mitral valve, categorized by papillary muscle number and position, and the ratio of chords to muscles. In 10 (21%) patients, data on the myocardial bridge of a coronary artery were obtained, whereas 3 (14%) of them had dynamic stenosis. All patients had focal iodine uptake on dual-energy computed tomography maps. An extracellular volume increase was observed in 10 out of 13 (76%) patients. As shown by dual-energy computed tomography, the mean extracellular volume of the left ventricular myocardium was 30.58% (95% confidence interval, 27–34%).
CONCLUSION: Our scanning protocols developed with computed tomography scanners of various generations enable to evaluate the specific morphological patterns of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a single study and provide a detailed interpretation of the geometry of cardiac valves and chambers, left ventricular function, state of the coronary bed, and structural changes of the left ventricular myocardium.
 467-479
467-479


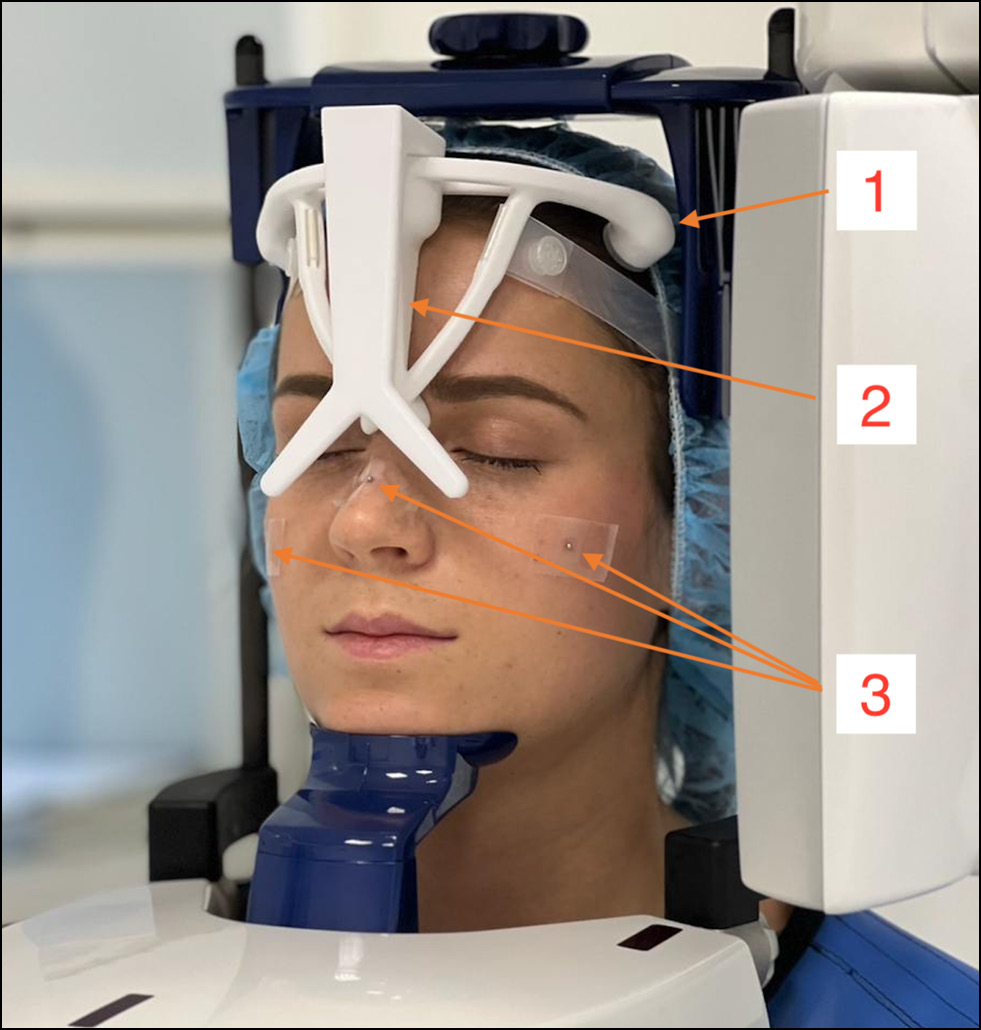
Application of augmented reality navigation in oral surgery
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Augmented reality is a potential alternative for surgical navigation, as it can provide visualization of various anatomical structures of the maxillofacial region. We have developed a specific platform for three-dimensional model management and intraoperative augmented reality navigation for surgical procedures.
AIM: To evaluate surgeons’ perceptions and the usability of augmented reality navigation for the most common surgical procedures in oral surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We performed a phantom study to determine the accuracy of the augmented reality system in the maxillofacial region. Registration errors typical in image-guided surgery were measured: fiducial registration error, target registration error, and fiducial localization error. Thereafter, a clinical trial with several surgeons performing surgical procedures on jaws using augmented reality technology was conducted. Surgeons filled out a dedicated questionnaire after their experience with augmented reality navigation.
RESULTS: The mean fiducial registration error was 0.9 mm (standard deviation 0.7 mm; 95% confidence interval 0.4–1.3 mm). The mean target registration error was 1.3 mm (standard deviation 0.5 mm; 95% confidence interval 1.1–1.5 mm). The fiducial localization error was the most significant with 2.2 mm (standard deviation 0.9; 95% confidence interval 1.9–2.5 mm). The higher rankings in the user experience questionnaire were related to the novelty and excitement of using augmented reality navigation in maxillofacial surgery. The pragmatic quality aspect explains the technical focus of perception to achieve goals in a product, system, or service design. Efficiency was expected to be slightly higher; however, in our opinion, this is due to the technical difficulties of the system for novel augmented reality technology.
CONCLUSION: The results revealed the satisfactory accuracy of the augmented reality system in the maxillofacial region and the user experience of the augmented reality navigation system for oral surgery.
 450-466
450-466


Effect of X-ray scan quality on the collective effective dose in patients in telemedicine
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The key objective of a healthcare provider is to ensure the quality and increase the efficiency of X-ray diagnostics in both municipal and private medical facilities. A poor-quality radiologic image requires repeated procedures, which results in further reputation, time, and economic losses for the medical organization. Moreover, repeated examinations further contribute to the patient’s total radiation exposure.
AIM: To assess the contribution of poor-quality X-ray examinations to patient exposure in outpatient medical organizations with telemedicine services.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study aimed to evaluate poor-quality X-ray examinations recorded by radiologists at the Moscow Reference Center in 2022 by applying a specially developed quality control system for diagnostic examinations based on information technology. In addition, during X-ray examinations, the methods for finding effective doses received by patients were applied in compliance with current regulatory requirements. Statistical methods were also used.
RESULTS: In this study, 2,059 poor-quality examinations were recorded, accounting for 0.084% of the total number of examinations interpreted with telemedicine. The collective effective dose from poor-quality examinations was 3.613 man-Sv, which was <0.11% of the total collective dose of patients in outpatient medical organizations.
CONCLUSION: The implementation of a quality control system for diagnostic examinations based on information technology proved to be efficient for medical organizations rendering telemedicine services.
 491-504
491-504


Radiological assessment of pulmonary vascular changes and gastrointestinal changes in patients with COVID-19 referred to a tertiary health care center in Chennai, India: a prospective cross-sectional study
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The coronavirus disease pandemic (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, has led to significant morbidity and mortality worldwide since its emergence in 2019. Although primarily a respiratory illness, COVID-19 can also affect other organ systems, including the vascular and gastrointestinal systems. COVID-19 is linked to both venous and arterial thrombosis, and numerous studies have indicated a heightened risk of pulmonary embolism. Autopsies have revealed pulmonary vasculature thrombosis and bowel ischemia in patients with COVID-19.
AIM: To assess radiological pulmonary vascular changes, specifically pulmonary embolism, and gastrointestinal changes in patients with COVID-19 referred to a tertiary healthcare center in Chennai, India.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Computed tomography pulmonary angiography and contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen were conducted in 100 patients with COVID-19 who met the selection criteria. A radiologist with 5 years of experience evaluated pulmonary vascular and bowel changes. Subsequently, statistical analysis was performed to determine the significance of the relationship between patients with COVID-19 and the occurrence of pulmonary vascular and bowel changes.
RESULTS: In this study, 11 patients exhibited pulmonary thromboembolism, and 7 showed significant bowel changes such as bowel wall thickening, mesenteric ischemia, and omental infarction, indicative of potential gastrointestinal involvement of patients with COVID-19. A positive correlation was found between pulmonary embolism prevalence in patients with COVID-19. Pulmonary embolism was diagnosed at a mean of 11 days from disease onset. Of the 24 patients with severe acute respiratory illness, 7 showed pulmonary embolism, detected by computed tomography pulmonary angiography. In addition, of the 10 patients on mechanical ventilation, pulmonary embolism was found in 7. Among the seven patients with bowel changes, four had pulmonary embolism, as detected by computed tomography pulmonary angiography, indicating a significant association between the two concomitant complications. The observed bowel changes were attributed to intravascular thrombosis.
CONCLUSIONS: Based on our findings, pulmonary emboli and bowel changes often occur in patients with COVID-19. Multivariate analyses also revealed a connection between invasive mechanical ventilation and pulmonary embolism. The results indicate that patients with severe COVID-19 may also experience concurrent acute pulmonary embolism. Thus, for these patients, the use of contrast-enhanced computed tomography instead of standard non-contrast computed tomography may aid in treatment decision-making.
 480-490
480-490


Experience with artificial intelligence algorithms for the diagnosis of vertebral compression fractures based on computed tomography: from testing to practical evaluation
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Osteoporosis is often diagnosed at the stage with complications, i.e., low-energy fractures. Vertebral compression fractures, which are complications of osteoporosis and predictors of subsequent fractures, are often asymptomatic. Compression fractures can be found by computed tomography performed for other indications with vertebral morphometry. Approaches to using artificial intelligence algorithms designed for diagnosing vertebral compression fractures were analyzed.
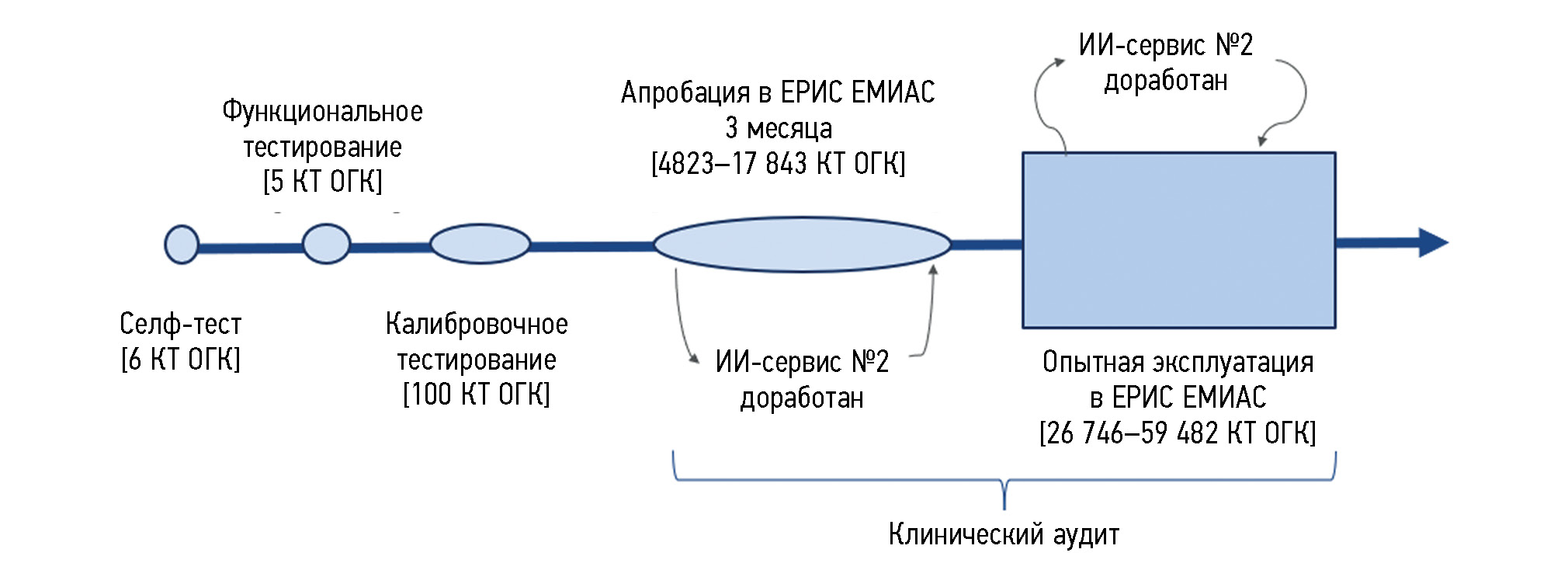
AIM: Testing artificial intelligence algorithms to conduct morphometric analysis of vertebrae on chest computed tomography scans and assess the possibility of their implementation in medical organizations of the Moscow Healthcare Department.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: To set a clinical task for artificial intelligence algorithms, basic diagnostic requirements in the area of “vertebral compression fractures (osteoporosis)” were formulated. The testing of the artificial intelligence algorithms included the following stages: self-testing, functional and calibration testing, practical evaluation, and operation testing. The first three stages of testing were performed using previously generated datasets. At practical evaluation and operation testing, artificial intelligence algorithms analyzed the data from computed tomography performed in medical organizations. The expert group of radiologists assessed the diagnostic accuracy and functional capacity of the AI algorithms at all stages. The resulting quantitative metrics of the accuracy of artificial intelligence algorithms were compared with the required target values.
RESULTS: From June 2021 to June 2022, two artificial intelligence algorithms (Nos. 1 and 2) with different methods of detecting compression fractures were tested. Both artificial intelligence algorithms successfully passed the self-testing (6 tests), functional (5 tests), and calibration (100 tests) stages. The area under the ROC curve for artificial intelligence algorithm No. 1 was 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98–1), and for artificial intelligence algorithm No. 2, it was 0.91 (95% CI, 0.85–0.96). Artificial intelligence algorithm No. 1 passed the practical evaluation stage without any significant remarks, whereas algorithm No. 2 was sent for fine-tuning. After the operation testing stage, the following accuracy metrics were obtained: the areas under the ROC curve for artificial intelligence algorithm Nos. 1 and 2 were 0.93 (95% CI, 0.89–0.96) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.90–0.94), respectively. At all stages, both artificial intelligence algorithms demonstrated sufficient metrics for clinical validation.
CONCLUSION: Artificial intelligence algorithms for the automatic diagnosis of vertebral compression fractures have been tested, demonstrating the high quality of their operation. artificial intelligence algorithms can be applied as a supplementary tool in the medical decision support system.
 505-518
505-518


Parameters of oculomotor activity and cerebral hemodynamics in students with different types of autonomic reactivity while performing cognitive tasks
Abstract
BACKGROUND: At the current state of human development, with the high rates of knowledge accumulation and accelerated social and technical evolution, studying the psychophysiological features of cognitive activity within a limited time is essential.
AIM: To examine oculomotor activity and cerebral hemodynamics parameters in students with different types of autonomic reactivity while performing cognitive tasks.
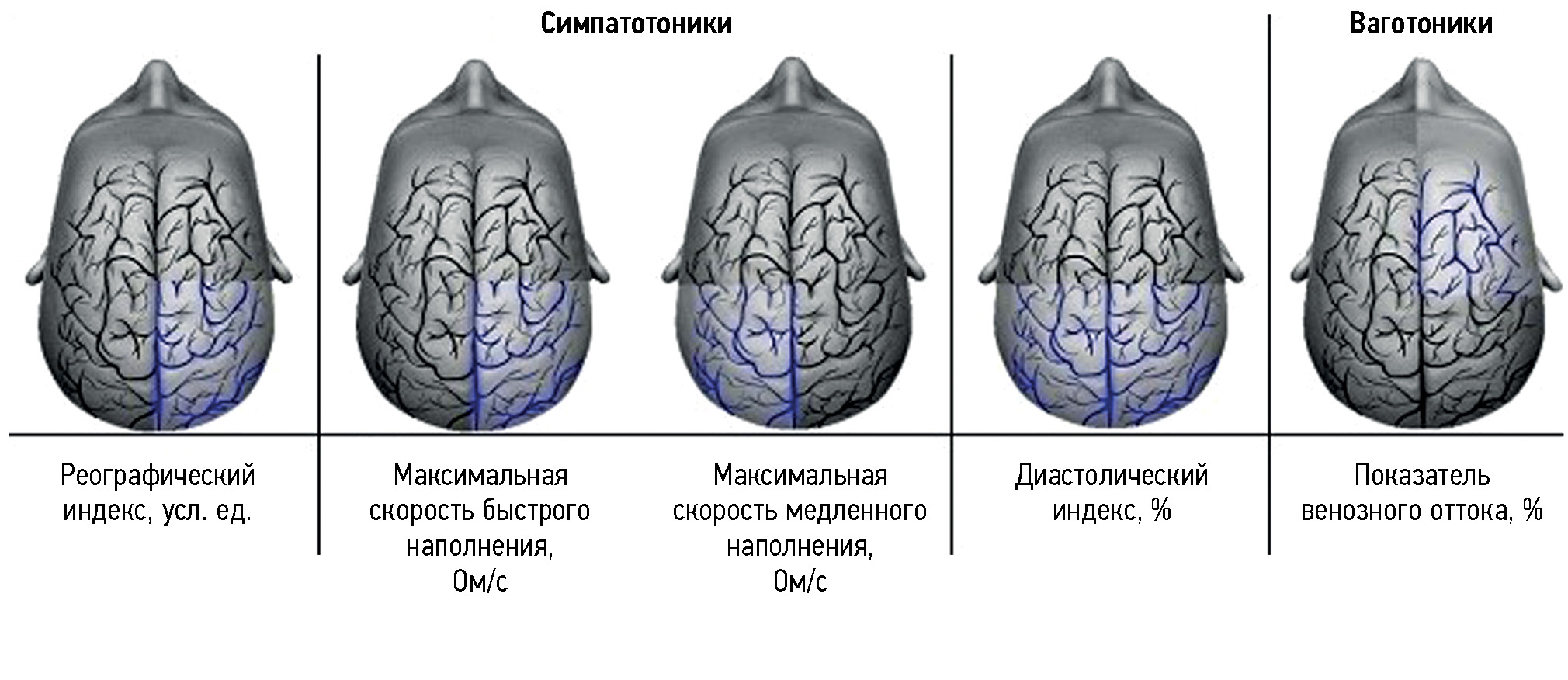
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study enrolled 110 students of the Northern (Arctic) Federal University named after M.V. Lomonosov (mean age, 19.0±0.5 years). To identify specific features of cognitive activity in various timing conditions, the type of autonomic nervous system reactivity was determined. Eye movements were tracked when solving cognitive tasks at various timing conditions. A rheoencephalogram was simultaneously recorded to assess cerebral hemodynamics. The efficiency of cognitive activity was assessed in various timing conditions with consideration of the identified individual typological features.
RESULTS: The participants demonstrated different efficiency levels of cognitive activity when performing cognitive tasks at various timing conditions. Students with a sympathetic-tone type of autonomic reactivity revealed the most efficient and rapid processing of visual information under a time-constraint setting owing to the presence of a more stable relationship between oculomotor activity and cerebral hemodynamics parameters. Participants with parasympathetic-tone reactivity showed the lowest success rates in cognitive activity and the least stable relationships between oculomotor activity and cerebral hemodynamics.
CONCLUSIONS: Young individuals with different types of autonomic reactivity exhibited general and specific alterations in cerebral hemodynamics and oculomotor activity when performing cognitive tasks under a time-constraint setting. They showed different efficiency levels of cognitive activity. Thus, human cognitive abilities under stress depend on the reactivity type of the nervous system. The specific changes in oculomotor reactions and cerebral hemodynamics parameters may be considered success markers of cognitive activity. The most successful cognitive activity under limited time conditions is ensured with a more stable statistical relationship between cerebral hemodynamics and oculomotor activity parameters. This is reflected in a stable factor model of visual cognitive activity, regardless of time limitations.
 519-533
519-533


Systematic reviews
Diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence for the screening of prostate cancer in biparametric magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic review
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Based on the latest published data, 40,137 new cases of prostate cancer were reported in Russia in 2021, ranking second after lung cancer in men.
Thus, prostate cancer is one of the most common malignant neoplasms in men. Accurate and timely detection of prostate cancer is important under the current conditions.
AIM: This systematic review aimed to assess the quality of prediction models designed to detect prostate cancer during initial presentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A systematic search was performed in eLibrary.ru, PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and ResearchGate for relevant publications indexed from January 2019 to September 2023 in accordance with the PRISMA protocol. Two authors independently assessed the relevant studies for potential inclusion or exclusion.
RESULTS: This systematic review meta-analysis included 21 studies. In total, data from 3,630 patients were analyzed, of which 47% had prostate cancer and 53% had benign prostate neoplasms. The mean age of the patients was 67.1 (36–90) years. In addition, 81% of the studies were based on T2-weighted imaging, 57% on diffusion-weighted imaging, and 76% on apparent diffusion coefficient. Moreover, 43% and 33% of the studies were dedicated to transition zone and prostate peripheral zone neoplasms, respectively, and 52% of the authors examined the whole prostate gland, without dividing it into zones. The most common machine-learning algorithms applied by the investigators were as follows: multiple logistic regression (76%), support vector machine (38%), and random forest (24%). Based on the meta-analysis performed for the receiver operating characteristic-area under the curve (ROC–AUC) assessment with random-effect approach in 73 prediction models described in the publications, the final ROC–AUC was 0.793 [95% CI 0.768–0.818], I2 = 86.71%, p <0.001. The most accurate prediction models were based on the T2-weighted imaging + apparent diffusion coefficients imaging protocol: 0.860 [95% CI 0.813–0.907], and models created according to the “white box” principle (0.834 [95% CI 0.806–0.861]) were more accurate than the “black box” ones (0.733 [95% CI 0.695–0.771]). The models using radiomics and clinical features were slightly more accurate than those using the radiomics parameters alone (0.869 [95% CI 0.844–0.895] vs. 0.779 [95% CI 0.751–0.807]). Model accuracy was nearly identical across transitional and/or peripheral zone studies.
CONCLUSIONS: Artificial intelligence demonstrated promising results. However, the clinical applicability may require more intensive expert inspection in healthcare institutions and evaluation of efficacy in prospective studies.
 534-550
534-550


Reviews
Fundamentals of dual-energy computed tomography and its emerging applications in bladder cancer
Abstract
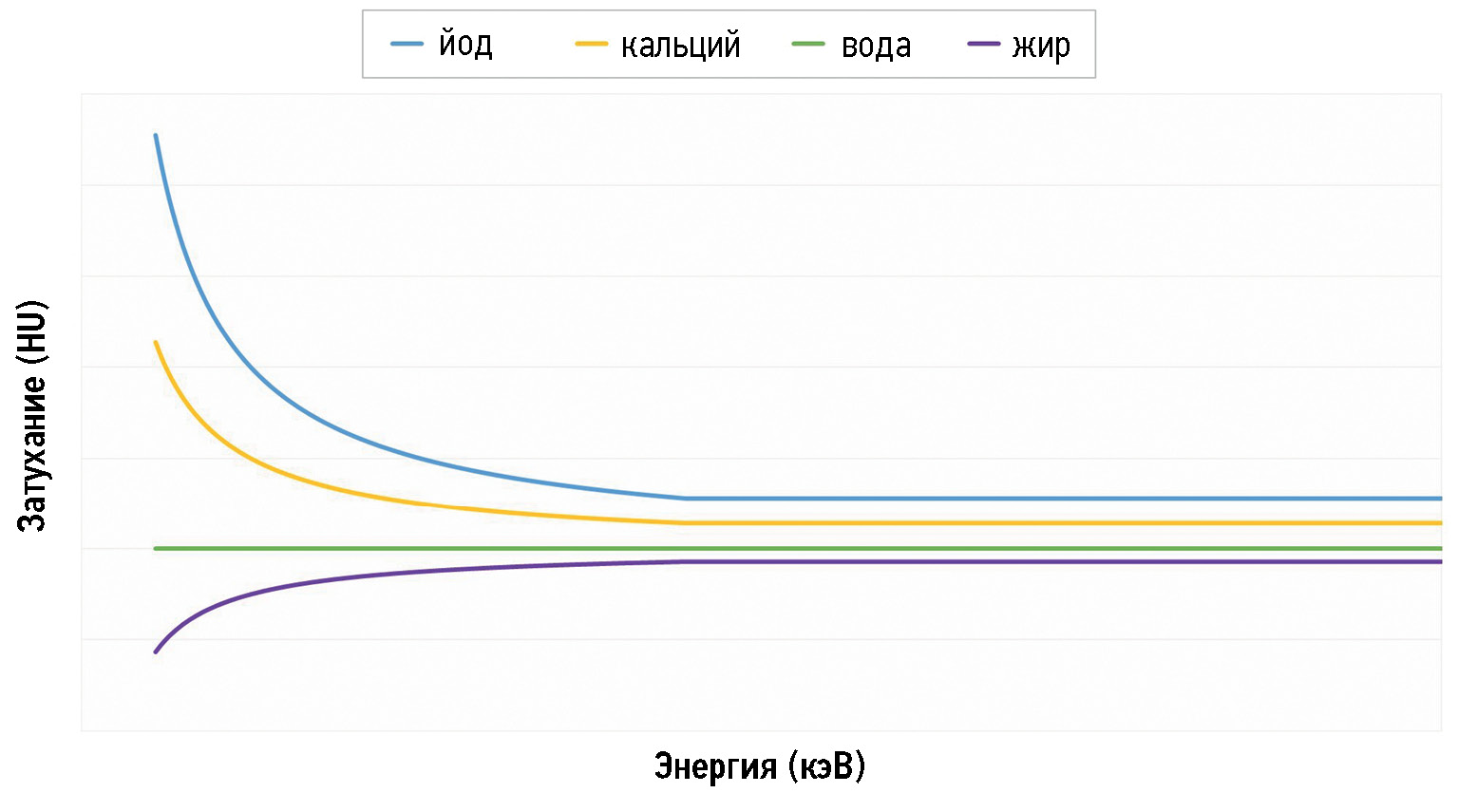
Nowadays, computed tomography urography and multiparametric magnetic resonance are the most often used imaging techniques in patients with bladder cancer; however, dual-energy computed tomography is making its way into the oncological field. This narrative review article aimed to show the fundamentals of dual-energy computed tomography by outlining its physical principles, techniques, protocols, and postprocessing images to help those who used this cutting-edge technology as the first approach to fully understand its emerging applications in the evaluation of bladder cancer, a field yet to be explored. In particular, we discuss the usefulness of dual-energy computed tomography by focusing on the main images obtained, such as the iodine map, comparing them to the images obtained with conventional computed tomography scans.
Dual-energy computed tomography applications may be beneficial for bladder cancer diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning. Nevertheless, its application is limited to its availability in healthcare structures and the training of healthcare personnel who can perform and interpret the scans correctly.
 551-566
551-566


Prospects for the application of radiomics to brain tumors
Abstract
Radiomics is a new branch in diagnostics based on a quantitative approach to medical imaging able to ensure more efficient use of medical equipment, optimize imaging time per patient, and increase the accuracy of differential diagnostics in various areas of medicine. Radiogenomics is a branch of radionics intended to establish a connection between the patient’s genotype and phenotypic presentation obtained from medical imaging. The review dwells on general issues for radiomics and radiogenomics in oncology with the recent study findings, focusing on the role of these methods in neurooncology and solving problems in diagnosing brain tumors. One of the current topics in neurooncology is disease prognosis in patients with unverified midline gliomas because morphological confirmation of the diagnosis and molecular genetic testing of tissues is impossible. Besides, the high spatial and temporal heterogeneity of malignant neoplasms prevents a complete assessment of the biological properties of the tumor and even using stereotactic biopsy methods. Radiomics methods can help doctors differentiate the tumor grade, acting as a “virtual biopsy” while avoiding invasive procedures. The study findings on radiomics and radiogenomics in neurooncology indicate the undeniable promise of these methods; however, as in other areas of medicine and biology, errors cannot be completely excluded, so the expert team must aim to minimize them.
 567-577
567-577


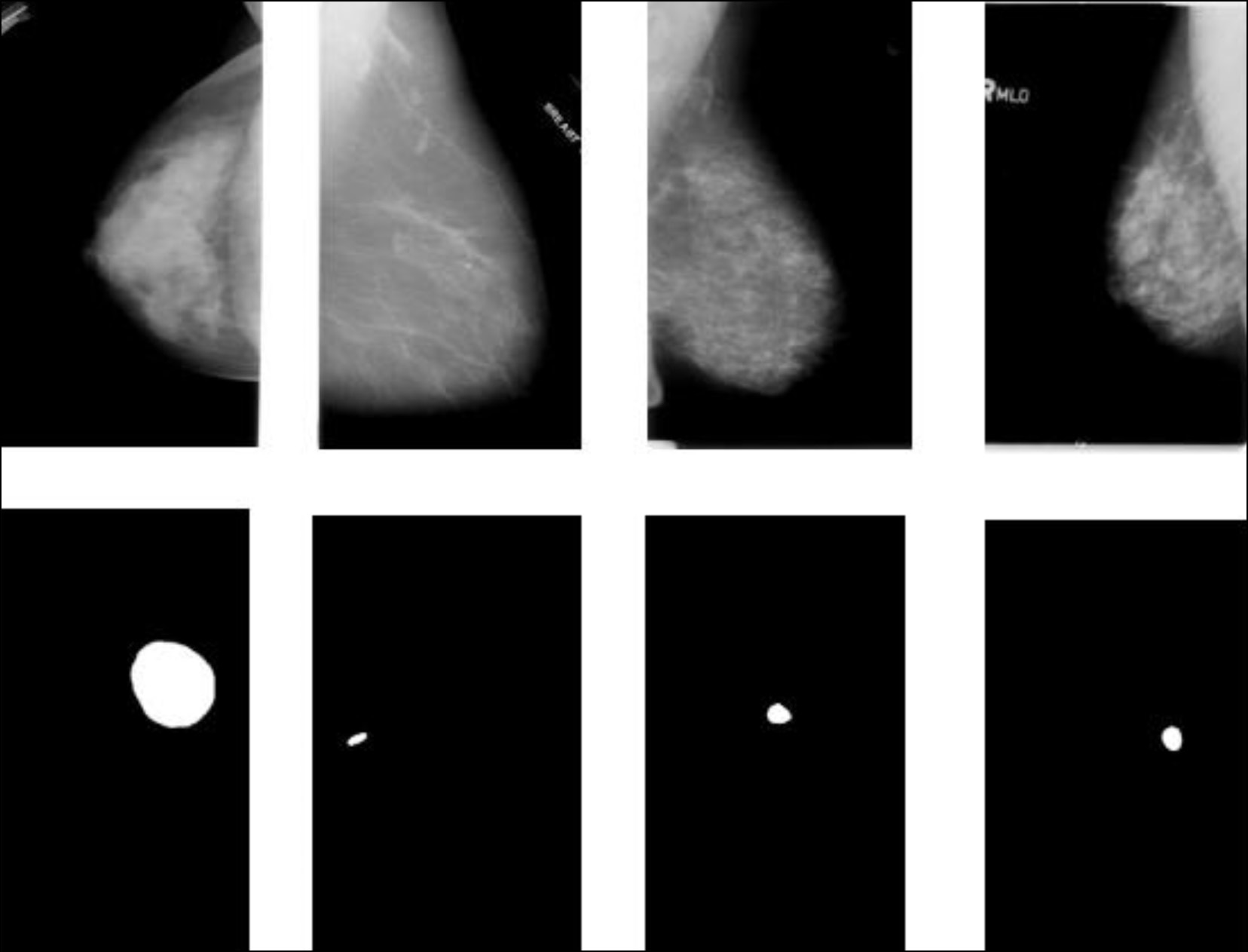
Machine learning techniques for breast cancer diagnosis
Abstract
In the last few years, machine learning techniques have been attracting even greater attention in the field of diagnostics, particularly when detecting breast cancer. Relevant studies dedicated to machine learning techniques in breast cancer diagnosis were analyzed in three areas: solving secondary problems that occur in modern-day breast cancer diagnostics, role in an intelligent assessment of the patient’s condition for preliminary diagnostic decisions, and capability to detect breast cancer risk factors. The results revealed that machine learning techniques applied in breast cancer diagnosis have great potential for improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency and solving secondary problems. The medical literature analysis has determined the parameters that are used as input data in machine learning techniques. Furthermore, the collected information will be applied to create a parameter system for breast cancer diagnosis using machine learning techniques.
 578-591
578-591


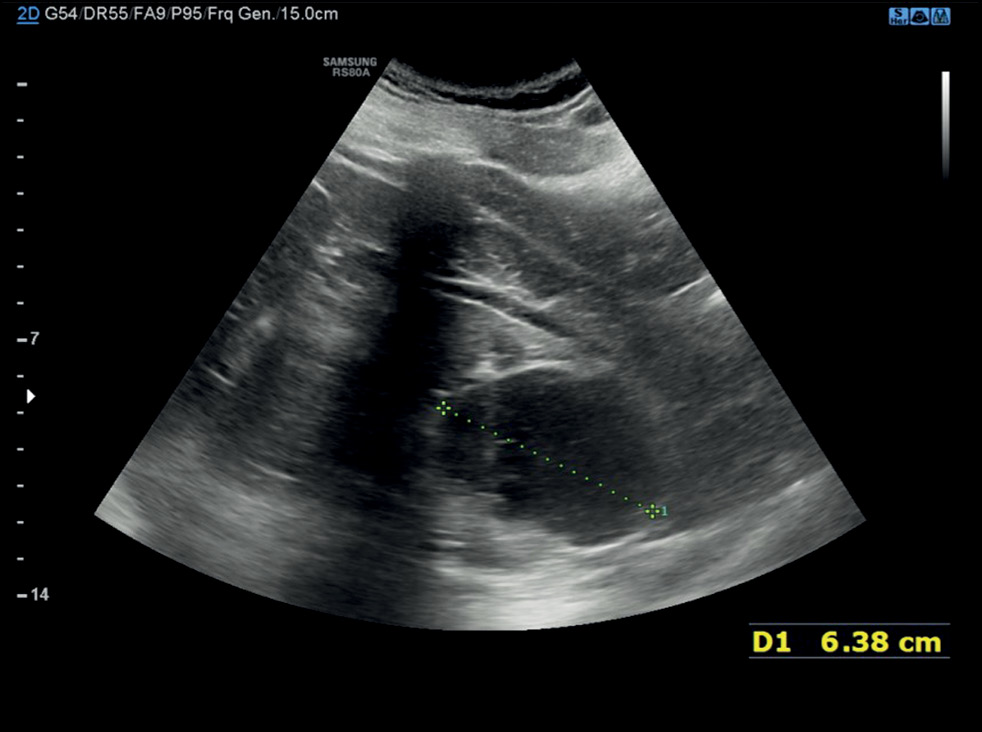
Radiological evaluation of a calyceal diverticulum presenting with hematuria
Abstract
Calyceal diverticula, also known as pyelogenic cysts, are a relatively uncommon condition, which is usually asymptomatic and incidentally diagnosed during routine imaging. In some cases, they may lead to concerning symptoms such as hematuria and flank pain, mimicking a renal tumor. In this case report, the patient suffered from hematuria that was initially suspected as a renal malignancy but was ultimately attributed to a calyceal diverticulum. The presented case allows evaluating one of the rarest and underestimated causes of hematuria and describes the main imaging features of calyceal diverticula. In particular, ultrasonography, computed tomography urography, dual-energy computed tomography, and magnetic resonance urography were performed. Subsequently, this case report also serves an educational purpose.
 592-600
592-600


Case reports
A case report of a mild neurologic deficit with extensive poststroke damage to the subdominant brain hemisphere: analysis of data obtained from magnetic resonance tractography, functional magnetic resonance imaging, and electroencephalography
Abstract
The severity of damage to different brain areas, including the cortex, can vary significantly in the associated neurologic deficit and reduction in the quality of life, often regardless of the lesion volume. The localization of the abnormalities plays a large part. Lesions of the dominant and subdominant hemispheres can differ greatly in both clinical features and effects on the patient’s quality of life. In this case report, a patient admitted for rehabilitation after two ischemic strokes underwent neurological and neuropsychological examination, complex instrumental diagnostics using electroencephalography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography perfusion, magnetic resonance tractography, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. The patient had minimal left-sided hemiparesis, impaired regulation of voluntary activity, mild decrease in neurodynamic indicators, mildly impaired concentration, and a critical view of his condition. Neuroimaging findings demonstrated extensive postinfarction damage to the right subdominant hemisphere of the brain in the middle cerebral artery circulation. A nonconformity between the brain damage volume and the severity of its clinical signs was observed. Based on functional examination data, the dominant hemisphere was determined, and restructuring the functional centers was suggested. This clinical case was compared with similar ones, and their relationship with the data was analyzed. Information that expands the knowledge of the topography of the altered zones involved in motor and speech functions and the ability to perform arithmetic counting was obtained.
 601-612
601-612


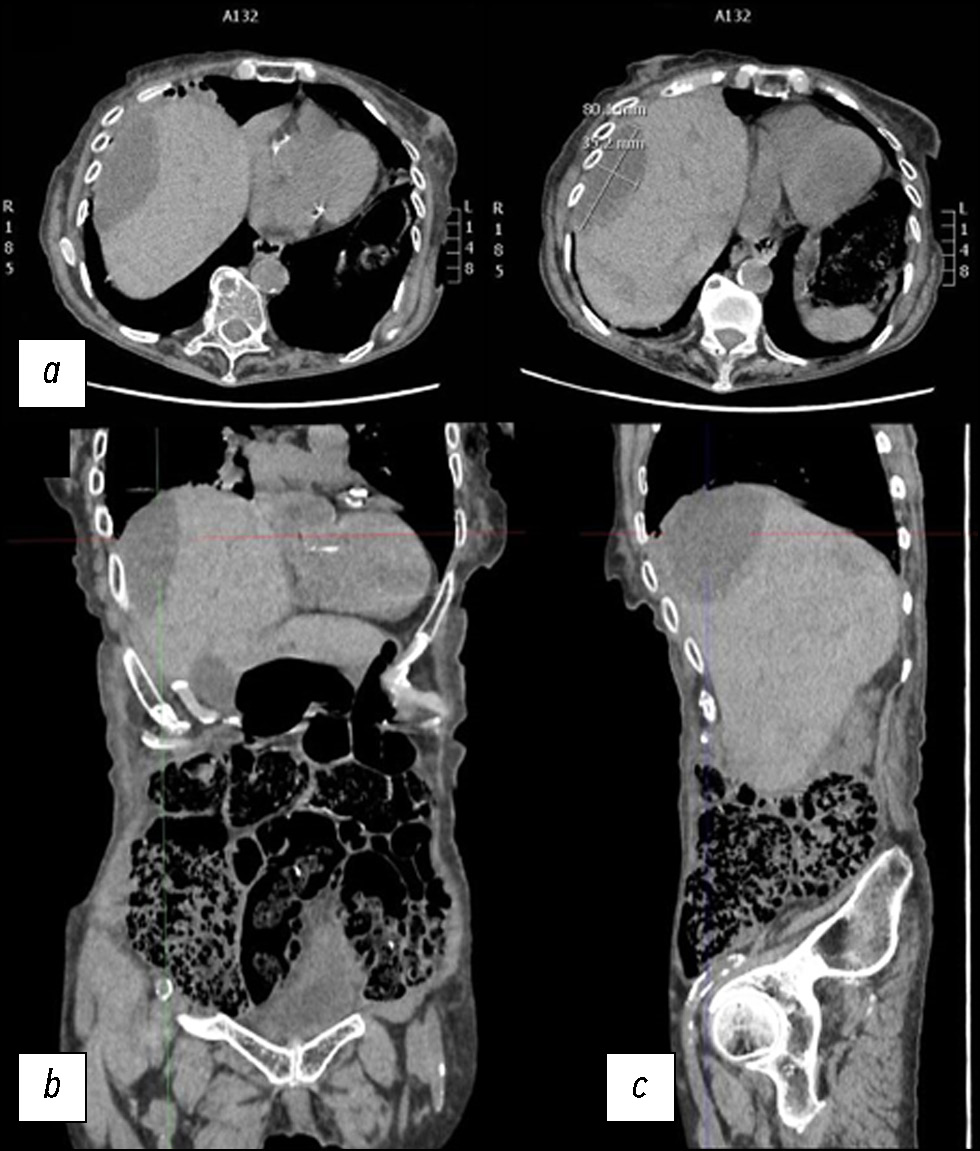
A case of spontaneous liver rupture and the role of imaging: from computed tomography to interventional treatment
Abstract
Hepatic parenchymal rupture is a rare but potentially fatal condition that can be caused by trauma, iatrogenic factors, spontaneous causes, etc. This case report describes the diagnostic and therapeutic steps employed in a patient with spontaneous hepatic parenchymal rupture. An older woman came to the emergency department with diffuse stomach pain. After clinical evaluation, she underwent computed tomography. The first computed tomography did not reveal a full-blown parenchymal rupture. Owing to data ambiguity, indicating that the abdominal discomfort could be caused by renal or biliary colic, obtaining an early diagnosis was very difficult. In truth, only few hypodense oval shapes with characteristic suprafluid densitometry were found in the liver parenchyma. However, after a few days, the discomfort persisted, and as the condition worsened, the patient underwent additional radiological examinations, which revealed the rupture of the liver parenchyma that required arteriography, and a long hospital stay until clinical resolution.
 632-641
632-641


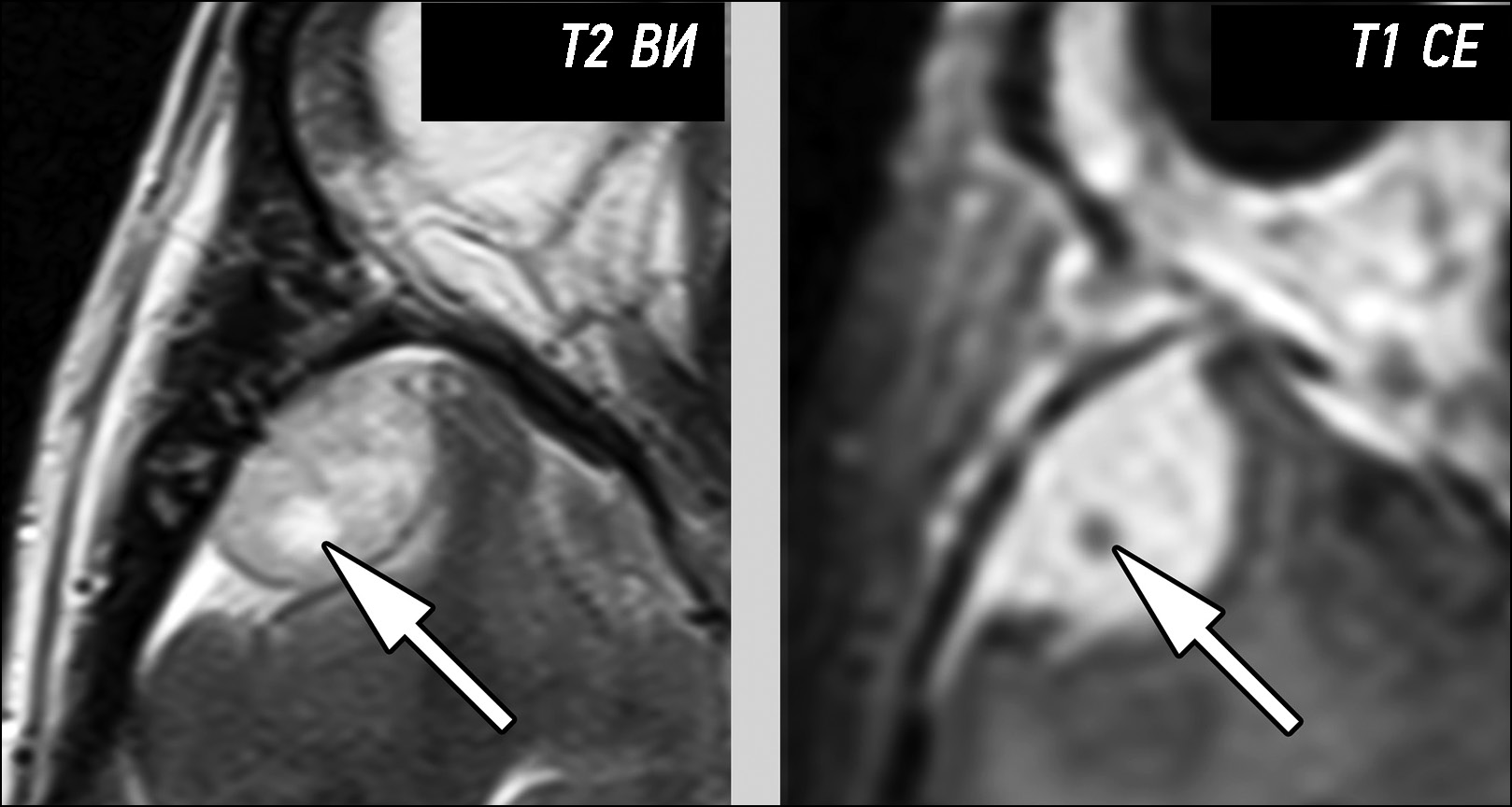
A young patient complaining of left scrotal pain diagnosed with testicular ischemia: a potentially fatal consequence of epididymitis
Abstract
Rare complications of acute epididymitis include ischemia and infarction of the testicles. Both clinically and radiologically, it is challenging to distinguish testicular torsion. In this article we have tried to expand the library of digital images of radiological diagnostic methods used for fast and accurate differential diagnostics. This case emphasizes the significance of a comprehensive radiological assessment and how a multidisciplinary approach is necessary to guarantee an accurate diagnosis. A 24-year-old man experienced severe left testicular pain and came to the hospital 2 weeks later. At the radiology department, he reported that he had for some time painful ejaculations, pain during intercourse (dyspareunia), scrotal redness/swelling, genital inflammation, chills, swollen inguinal lymph nodes, dysuria, and scrotal pain. All diagnostic procedures were performed, first ultrasonography and then magnetic resonance imaging, as required by the urologist. The imaging studies revealed left testicular ischemia, and based on the referred clinical history, a chronic orchid-epididymitis was suspected. Thus, the condition was resolved, not with a left orchidectomy but with medical therapy because the ischemia area was not too large. The patient also had a left varicocele. Images acquired with different magnetic resonance imaging sequences were carefully examined. A rare instance of epididymal orchitis is described as a potentially dangerous complication of epididymitis and must be considered if sudden, severe scrotal pain is experienced to avoid severe consequences. This case can help with optimal patient management and prevent unnecessary interventions.
 613-622
613-622


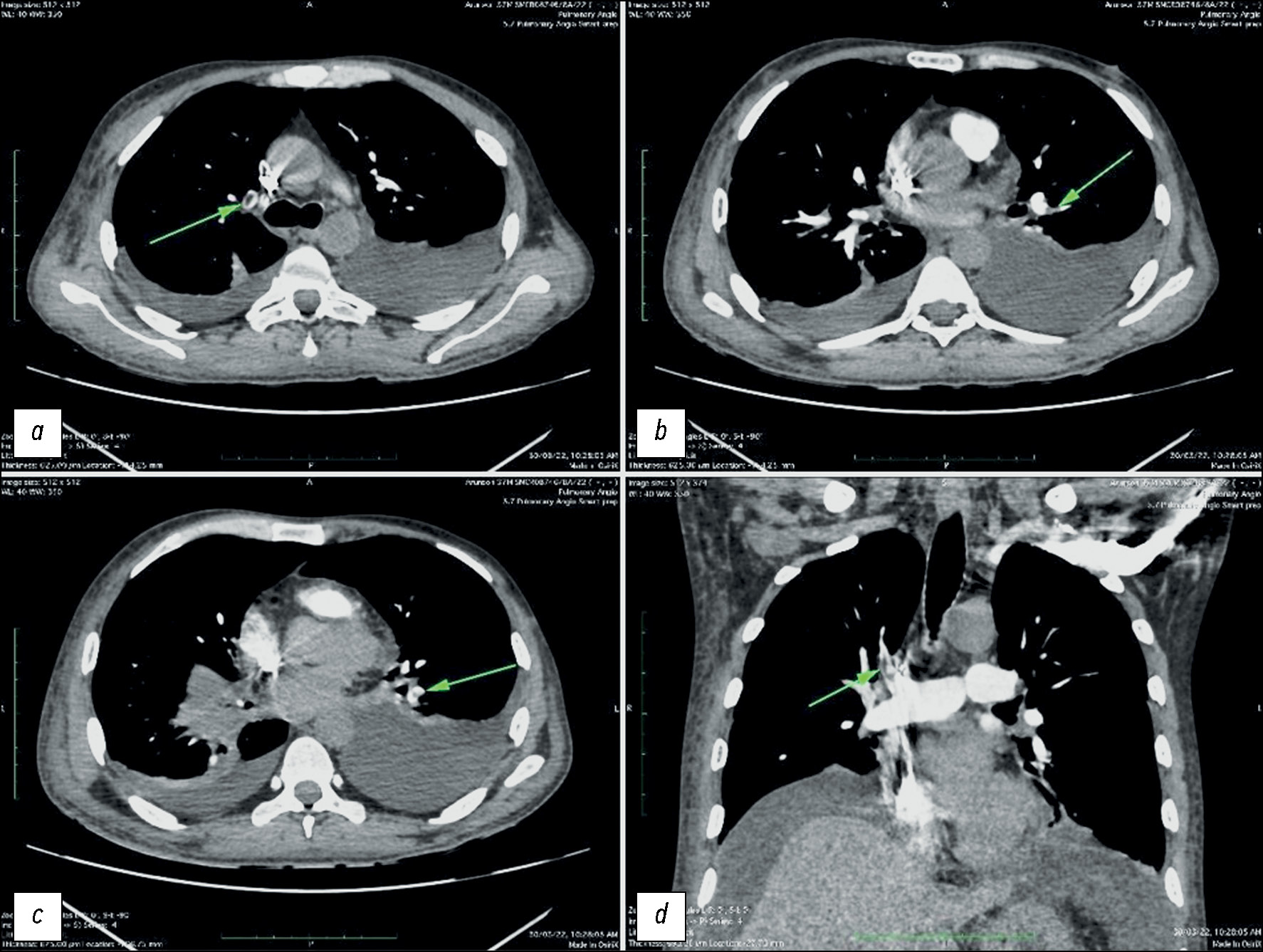
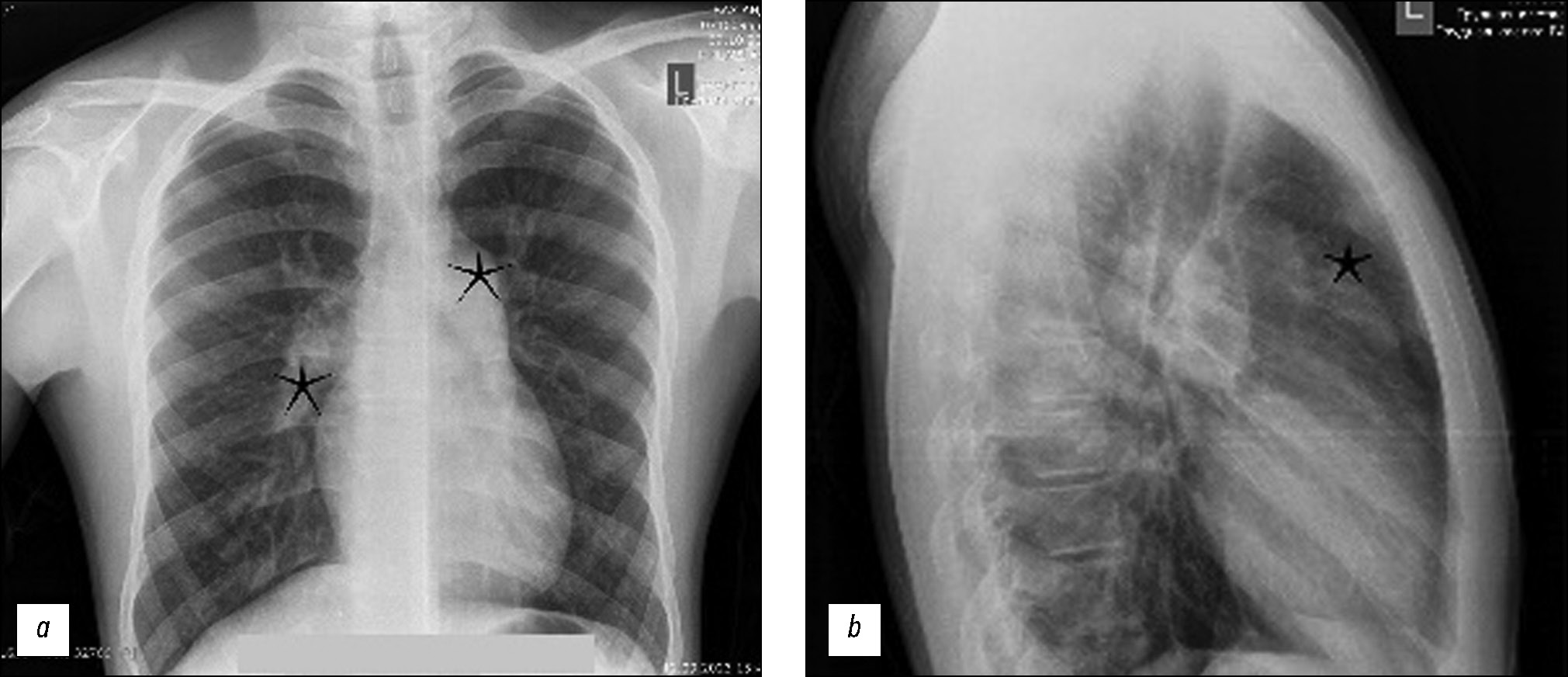
Pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm in a young man with pulmonary hypertension on computed tomography angiography
Abstract
Pulmonary artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are uncommon anomalies; however, their associated morbidity underscores the importance of recognizing them. Herein, we present a clinical case involving a 15-year-old male patient who presented at our clinic with complaints of hemoptysis. Upon diagnosis, a left lung aneurysm was found. Subsequent computed tomography angiography and intervention on the pulmonary arteries confirmed the presence of pulmonary artery aneurysms, elucidating that the hemoptysis was caused by the rupture of the aneurysm. The intervention on the pulmonary artery further confirmed the diagnosis. Early detection and management of pulmonary artery aneurysms are crucial, particularly in young patients, as timely intervention can prevent severe complications and improve patient outcomes. Raising awareness of these vascular abnormalities and promptly addressing them through appropriate diagnostic measures and interventions can help healthcare providers effectively mitigate the potential risks associated with pulmonary artery aneurysms, thereby enhancing patient care and prognosis.
 623-631
623-631


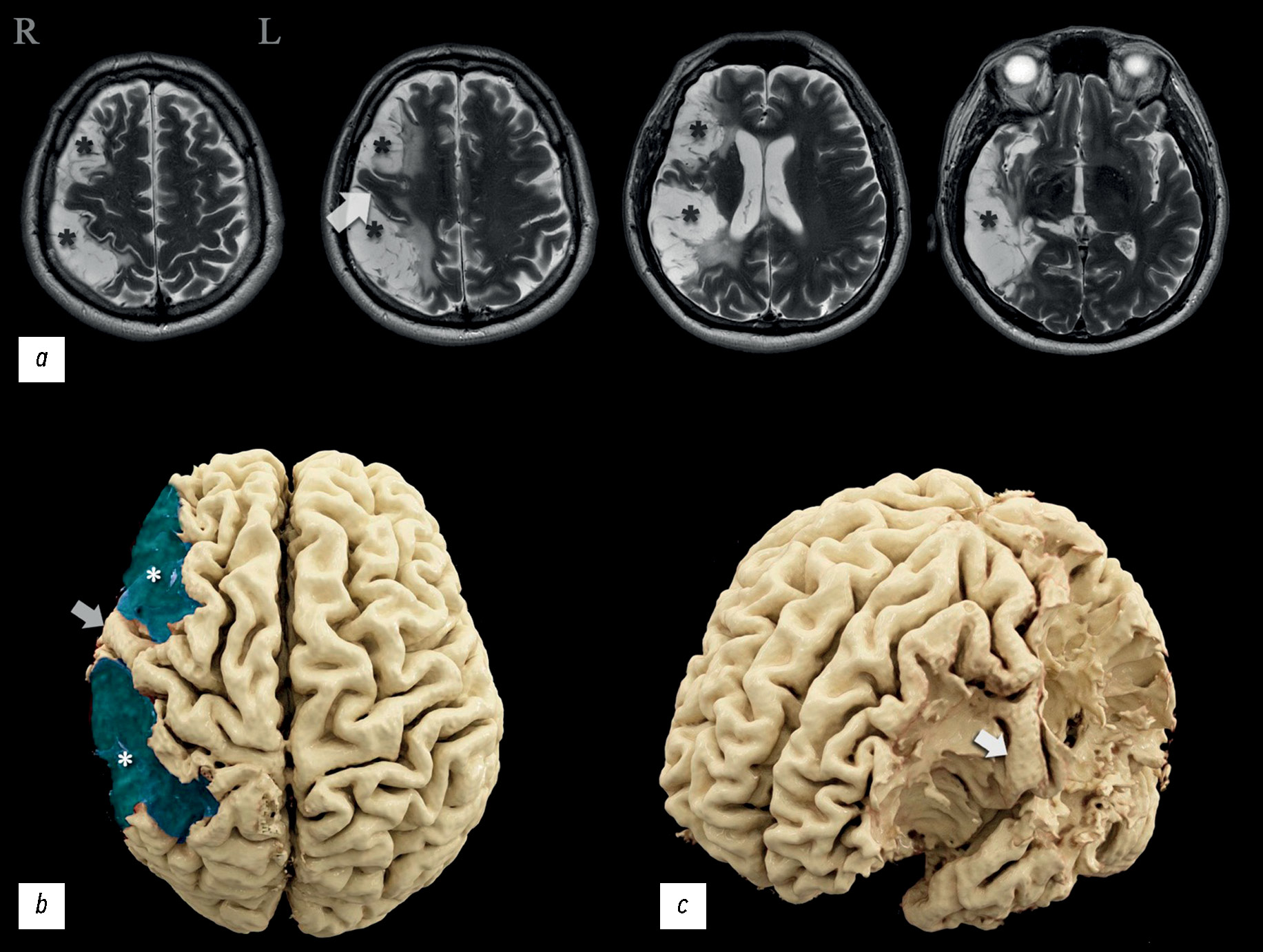
Diagnostic errors in assessing magnetic resonance imaging semiotics of primary extracerebral tumors: a case series
Abstract
Primary extracerebral tumors are represented by benign and malignant neoplasms of the meninges and cranial nerves. Their presurgical differential diagnosis is based on the analysis of magnetic resonance imaging semiotics. The critically significant aspects for classifying tumors of this group include the following: neoplasm structure, contrast enhancement type, delimiting from the brain tissue, and relationship with the meninges or cranial nerves. Differential diagnosis of extracerebral tumors based on visual analysis of magnetic resonance imaging data is generally not challenging because most tumors have typical magnetic resonance imaging semiotics. However, in cases with atypical magnetic resonance imaging signs, reliable differentiation of tumors can be challenging. Moreover, the greatest complexity is the differentiation of meningioma grades, distinction between solitary fibrous tumors and meningiomas, and identification of the tumor type when localized in the cerebellopontine angles. The case series presented the most typical features leading to errors in the differential diagnosis of primary extracerebral tumors. All the presented tumors were verified with postsurgical histological examination. The analysis of the case reports demonstrates that a review of the combined semiotic signs can lower the number of diagnostic errors.
 642-655
642-655


Navigating secondary breast angiosarcoma: a case report
Abstract
We describe a rare case of secondary breast angiosarcoma in a 72-year-old woman with a history of breast cancer who presented to our clinic with a painless palpable mass in the outer upper quadrant of the left breast. The diagnosis required a multidisciplinary approach involving a senologist, anatomopathologist, and oncologist. Imaging modalities such as mammography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging made it possible to assess the extent of the tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastases. The diagnosis was confirmed by a tissue biopsy. Herein, a rare case is presented, with the main educational purpose of describing the clinical presentation and complex diagnostic evaluation and discussing the differential diagnosis and management. Indeed, secondary mammary angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive neoplasm, and understanding its unique features is essential for clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. The tumor has a worse prognosis because of its late diagnosis, higher risk of rapid distant spread, and limited treatment options. Such cases require close monitoring, aggressive strategies, and supportive care.
 656-663
656-663